Do You Pay Taxes On Life Insurance
Taxation is a complex topic that varies across jurisdictions, and understanding how it applies to life insurance policies is crucial for financial planning. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of tax obligations surrounding life insurance, providing clarity and insights for policyholders and those considering such coverage.
The Intersection of Life Insurance and Taxes

Life insurance is a financial tool designed to provide a safety net for beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s death. However, the world of taxation adds an extra layer of complexity to this seemingly straightforward concept. Whether you’re a policyholder, a beneficiary, or simply curious about the financial implications, it’s essential to navigate the tax landscape surrounding life insurance with precision.
Understanding the Basics
At its core, life insurance operates as a contractual agreement between an individual (the policyholder) and an insurance company. The policyholder pays premiums, and in return, the insurance company promises to pay a specified amount (the death benefit) to designated beneficiaries upon the policyholder’s demise. This death benefit is intended to offer financial support and stability to loved ones during a challenging time.
However, the tax implications can vary significantly based on the type of life insurance policy, the purpose for which it was purchased, and the jurisdiction in which the policyholder resides. This guide aims to shed light on these variations and provide a comprehensive understanding of the tax landscape related to life insurance.
Taxation of Life Insurance Premiums

One of the primary questions that arise when discussing life insurance and taxes is whether policyholders are required to pay taxes on their premiums. The answer, much like many aspects of taxation, is dependent on the specific circumstances and the applicable laws.
General Premium Taxation
In most cases, the premiums paid for life insurance policies are not tax-deductible. This means that policyholders typically cannot reduce their taxable income by claiming these premiums as a deduction on their tax returns. Life insurance premiums are considered a personal expense and are treated similarly to other insurance premiums, such as health or auto insurance.
However, there are certain exceptions and specific circumstances where premium deductions might be allowed. For instance, if the life insurance policy is part of a qualified retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or an IRA, the premiums could potentially be tax-deductible. This is because these plans offer tax advantages and often include provisions for life insurance coverage.
| Plan Type | Premium Deduction |
|---|---|
| 401(k) | Depends on plan design |
| IRA | Traditional IRA: Deduction may be available |

