Average Cost Of Health Insurance Individual

Understanding the average cost of health insurance for individuals is crucial for anyone seeking affordable and comprehensive healthcare coverage. This article delves into the various factors influencing these costs, providing a comprehensive guide to help individuals make informed decisions about their health insurance plans. From the basics of health insurance to the intricacies of premium calculations, we'll explore the data and insights necessary for effective financial planning.
Health Insurance Fundamentals
Health insurance is a vital component of modern healthcare systems, offering individuals financial protection against the often-high costs of medical care. It serves as a contractual agreement between an individual and an insurance company, whereby the insured pays regular premiums in exchange for coverage of specified health services.
The average cost of health insurance for individuals can vary significantly based on a multitude of factors, including the individual's age, location, medical history, and the specific coverage plan chosen. These plans can range from basic catastrophic coverage to more comprehensive plans that cover a wide array of medical services.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Demographic Factors
Age and location are two critical demographic factors that impact health insurance costs. Generally, younger individuals tend to pay lower premiums as they are less likely to require extensive medical care. On the other hand, older individuals, particularly those above 65 years of age, often face higher premiums due to an increased likelihood of health issues.
The cost of health insurance also varies by geographic location. States with higher living costs or a greater demand for healthcare services may have higher insurance premiums. Additionally, the cost of living and the availability of healthcare providers in a particular area can significantly influence insurance rates.
Medical History and Pre-existing Conditions
An individual’s medical history, including any pre-existing health conditions, is a key factor in determining insurance premiums. Those with a history of serious illnesses or chronic conditions may face higher costs, as insurance companies assess the risk of providing coverage for these individuals.
However, it's important to note that with the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) in the United States, insurance companies are no longer allowed to deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. This means that individuals with pre-existing conditions now have more options and protection when seeking health insurance.
Plan Type and Coverage
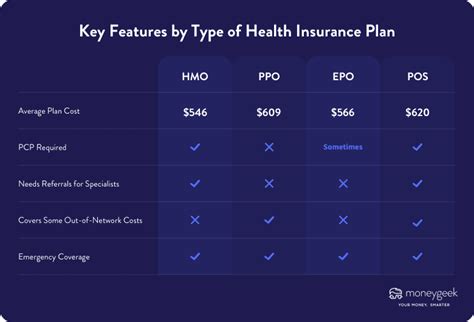
The type of health insurance plan and the level of coverage chosen also significantly affect the cost of premiums. There are various types of plans available, including Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs), each with its own network of healthcare providers and different levels of coverage.
Additionally, the level of coverage chosen, such as the deductible, copayment, and coinsurance, can greatly impact the premium. Plans with lower deductibles and out-of-pocket costs typically have higher premiums, while those with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs are generally more affordable.
Calculating Health Insurance Premiums
The calculation of health insurance premiums is a complex process that involves assessing the risk associated with insuring a particular individual or group. Insurance companies use actuarial science to predict the likelihood and cost of future medical claims, which directly influences the premiums they charge.
Actuaries analyze a multitude of data points, including an individual's age, gender, location, medical history, and the overall health of the population they serve. They also consider broader trends in healthcare costs, such as the rising prices of medications and medical procedures, to determine appropriate premium levels.
Furthermore, insurance companies often offer a range of plans with different levels of coverage to cater to diverse consumer needs. These plans can vary in terms of the types of services covered, the network of healthcare providers, and the cost-sharing responsibilities of the insured. This allows individuals to choose a plan that best fits their budget and healthcare needs.
Understanding Out-of-Pocket Costs
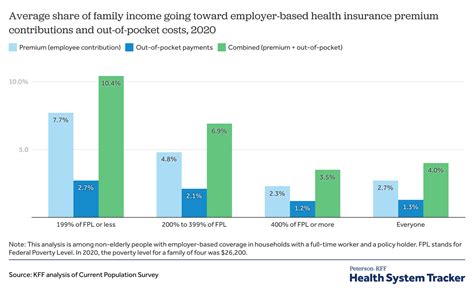
When evaluating health insurance plans, it’s crucial to consider not only the premium but also the out-of-pocket costs, such as deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. These costs can significantly impact the overall financial burden of healthcare.
| Out-of-Pocket Cost Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Deductible | The amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance company starts covering costs. |
| Copayment | A fixed amount paid by the insured for a specific service or prescription, typically at the time of service. |
| Coinsurance | The percentage of costs the insured must pay after the deductible is met, up to a specified limit. |

