Flood Zone Insurance Cost
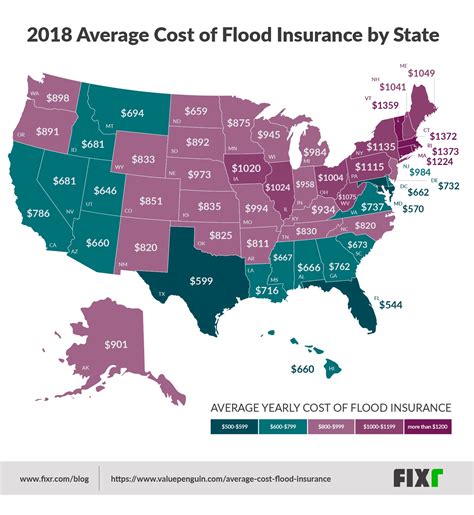
Understanding the cost of flood zone insurance is crucial for homeowners and businesses alike, especially in areas prone to flooding. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the various factors influencing these insurance premiums and provide valuable insights into the financial protection needed in flood-prone regions.
Navigating the Complex World of Flood Zone Insurance Costs

The cost of flood insurance in designated flood zones can vary significantly based on numerous factors. These include the specific flood zone classification, the type of structure being insured, its location, and the value of the property at risk. Understanding these variables is essential for property owners to make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
Flood zone insurance costs are influenced by the level of risk associated with a particular area. The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) categorizes flood zones into different classes, each with its own level of flood risk. For instance, a property located in a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), indicated by zones beginning with the letter "A" or "V," generally faces a higher risk and thus may require more extensive and costly insurance coverage.
Factors Influencing Flood Zone Insurance Premiums
Several key factors contribute to the variability in flood insurance premiums:
- Flood Zone Classification: As mentioned, the specific flood zone a property falls into plays a pivotal role in determining insurance costs. Higher-risk zones typically attract higher premiums.
- Property Type: The type of structure, whether it’s a residential home, a commercial building, or a mobile home, can significantly impact insurance rates. For instance, residential properties often have different coverage requirements and costs compared to commercial establishments.
- Location: The geographical location of a property can influence insurance costs. Factors such as proximity to bodies of water, historical flood data, and local flood control measures can all affect the perceived risk and, consequently, the insurance premium.
- Property Value: The value of the property being insured is a critical factor. Higher-value properties often require more extensive coverage, which can result in higher insurance premiums.
| Flood Zone Classification | Premium Range |
|---|---|
| Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA) | $1,000 - $2,500 per year |
| Moderate- to Low-Risk Areas | $500 - $1,200 per year |
| Undetermined Risk Zones | $300 - $800 per year |

These ranges are estimates and can vary significantly based on the specific factors mentioned earlier.
Analyzing the Impact of Flood Zone on Insurance Costs

