Dtcs Code
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes) system, an essential aspect of modern automotive diagnostics. This article aims to delve into the world of DTCs, providing an in-depth understanding of their role, functionality, and significance in vehicle maintenance and repair. With the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, staying informed about DTCs is crucial for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
The Role and Functionality of DTCs
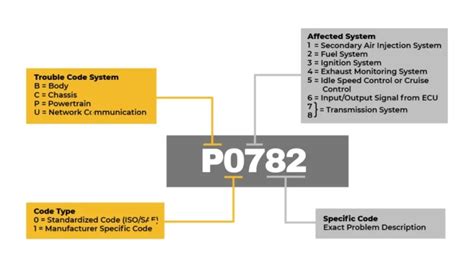
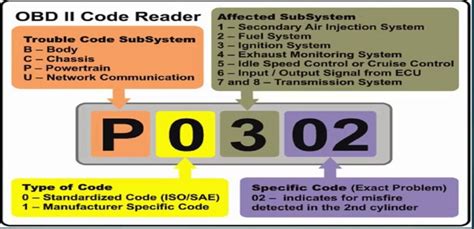
Diagnostic Trouble Codes, or DTCs, are alphanumeric codes used by vehicle onboard diagnostic (OBD) systems to identify and report malfunctions or potential issues within a vehicle’s various systems and components. These codes are generated and stored by the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU) when it detects a problem, providing valuable insights to mechanics and technicians for accurate troubleshooting and repair.
The primary purpose of DTCs is to streamline the diagnostic process, enabling technicians to quickly identify the source of a problem without the need for extensive and time-consuming manual testing. By interpreting these codes, mechanics can efficiently narrow down the scope of an issue, leading to faster and more accurate repairs.
The Evolution of DTCs
The concept of DTCs has evolved significantly since their inception. Initially introduced with the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-I) system, DTCs have become more sophisticated with the advancements in vehicle technology. The OBD-II system, which became mandatory for all light-duty vehicles sold in the US from 1996 onwards, brought about a standardized system of DTCs, making diagnostics more consistent across different vehicle makes and models.
Today, DTCs are an integral part of modern vehicle diagnostics, with each code representing a specific issue or error. The format of these codes typically consists of a prefix indicating the system or subsystem in which the issue has been detected, followed by a numerical code that provides further details about the problem.
| DTC Prefix | System Indication |
|---|---|
| P0XXX | Powertrain |
| B1XXX | Body Control Module |
| C1XXX | Chassis |
| U1XXX | Network Communications |
| etc. | ... |

Interpreting DTCs: A Practical Guide

Interpreting DTCs is a skill that every automotive professional should master. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the world of DTC diagnostics.
Step 1: Retrieving DTCs
The first step in interpreting DTCs is to retrieve them from the vehicle’s ECU. This is typically done using an OBD-II scanner or code reader, which can be connected to the vehicle’s diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard near the steering wheel.
Once connected, the scanner will communicate with the ECU to retrieve any stored DTCs. It's important to note that some vehicles may have multiple DTCs stored, especially if multiple issues have been detected.
Step 2: Understanding the DTC
Once you have retrieved the DTCs, the next step is to understand what they mean. Each DTC is associated with a specific issue or malfunction. Online resources, vehicle service manuals, and diagnostic software can provide detailed explanations of each code.
For instance, a code like P0420 indicates an issue with the vehicle's catalytic converter, while B1416 might relate to a malfunction in the driver's side airbag system.
Step 3: Diagnostic Procedures
With the DTCs understood, the next step is to follow the recommended diagnostic procedures. These procedures are often outlined in the vehicle’s service manual or can be found in online resources. They typically involve a series of tests and inspections to confirm the issue and identify the root cause.
Diagnostic procedures may involve visual inspections, testing individual components, or using specialized tools to measure and analyze system performance.
Step 4: Repair and Verification
Once the issue has been diagnosed, the necessary repairs can be made. This may involve replacing faulty components, adjusting or reprogramming the ECU, or addressing other system issues.
After the repairs are completed, it's crucial to verify the success of the repair by clearing the DTCs and conducting a post-repair test drive. This ensures that the issue has been resolved and that the vehicle is operating as intended.
The Impact of DTCs on Vehicle Maintenance and Performance
DTCs play a critical role in maintaining vehicle performance and reliability. By promptly addressing the issues indicated by DTCs, vehicle owners can prevent small problems from escalating into major, costly repairs.
Improved Diagnostics and Repair Accuracy
DTCs provide a standardized and efficient way to diagnose vehicle issues. By quickly identifying the affected system or component, mechanics can save time and resources, leading to faster and more accurate repairs. This precision in diagnostics can significantly reduce the downtime of a vehicle, keeping it on the road and operational.
Proactive Maintenance and Preventive Care
DTCs can also serve as an early warning system, alerting vehicle owners and mechanics to potential issues before they become major problems. Regularly monitoring DTCs can help identify developing problems, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventive care. This can extend the lifespan of various vehicle components and systems, reducing the need for frequent and costly repairs.
Enhanced Vehicle Safety and Reliability
Many DTCs are related to safety-critical systems, such as the braking system, airbag deployment, or stability control. By promptly addressing these issues, vehicle owners can ensure the safety and reliability of their vehicles, reducing the risk of accidents or breakdowns.
Performance Optimization
DTCs can also help optimize vehicle performance. For instance, if a DTC indicates an issue with the engine management system, addressing this issue can lead to improved fuel efficiency, smoother operation, and better overall performance.
Conclusion: The Future of DTCs
The world of automotive diagnostics is constantly evolving, and DTCs are at the forefront of this evolution. With the increasing complexity of vehicle systems and the integration of advanced technologies like electric powertrains and autonomous driving features, DTCs will continue to play a pivotal role in vehicle maintenance and repair.
As vehicle technology advances, DTCs will likely become more sophisticated, providing even more detailed information about vehicle systems and components. This will further enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostics, benefiting both automotive professionals and vehicle owners.
In conclusion, understanding DTCs is not just a skill for mechanics; it's a valuable asset for anyone interested in maintaining their vehicle's health and performance. By staying informed about DTCs and their role in vehicle diagnostics, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable, safe, and efficient for years to come.
How often should I check for DTCs in my vehicle?
+It’s recommended to check for DTCs regularly, especially if you notice any unusual behavior or performance issues with your vehicle. Many modern vehicles have systems that monitor for issues and will alert you with a warning light or message on the dashboard when a DTC is detected. Regular check-ups with an OBD-II scanner or code reader can also help catch potential issues early.
Can I clear DTCs myself, or should I take my vehicle to a professional?
+While it is possible to clear DTCs using an OBD-II scanner or code reader, it’s important to understand that clearing DTCs only erases the error code, not the underlying issue. It’s recommended to take your vehicle to a professional mechanic or technician who can properly diagnose and address the problem indicated by the DTC. They will have the necessary tools and expertise to ensure the issue is fully resolved.
Are DTCs the same for all vehicle makes and models?
+While the general concept of DTCs is standardized across vehicles, the specific codes and their meanings can vary between different makes and models. This is because each vehicle manufacturer may use slightly different systems and components, leading to unique DTCs for specific issues. However, the OBD-II system has made DTCs more consistent across vehicles, especially for common issues.



