American Health Care Insurance

The American healthcare system, including its insurance landscape, is a complex and multifaceted topic that often sparks discussions and debates. Health care insurance is an essential component of the healthcare ecosystem, providing financial protection and access to essential medical services for millions of Americans. This comprehensive article aims to delve into the intricacies of American health care insurance, exploring its history, current trends, key players, and the impact it has on individuals and the broader healthcare industry.
The Evolution of American Health Care Insurance
The journey of health care insurance in the United States can be traced back to the early 20th century when it primarily served as a means to protect workers from financial ruin due to unexpected medical expenses. Over the decades, the landscape has transformed significantly, influenced by various economic, social, and political factors.
Early Beginnings: Blue Cross and Blue Shield
One of the earliest and most influential players in the health care insurance industry was the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (BCBSA). Founded in the 1920s, BCBSA introduced the concept of pre-paid hospital services, allowing individuals to pay a fixed amount for healthcare coverage. This model, known as the "Blue Cross" plan, gained popularity and became a cornerstone of the industry.
Simultaneously, the "Blue Shield" plan emerged, focusing on outpatient services and physician care. Together, these plans laid the foundation for the comprehensive health insurance coverage we know today.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1929 | The first Blue Cross plan was introduced in Dallas, Texas. |
| 1939 | Blue Shield plans began offering coverage for physician services. |
| 1945 | The Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans merged, forming a powerful alliance. |
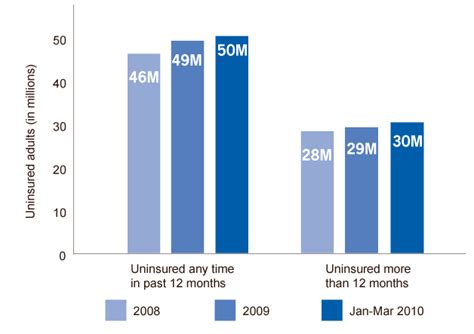
The Rise of Employer-Sponsored Insurance
Post-World War II, the United States experienced significant economic growth, leading to a surge in employer-sponsored health insurance plans. This trend was fueled by a combination of factors, including the need to attract and retain employees, the influence of labor unions, and the rising cost of healthcare.
By offering health insurance as an employment benefit, companies could provide a valuable incentive to their workforce, helping to reduce turnover and boost productivity. This practice became increasingly common, with many employers negotiating group rates with insurance providers, making health coverage more accessible to their employees.
The Impact of Government Interventions
Throughout the 20th century, various government interventions and policies shaped the American health care insurance landscape. Notable among these was the passage of the Medicare and Medicaid programs in 1965. These federally funded initiatives provided health insurance coverage to senior citizens, individuals with disabilities, and low-income families, significantly expanding access to healthcare.
Additionally, the implementation of the Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Act of 1973 encouraged the growth of managed care organizations, introducing a new era of cost-containment strategies in the healthcare industry.
Understanding the Current Landscape
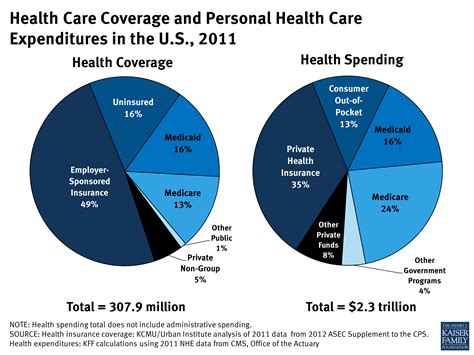
Today, the American health care insurance market is a dynamic and diverse ecosystem, characterized by a range of players, products, and services. Let's explore some of the key aspects and trends that define this landscape.
Major Players and Market Share
The health care insurance industry in the United States is dominated by a handful of major players, each with its unique offerings and market share. Some of the prominent names include:
- UnitedHealthcare: One of the largest health insurance providers in the country, offering a wide range of plans and services. UnitedHealthcare's market share spans across various sectors, including employer-sponsored plans, individual market coverage, and Medicare Advantage plans.
- Anthem: Known for its Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans, Anthem operates in several states, providing coverage to millions of Americans. The company focuses on a diverse range of health insurance products, catering to individuals, families, and businesses.
- Aetna: With a rich history dating back to the 19th century, Aetna has evolved into a leading health care insurance provider. Aetna offers a comprehensive suite of health insurance plans, including medical, dental, and vision coverage, and is particularly well-known for its Medicare and Medicaid offerings.
- Humana: Humana is a prominent player in the Medicare and Medicare Advantage markets, offering a range of plans designed specifically for senior citizens. Additionally, the company provides group health insurance for employers and their employees.
- Cigna: Cigna has a global presence and offers a variety of health insurance products, including medical, dental, vision, and behavioral health coverage. The company's focus on personalized care and wellness programs sets it apart in the market.
Types of Health Care Insurance Plans
The American health care insurance market offers a wide array of plan options, catering to the diverse needs of individuals and families. Some of the common types of plans include:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs are managed care plans that typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals from the PCP for specialty care. These plans often have lower out-of-pocket costs but may have more limited provider networks.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs offer more flexibility than HMOs, allowing members to choose their healthcare providers without referrals. PPOs often have a larger network of providers and may have higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are similar to PPOs but typically have a more restricted network of providers. Members can visit any in-network provider without referrals but may incur higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network care.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs. Members typically choose a primary care physician and receive in-network benefits, but they can also opt for out-of-network care with higher out-of-pocket costs.
