Cost Of Business Insurance

Understanding the cost of business insurance is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners as it directly impacts their financial planning and overall business strategy. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing these costs, offering valuable insights for businesses seeking to secure their operations and mitigate risks effectively.
Factors Influencing Business Insurance Costs
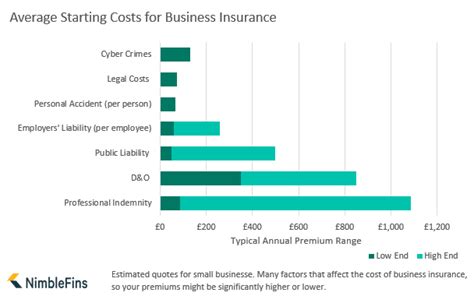
The expense associated with business insurance can vary significantly depending on a multitude of factors. By examining these elements, businesses can gain a clearer understanding of how to navigate the insurance landscape and make informed decisions.
Industry and Business Type
One of the primary determinants of insurance costs is the industry a business operates in. Different industries present unique risks, and insurers factor this into their premium calculations. For instance, a construction company will likely face higher insurance premiums due to the inherently hazardous nature of the work, whereas a software development firm may enjoy more competitive rates.
Additionally, the specific business type within an industry can also impact costs. A large-scale manufacturing plant will have different insurance needs and costs compared to a small boutique selling similar products. The size and scale of operations, as well as the potential for liability, play significant roles in determining insurance premiums.
Business Location
The geographical location of a business is another critical factor. Insurance rates can vary widely based on regional differences in crime rates, natural disaster risks, and local regulations. For example, a business located in an area prone to hurricanes or earthquakes may face higher insurance costs to cover potential property damage.
Furthermore, the local business environment can also influence insurance rates. A business operating in a highly competitive market may need to pay more for coverage to protect its intellectual property or trade secrets. Conversely, a business in a stable, less competitive market might enjoy more affordable insurance options.
Business Size and Operations
The size and scope of operations of a business are key considerations for insurers. Larger businesses with extensive operations and a broader customer base often face higher insurance premiums due to the increased potential for liability and claims. On the other hand, smaller businesses may benefit from more affordable rates, but they still need to ensure their coverage adequately protects their assets and operations.
In addition, the nature of operations can impact insurance costs. Businesses that handle sensitive customer data, for example, may need to invest in cyber liability insurance, which can add to their overall insurance expenses. Similarly, businesses with a high volume of customer interactions or a significant physical presence may require more comprehensive coverage, driving up their insurance costs.
Type of Insurance Coverage
The specific type of insurance coverage chosen by a business is another significant factor in determining insurance costs. Different types of insurance, such as property insurance, liability insurance, workers’ compensation, and business interruption insurance, each carry their own costs and considerations.
Businesses need to carefully assess their unique risks and choose the appropriate coverage. While it's essential to have adequate protection, over-insuring can lead to unnecessary expenses. Conversely, under-insuring can leave a business vulnerable to significant financial losses in the event of a claim.
Claims History and Risk Management
A business’s claims history is a critical factor that insurers consider when determining insurance costs. Businesses with a history of frequent or large claims may be seen as higher risk and face higher premiums. On the other hand, businesses with a strong track record of effective risk management and few claims may enjoy more competitive rates.
Implementing robust risk management strategies can not only help prevent accidents and reduce the likelihood of claims but can also lead to lower insurance costs. This includes investing in employee training, implementing safety protocols, and regularly reviewing and updating risk assessment procedures.
Insurance Provider and Market Conditions
The choice of insurance provider is another important consideration. Different insurers may offer varying rates and levels of service for similar coverage. It’s essential for businesses to shop around and compare quotes from multiple providers to find the best fit for their needs and budget.
Additionally, market conditions can influence insurance costs. During periods of economic uncertainty or high claim activity, insurers may raise premiums across the board to offset potential losses. Conversely, in a stable market with low claim rates, businesses may enjoy more competitive insurance rates.
Discounts and Bundling Options
Businesses can often take advantage of discounts and bundling options to reduce their insurance costs. Many insurers offer discounts for businesses that maintain good safety records, install security systems, or implement other risk-mitigating measures. Additionally, bundling multiple insurance policies with the same provider can often lead to cost savings.
For example, a business that purchases property insurance, liability insurance, and business interruption insurance from the same provider may be eligible for a bundled discount. This not only simplifies insurance management but also can result in significant cost savings.
Strategies for Managing Business Insurance Costs

While the cost of business insurance is influenced by various factors, there are strategies that businesses can employ to manage and potentially reduce these expenses. By implementing the following approaches, businesses can ensure they have adequate coverage without breaking the bank.
Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
The first step in managing insurance costs is conducting a thorough risk assessment. This involves identifying all potential risks and hazards that the business may face, from property damage to liability claims. By understanding these risks, businesses can make informed decisions about the type and level of insurance coverage they require.
A risk assessment should consider both internal and external factors. Internal factors might include the business's safety record, employee training, and existing safety protocols. External factors could encompass the business's location, industry trends, and potential changes in regulations or market conditions.
Shop Around for the Best Rates
As mentioned earlier, comparing quotes from multiple insurance providers is essential to finding the most cost-effective coverage. Businesses should take the time to research and reach out to various insurers, providing detailed information about their operations and risk profile to receive accurate quotes.
Online insurance marketplaces can be a useful tool for quickly comparing quotes from multiple providers. However, it's important to carefully review the coverage details and ensure that the policies being compared offer similar levels of protection. The cheapest option may not always be the best if it leaves the business underinsured.
Review Coverage Regularly
Insurance needs can change over time as a business evolves and grows. It’s important for businesses to regularly review their insurance coverage to ensure it remains adequate and cost-effective. This might involve reassessing risks, updating policies, or making changes to coverage limits or deductibles.
For example, if a business expands its operations or enters new markets, its insurance needs may change. In such cases, the business should review its policies to ensure they provide sufficient coverage for the new operations. Conversely, if a business scales back its operations or implements effective risk-mitigating measures, it may be able to reduce its insurance coverage and associated costs.
Implement Risk Mitigation Measures
By taking steps to reduce risks, businesses can often qualify for lower insurance premiums. Insurers view businesses that actively manage and mitigate risks as less likely to file claims, which can result in more favorable rates.
Risk mitigation measures can vary depending on the business and its unique risks. For example, a manufacturing business might invest in advanced safety equipment and implement rigorous employee training programs to reduce the risk of workplace accidents. A retail business, on the other hand, might focus on enhancing security systems and implementing robust inventory management practices to prevent theft and loss.
Consider Alternative Risk Transfer Methods
In some cases, businesses may find that alternative risk transfer methods can help manage insurance costs. These methods include options such as captives, risk retention groups, and self-insurance.
Captives are insurance companies owned by one or more non-insurance companies, often referred to as the parent company or companies. By creating a captive, a business can effectively become its own insurer, allowing for more control over insurance costs and coverage. However, captives require significant financial investment and expertise to manage effectively.
Risk retention groups are another alternative risk transfer method. These are groups of similar businesses that band together to provide liability insurance to each other. By pooling their resources, members can often secure more affordable insurance rates. However, like captives, risk retention groups require careful management and may not be suitable for all businesses.
Self-insurance is yet another option. This involves a business setting aside funds to cover potential losses rather than purchasing insurance. While this can save on insurance premiums, it requires a substantial financial commitment and carries the risk of significant financial loss if a large claim occurs.
Conclusion: Understanding the Cost of Business Insurance
Navigating the complex landscape of business insurance and understanding the associated costs can be a challenging task for business owners. By thoroughly understanding the factors that influence insurance costs and implementing effective strategies to manage these expenses, businesses can ensure they have the coverage they need without compromising their financial health.
From conducting comprehensive risk assessments to exploring alternative risk transfer methods, there are numerous approaches businesses can take to optimize their insurance coverage and costs. By staying informed and proactive, businesses can effectively protect their operations and mitigate risks while maintaining a healthy bottom line.
What is the average cost of business insurance for a small business?
+The average cost of business insurance for a small business can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the industry, location, size of the business, and the specific types of coverage required. On average, small businesses can expect to pay anywhere from 500 to 2,000 per year for a basic business owner’s policy (BOP), which typically includes property and liability insurance. However, this range can be much wider, with some businesses paying as little as a few hundred dollars while others pay several thousand dollars annually.
How can a business reduce its insurance costs without compromising coverage?
+There are several strategies businesses can employ to reduce insurance costs without sacrificing coverage. These include conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify areas where coverage can be tailored or reduced, shopping around for quotes from multiple insurers to compare rates, and negotiating with insurers to find the best value. Additionally, implementing effective risk management strategies can reduce the likelihood of claims, which can lead to lower premiums. Businesses can also consider bundling multiple insurance policies or increasing deductibles to lower costs, but these decisions should be made carefully to ensure adequate coverage.
What are some common mistakes businesses make when it comes to business insurance costs?
+One common mistake businesses make is failing to adequately assess their unique risks and needs, which can lead to either over- or under-insuring. Not shopping around for quotes from multiple insurers can also result in higher costs, as businesses may not be aware of more competitive rates available in the market. Additionally, failing to regularly review and update insurance policies can leave businesses with outdated coverage that may not adequately protect them in the event of a claim. Finally, not taking advantage of discounts and bundling options can mean businesses are missing out on potential cost savings.