For example, if an individual has a health insurance plan with a $1,000 deductible and 20% coinsurance, they would be responsible for paying the full cost of healthcare services until the deductible is met. After that, they would pay 20% of the cost of covered services, while the insurance company would cover the remaining 80%.
Average Health Insurance Costs for Individuals

The average cost of health insurance for individuals varies significantly across different countries and regions. In the United States, for instance, the average annual premium for individual health insurance plans in 2021 was $7,788, according to data from the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). This represents a notable increase from previous years, reflecting the rising costs of healthcare.
However, it's important to note that these averages can be misleading, as they don't account for the wide variation in costs based on the factors mentioned earlier. For example, younger individuals might pay an average of $4,500 per year, while older individuals could pay upwards of $12,000 annually.
International Perspectives
In countries with universal healthcare systems, such as the United Kingdom and Canada, the concept of individual health insurance is different. While there may be private insurance options available for additional coverage, the basic healthcare services are typically covered by the government, ensuring universal access to healthcare.
In these countries, the focus on healthcare costs often shifts to the overall funding and sustainability of the public healthcare system, rather than individual premiums. This highlights the diverse approaches to healthcare financing and delivery across different nations.
Tips for Choosing Affordable Health Insurance
Selecting an affordable health insurance plan requires careful consideration and research. Here are some tips to guide your decision-making process:
- Understand your healthcare needs: Assess your current and potential future healthcare requirements to choose a plan that provides adequate coverage.
- Compare plans: Shop around and compare different insurance plans to find the one that offers the best value for your money.
- Consider your budget: Ensure that the premium and out-of-pocket costs align with your financial capabilities.
- Understand the coverage: Read the fine print to ensure you're aware of what is and isn't covered by the plan.
- Explore government programs: In the United States, programs like Medicaid and the Health Insurance Marketplace can offer affordable coverage options for eligible individuals.
Future Trends in Health Insurance Costs
The landscape of health insurance is continually evolving, influenced by technological advancements, policy changes, and demographic shifts. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Telehealth: The increasing adoption of telehealth services is expected to reduce healthcare costs and improve accessibility, potentially leading to more affordable insurance plans.
- Value-based care: Shifting towards value-based care models, where providers are incentivized to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care, could help curb rising healthcare costs.
- Policy changes: Ongoing policy debates and reforms, such as the future of the Affordable Care Act, will significantly impact the cost and accessibility of health insurance.
As the healthcare industry adapts to these changes, individuals can expect more innovative and potentially more affordable health insurance options in the future.
Conclusion
Understanding the average cost of health insurance for individuals is a complex but crucial task. By considering various factors, from demographics and medical history to plan type and out-of-pocket costs, individuals can make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable is key to navigating the complexities of health insurance and accessing affordable, high-quality care.
How does the Affordable Care Act (ACA) impact health insurance costs for individuals with pre-existing conditions?
+The ACA prohibits insurance companies from denying coverage or charging higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. This means individuals with pre-existing conditions now have more options and protection when seeking health insurance, which can help lower costs.
What are some ways to reduce the cost of health insurance premiums?
+There are several strategies to consider: opting for a higher deductible plan, choosing a provider within your insurance network, maintaining a healthy lifestyle to qualify for wellness incentives, and exploring government programs like Medicaid or the Health Insurance Marketplace for eligible individuals.
How do insurance companies determine health insurance premiums?
+Insurance companies use actuarial science to assess risk and predict the likelihood and cost of future medical claims. They consider factors such as age, gender, location, medical history, and broader healthcare trends to set appropriate premium levels.



