Employment Insurance Reporting

Employment Insurance (EI) is a vital program in many countries, offering financial support and benefits to individuals who find themselves unemployed. Effective management and reporting of EI claims are crucial for both claimants and the government to ensure a smooth and efficient process. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of EI reporting, exploring the key aspects, best practices, and potential challenges faced by claimants and administrators alike.
Understanding Employment Insurance
Employment Insurance is a social safety net designed to provide temporary financial assistance to eligible workers who have lost their jobs through no fault of their own. It aims to offer income support during periods of unemployment, help workers develop new skills, and facilitate their re-entry into the workforce. The program is funded by premiums paid by employees and employers, with the government overseeing its administration and management.
EI programs vary in structure and eligibility criteria from country to country, but they generally share common goals of ensuring financial stability for unemployed individuals and supporting their transition back into employment.
The Importance of EI Reporting

Accurate and timely reporting is essential for the effective functioning of the EI system. It serves several critical purposes, including:
- Claim Processing: EI administrators rely on claimant-reported information to process claims efficiently. Inaccurate or incomplete reporting can lead to delays in receiving benefits or even the rejection of valid claims.
- Program Integrity: Proper reporting helps maintain the integrity of the EI program by preventing fraud and ensuring that benefits are distributed fairly to those who truly need them.
- Data Analysis: Aggregated reporting data provides valuable insights for policymakers and economists. It aids in understanding labor market trends, identifying skill gaps, and formulating strategies to enhance employment opportunities.
- Claimant Support: Regular and accurate reporting ensures that claimants receive the correct benefit amount and duration, helping them plan their finances and transition back into the workforce.
Key Components of EI Reporting
EI reporting involves several interconnected steps and considerations. Here’s a breakdown of the key components:
1. Initial Claim Submission
Claimants must initiate the EI reporting process by submitting an initial claim, typically within a specific timeframe after becoming unemployed. This claim serves as the foundation for benefit eligibility and provides essential information such as:
- Personal details (name, address, contact information)
- Employment history
- Reason for unemployment
- Earnings and hours worked
- Bank account details for direct deposit of benefits
Claimants are often required to provide supporting documentation, such as employment records or termination notices, to validate their claim.
2. Regular Reporting
Once a claim is approved, claimants are responsible for regular reporting, usually on a bi-weekly or monthly basis. This reporting period is known as a reporting cycle. During each cycle, claimants must report on their employment status, earnings, and any other relevant changes that may impact their benefit eligibility.
For instance, claimants must report if they:
- Find new employment
- Work any number of hours, even if it's a short-term or casual job
- Earn income from self-employment or contract work
- Have reduced work hours or are on unpaid leave
- Are sick, injured, or have a disability that impacts their ability to work
Claimants typically report their earnings and employment status through online portals, phone calls, or mailed forms. Failure to report accurately or within the specified timeframe can result in benefit interruptions or penalties.
3. Documenting Employment Efforts
To maintain benefit eligibility, claimants are often required to actively seek new employment opportunities. This process, known as job search, is an integral part of EI reporting. Claimants must document their job search efforts, including:
- Resumes sent
- Interviews attended
- Job applications submitted
- Training or skill development programs attended
EI administrators may request claimants to provide evidence of their job search activities, such as copies of resumes, application confirmations, or references from job fairs.
4. Reporting Changes in Circumstances
Throughout the duration of their EI claim, claimants must promptly report any significant changes in their circumstances that could impact their benefit eligibility. This includes changes in:
- Address or contact information
- Bank account details
- Marital status
- Dependents or childcare arrangements
- Medical conditions or disabilities
Failing to report such changes accurately and in a timely manner can result in overpayments or underpayments, which claimants may be required to repay.
5. Record Keeping
Maintaining thorough and organized records is crucial for claimants. This includes:
- Saving all correspondence with EI administrators
- Keeping track of reporting cycles and due dates
- Retaining copies of all submitted forms and supporting documents
- Documenting job search activities and outcomes
Proper record keeping not only helps claimants stay organized but also provides evidence in case of audits or appeals.
Best Practices for EI Reporting
To ensure a smooth and stress-free EI reporting experience, claimants can follow these best practices:
- Stay Informed: Understand the EI program rules and regulations specific to your country or region. Familiarize yourself with the eligibility criteria, benefit calculation methods, and reporting requirements.
- Set Reminders: Create a calendar or use reminder apps to stay on top of reporting deadlines. Missing a reporting cycle can result in benefit interruptions.
- Keep Records: Maintain a well-organized file with all EI-related documents, including claim forms, correspondence, and evidence of job search activities.
- Report Accurately: Be honest and provide accurate information in your reports. Overstating or understating earnings or employment status can lead to penalties and legal consequences.
- Seek Assistance: If you're unsure about any aspect of the EI program or reporting process, don't hesitate to reach out to EI administrators or seek advice from employment agencies or legal professionals.
Challenges and Potential Pitfalls
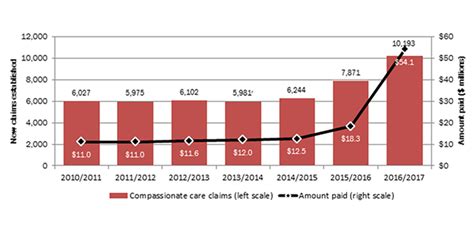
While EI reporting is a straightforward process for many claimants, it can present challenges for others. Some common obstacles include:
- Complex Eligibility Rules: The EI program often has intricate eligibility criteria, which can be confusing for claimants, especially those with unique employment circumstances or multiple jobs.
- Reporting Errors: Accidental or intentional errors in reporting can lead to benefit interruptions or penalties. Claimants may mistakenly report incorrect earnings or fail to disclose all sources of income.
- Job Search Requirements: Actively seeking employment while managing the reporting process can be daunting, especially for those with limited job prospects or those who face barriers due to disabilities or caregiving responsibilities.
- Technology Barriers: Some claimants, particularly older adults or those with limited access to technology, may struggle with online reporting systems or phone-based services.
Conclusion: Empowering Claimants and Administrators
Employment Insurance reporting is a critical aspect of the social safety net, ensuring that unemployed individuals receive the financial support they need while also maintaining the integrity of the program. By understanding the key components, best practices, and potential challenges, claimants can navigate the reporting process with confidence and efficiency.
Additionally, EI administrators play a vital role in educating claimants, providing clear guidance, and implementing technologies that streamline the reporting process. Together, claimants and administrators can work towards a more effective and inclusive EI system, fostering economic resilience and supporting individuals during periods of unemployment.
How often do I need to report my employment status and earnings during an EI claim?
+Reporting frequency varies depending on the EI program in your country. Generally, you’ll need to report your employment status and earnings on a bi-weekly or monthly basis. It’s crucial to stay informed about the specific reporting requirements in your region to avoid benefit interruptions.
What happens if I miss a reporting cycle or make a mistake in my EI report?
+Missing a reporting cycle or making an error in your report can have consequences. You may face benefit interruptions or even have to repay any benefits received during that cycle. It’s important to stay organized, set reminders, and report accurately to avoid such issues.
Can I appeal an EI decision if I disagree with it?
+Yes, most EI programs offer appeal processes if you believe a decision made about your claim is incorrect or unfair. It’s essential to understand the appeal process in your region and gather evidence to support your case. Seeking legal advice can also be beneficial in such situations.