- High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs): HDHPs are designed to be paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs). These plans have higher deductibles, meaning members pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in. However, they often have lower monthly premiums.
Affordability and Access to Care
Affordability and access to healthcare remain critical concerns in the American health care insurance landscape. Despite the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in 2010, which aimed to increase coverage and reduce costs, many individuals and families still struggle with the financial burden of healthcare.
The rising cost of premiums, deductibles, and copayments has led to a growing number of underinsured individuals, who may have insurance coverage but cannot afford the out-of-pocket expenses associated with their plans. This issue is particularly prevalent among those with lower incomes and those living in rural areas with limited healthcare options.
The Role of Technology and Digital Health
The integration of technology and digital health solutions has revolutionized the health care insurance industry. Insurance providers are leveraging digital platforms and tools to enhance member engagement, streamline processes, and improve overall healthcare experiences.
Telehealth services, for instance, have gained significant traction, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. These services allow members to access healthcare remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving access to care, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
Additionally, the use of wearable devices and health tracking apps has enabled insurance companies to offer personalized wellness programs and incentives, encouraging members to adopt healthier lifestyles and reduce their risk of chronic diseases.
Impact and Future Implications
The American health care insurance industry has a profound impact on the lives of individuals, shaping their access to healthcare and financial well-being. It also influences the broader healthcare ecosystem, including healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and medical device manufacturers.
Individual Impact
Health care insurance provides individuals and families with peace of mind, knowing that they have financial protection in the event of illness or injury. It allows them to access necessary medical services without the fear of crippling medical debt.
However, the complexity and cost of insurance plans can often be a source of confusion and anxiety. Individuals must carefully evaluate their options, considering factors such as premiums, deductibles, copayments, and provider networks, to ensure they choose a plan that aligns with their healthcare needs and budget.
Healthcare Provider Perspective
Health care insurance plays a crucial role in the financial viability of healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and individual practitioners. Insurance reimbursement rates and policies can significantly impact the revenue and profitability of these entities.
Additionally, the negotiation of insurance contracts and the management of billing and claims processes require significant administrative resources, adding to the operational complexities faced by healthcare providers.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the American health care insurance landscape is expected to undergo further transformations, driven by various factors.
The continued advancement of technology and digital health solutions is likely to shape the industry, with a focus on personalized medicine, precision health, and virtual care. Insurance providers will need to adapt their offerings to accommodate these emerging trends and ensure they remain relevant and competitive.
Additionally, the ongoing debate surrounding healthcare reform and the potential for future legislative changes will continue to influence the industry. The implementation of policies aimed at increasing access to healthcare, reducing costs, and improving quality will have significant implications for insurance providers and their customers.
As the United States grapples with the complexities of its healthcare system, health care insurance will remain a critical component, providing financial protection and access to essential medical services. The industry's ability to adapt, innovate, and meet the evolving needs of its customers will be pivotal in shaping its future success and impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the Affordable Care Act (ACA) impact health care insurance in the United States?
+The ACA, also known as Obamacare, has had a significant impact on the health care insurance landscape. It introduced several key provisions, including the expansion of Medicaid, the creation of health insurance marketplaces, and the requirement for individuals to have health insurance coverage or face a tax penalty (known as the individual mandate). The ACA aimed to increase access to healthcare, improve quality, and reduce costs. While it has faced challenges and criticisms, it has also led to an increase in insurance coverage and introduced important consumer protections.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some common challenges faced by individuals when choosing a health care insurance plan?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Choosing a health care insurance plan can be complex and challenging for individuals. Some common challenges include understanding the different types of plans (such as HMOs, PPOs, and HDHPs), comparing costs (premiums, deductibles, copayments), and evaluating provider networks to ensure access to preferred healthcare providers. Additionally, individuals may face challenges related to pre-existing conditions, coverage limitations, and the overall affordability of insurance plans.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How do health care insurance companies determine premiums and rates for their plans?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Health care insurance companies use a combination of factors to determine premiums and rates for their plans. These factors include the age and health status of the insured population, the cost of healthcare services in the area, the plan's benefits and coverage, and the insurance company's own administrative costs. Premiums are typically set to cover expected costs and allow for a profit margin. Insurance companies may also consider the risk pool, which is the overall health and demographics of the insured population, to ensure fair and stable premiums.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What are some strategies to reduce the cost of health care insurance for individuals and families?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Reducing the cost of health care insurance can be challenging, but there are several strategies individuals and families can consider. These include shopping around for different plans and comparing costs and benefits, utilizing employer-sponsored plans if available, considering high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) for tax advantages, and exploring government-sponsored programs like Medicaid or the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) if eligible. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing costly health issues can help reduce insurance costs over time.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does health care insurance impact the broader healthcare industry and economy?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Health care insurance plays a critical role in the broader healthcare industry and economy. It influences the financial viability of healthcare providers, impacting their ability to invest in new technologies, expand services, and provide quality care. Insurance coverage also affects the demand for healthcare services, as individuals with insurance are more likely to seek preventative care and treatment. Furthermore, the insurance industry contributes significantly to the economy through employment, taxes, and the overall healthcare spending it facilitates.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>