The flood zone classification system is a critical determinant of insurance costs. FEMA’s flood maps divide areas into different zones, each with its unique risk profile. Properties located in Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs) face the highest risk and, consequently, the highest insurance premiums. These zones, typically marked with the letters “A” or “V,” include areas that have a 1% annual chance of flooding (also known as the 100-year floodplain) or areas that have been historically flooded.
On the other hand, properties in moderate- to low-risk zones, denoted by the letters "B," "C," or "X," may experience lower insurance costs. These areas have a lower probability of flooding, often with a 0.2% annual chance (equivalent to the 500-year floodplain). While these zones are not immune to flooding, the perceived risk is lower, resulting in more affordable insurance premiums.
Additionally, there are undetermined risk zones, which are areas that have not been comprehensively studied or mapped for flood risk. Properties in these zones may have lower insurance costs, but it's essential to note that this could be due to a lack of available data rather than a genuine low-risk status.
Case Study: Impact of Flood Zone on Insurance Costs
To illustrate the impact of flood zone on insurance costs, let’s consider a hypothetical scenario involving two properties, one in a high-risk zone and the other in a moderate-risk zone.
Property A, located in a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), faces an annual insurance premium of approximately $2,000. This property, due to its high-risk location, requires extensive coverage to protect against potential flood damage. In contrast, Property B, situated in a moderate-risk zone, pays around $800 annually for flood insurance. While Property B is not immune to flooding, the lower risk profile allows for more affordable insurance coverage.
This case study highlights the significant difference in insurance costs based on flood zone classification. Property owners should be aware of their property's flood zone status and understand how it affects their insurance needs and costs.
The Role of Property Type and Location in Flood Insurance Costs
The type of property being insured and its geographical location are additional critical factors influencing flood insurance premiums. These elements can significantly impact the perceived risk and, consequently, the insurance rates.
Property Type
The type of structure being insured can have a substantial effect on insurance costs. For instance, residential properties, such as single-family homes or condominiums, generally have different coverage needs and costs compared to commercial properties like office buildings or warehouses. Residential properties often require more comprehensive coverage, including protection for personal belongings, which can drive up insurance premiums.
Additionally, the construction type of the property can also influence insurance costs. Properties built with flood-resistant materials or elevated to mitigate flood risk may qualify for lower insurance rates. Conversely, properties in high-risk areas that lack flood-resistant features may face higher premiums.
Location
The geographical location of a property is another key factor in determining insurance costs. Properties in areas with a history of flooding or those near bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, or coastal regions, often face higher insurance premiums. The proximity to these water sources increases the likelihood of flooding, which in turn raises the perceived risk and insurance costs.
Furthermore, local flood control measures can also impact insurance rates. Properties located in areas with effective flood protection systems, such as levees or dams, may benefit from lower insurance costs. In contrast, properties in regions lacking such infrastructure may face higher premiums due to the increased risk of flooding.
| Property Type | Premium Range |
|---|---|
| Residential (Single-Family Home) | $800 - $2,500 per year |
| Residential (Condominium) | $600 - $1,800 per year |
| Commercial (Office Building) | $1,500 - $4,000 per year |
| Commercial (Warehouse) | $2,000 - $5,000 per year |
These ranges are approximate and can vary based on the specific location and other factors.
Understanding the Value of Flood Insurance: A Comprehensive Analysis
Flood insurance is an essential financial safeguard for property owners in flood-prone areas. It provides coverage for damage caused by flooding, which is typically excluded from standard homeowners or renters insurance policies. Understanding the value of flood insurance involves a comprehensive analysis of the risks, costs, and benefits associated with this specialized coverage.
Risk Assessment and the Value of Flood Insurance
Flooding is one of the most common and costly natural disasters. It can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and personal belongings. The risk of flooding is not limited to properties located in designated flood zones; even areas not historically prone to flooding can experience flash floods or severe weather events that lead to flooding.
Flood insurance offers a critical layer of protection against these risks. It provides coverage for a wide range of flood-related damages, including structural damage to the building, damage to its contents, and, in some cases, additional living expenses if the property becomes uninhabitable due to flooding.
The Cost of Flood Insurance
While flood insurance can be costly, it’s important to consider the potential financial loss in the event of a flood. The average cost of flood insurance varies based on several factors, including the flood zone classification, property type, location, and the amount of coverage needed. For example, a residential property in a high-risk flood zone may pay an annual premium of 2,000 or more, while a property in a moderate-risk zone might pay closer to 1,000.
Despite the cost, flood insurance can provide significant financial protection. A single flood event can result in tens of thousands of dollars in damage, and without insurance, the property owner is responsible for covering these costs out of pocket. Flood insurance can help mitigate this financial burden, providing peace of mind and ensuring that property owners can recover and rebuild after a flood.
Benefits and Coverage of Flood Insurance
Flood insurance offers a wide range of benefits and coverage options. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), which is administered by FEMA, provides standard flood insurance policies that cover both the building and its contents. These policies typically have a deductible and coverage limits, which can be customized based on the property owner’s needs.
In addition to the standard NFIP policies, there are also private flood insurance options available. These policies may offer higher coverage limits, additional coverages, or more flexible deductibles. Private flood insurance can be especially beneficial for high-value properties or properties with unique coverage needs.
| Flood Insurance Type | Coverage Highlights |
|---|---|
| NFIP Standard Policy | Covers building and contents; offers flexible deductibles and coverage limits |
| Private Flood Insurance | Higher coverage limits, additional coverages, and more customization options |
Regardless of the type of flood insurance chosen, it's crucial to understand the policy's coverage and exclusions. Some common exclusions include flood-related damage caused by mold, earth movement (such as mudslides), and certain types of water damage that are not directly related to flooding.
FAQ

How often should I review my flood insurance policy and coverage limits?
+
It is recommended to review your flood insurance policy annually, especially after any significant changes to your property or its value. Regular reviews ensure that your coverage limits align with the current value of your property and any improvements made. This way, you can rest assured that you have adequate protection in the event of a flood.
Can I get flood insurance if my property is located in a high-risk flood zone?
+
Absolutely! While properties in high-risk flood zones typically require more extensive and costly insurance coverage, flood insurance is still available and highly recommended. The National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) offers policies for all types of properties, regardless of their flood zone classification. Private flood insurance providers may also offer coverage for high-risk properties.
What are some common exclusions in flood insurance policies?
+
Common exclusions in flood insurance policies include damage caused by mold, earth movement (like mudslides), and certain types of water damage not directly related to flooding. It’s important to carefully review your policy’s exclusions to understand what is and isn’t covered. Understanding these exclusions can help you make informed decisions about additional coverages or policies to ensure comprehensive protection.