It's crucial to note that the tax treatment of life insurance premiums can vary based on the country or region. In some jurisdictions, there might be specific regulations or incentives that encourage the purchase of life insurance, potentially offering tax benefits to policyholders.
Policyholder’s Tax Obligations
While policyholders generally do not pay taxes on their premiums, it’s essential to consider their overall tax obligations. Here are some key aspects to keep in mind:
- Income Tax: Policyholders must ensure that their premiums do not push them into a higher tax bracket, especially if they are close to the income threshold for a higher tax rate.
- Estate Planning: The value of a life insurance policy should be considered when planning an estate to ensure that it does not inadvertently trigger estate taxes upon the policyholder's death.
- Reporting Requirements: Depending on the jurisdiction, policyholders might need to report their life insurance policies and their associated values to tax authorities. This is particularly important for high-value policies.
Taxation of Life Insurance Benefits
The taxation of life insurance benefits, also known as death benefits, is another critical aspect to understand. The tax treatment of these benefits can significantly impact the financial situation of beneficiaries.
General Tax Treatment
In many jurisdictions, life insurance death benefits are typically exempt from income tax for the beneficiaries. This means that the recipients of the death benefit do not have to include it in their taxable income when filing their tax returns. This exemption is designed to provide financial relief to beneficiaries during a challenging period.
However, it's important to note that while death benefits are often exempt from income tax, they might still be subject to other taxes, such as estate or inheritance taxes, depending on the jurisdiction and the value of the policy.
Specific Scenarios
The tax treatment of life insurance benefits can vary based on specific circumstances. Here are some common scenarios to consider:
- Key Person Insurance: If a business purchases a life insurance policy on a key employee, the death benefit might be considered a taxable event for the business, depending on how the policy is structured.
- Business Succession Planning: In certain business structures, life insurance policies can be used as a tool for business succession planning. The tax implications in such cases can be complex and should be carefully evaluated.
- High-Value Policies: For extremely large life insurance policies, there might be additional tax considerations, especially if the policy is owned by a trust or a corporation.
Beneficiary Considerations
While beneficiaries typically do not pay taxes on the death benefit, they should still be mindful of their tax obligations. Here are some key points to consider:
- Income Reporting: Even though the death benefit itself is usually tax-free, any interest or earnings generated from the benefit might be subject to income tax. Beneficiaries should carefully track and report these earnings.
- Estate Planning: If the beneficiary receives a substantial death benefit, it might impact their overall estate value. Proper estate planning can help mitigate potential tax liabilities.
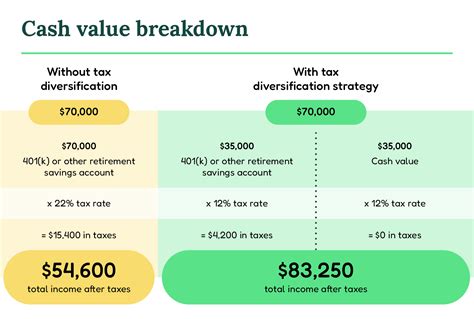
- Tax-Efficient Strategies: Beneficiaries should explore tax-efficient strategies to maximize the value of the death benefit, such as investing the proceeds in tax-advantaged accounts or using them to pay off high-interest debt.
Life Insurance and Tax Planning
Life insurance can be a valuable tool for tax planning, especially when used strategically. Here are some ways in which life insurance can be incorporated into tax planning strategies:
Wealth Transfer and Estate Planning
Life insurance can be a powerful tool for transferring wealth to beneficiaries while minimizing tax liabilities. By structuring the policy appropriately, policyholders can ensure that the death benefit is paid out efficiently and effectively, reducing the impact of estate taxes.
Business Continuity
For business owners, life insurance can be an essential component of business continuity planning. By purchasing life insurance policies on key individuals within the business, owners can ensure that the business has the financial resources to continue operations in the event of an unexpected death.
Charitable Giving
Life insurance policies can also be used for charitable purposes. By naming a charity as the beneficiary, policyholders can ensure that a portion of their estate goes towards a cause they support, potentially reducing their overall tax liability.
The Role of Professional Guidance

Navigating the complex world of life insurance and taxes can be challenging, and it’s essential to seek professional guidance. Financial advisors, tax professionals, and estate planning specialists can provide tailored advice based on individual circumstances.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of life insurance is a vital aspect of financial planning. By grasping the nuances of premium taxation and the tax-exempt status of death benefits, policyholders and beneficiaries can make informed decisions. Additionally, incorporating life insurance into tax planning strategies can offer a range of benefits, from wealth transfer to business continuity. As with any complex financial matter, seeking expert advice is always recommended to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of taxation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are life insurance premiums tax-deductible?
+
In most cases, life insurance premiums are not tax-deductible. However, if the policy is part of a qualified retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or IRA, the premiums might be deductible under certain conditions.
Are life insurance death benefits taxable for beneficiaries?
+
In many jurisdictions, life insurance death benefits are exempt from income tax for beneficiaries. However, they might be subject to other taxes, such as estate or inheritance taxes, depending on the policy’s value and the jurisdiction.
How do life insurance policies fit into tax planning strategies?
+
Life insurance policies can be used for wealth transfer, business continuity, and charitable giving. By structuring policies appropriately, individuals can minimize tax liabilities and ensure that their beneficiaries receive the intended benefits.
Do I need to report my life insurance policy to tax authorities?
+
Reporting requirements vary by jurisdiction. In some cases, high-value policies might need to be reported to tax authorities. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to understand your specific reporting obligations.
Can life insurance be used to reduce estate taxes?
+
Yes, life insurance can be a valuable tool for reducing estate taxes. By properly structuring the policy and naming the appropriate beneficiaries, policyholders can ensure that the death benefit is paid out efficiently, minimizing the impact of estate taxes.