Hmo Insurance Definition
HMO, an acronym for Health Maintenance Organization, represents a prevalent healthcare model in the United States. It is a managed care organization that provides healthcare services to its members through a network of contracted healthcare providers. HMO plans are designed to offer comprehensive and cost-effective healthcare by emphasizing preventative care and coordinated services.
The Core Principles of HMO Insurance

At the heart of HMO insurance are several fundamental principles that shape its operation and the overall healthcare experience for its members.
1. Pre-Designated Primary Care Physician (PCP)
One distinctive feature of HMO plans is the requirement for members to select a primary care physician (PCP) from within the HMO network. This PCP acts as the initial point of contact for all healthcare needs and coordinates the member’s care, including referrals to specialists when necessary.
The PCP plays a pivotal role in managing the member's healthcare journey, ensuring continuity of care, and facilitating timely access to specialized services. This approach not only fosters a strong doctor-patient relationship but also contributes to more efficient and effective healthcare delivery.
2. Emphasis on Preventative Care
HMO insurance places a strong emphasis on preventative care, recognizing its role in maintaining good health and reducing the need for costly medical interventions. This focus is evident in the coverage provided for preventative services such as annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings for various health conditions.
By encouraging regular preventative care, HMO plans aim to identify and address health issues early on, promoting better health outcomes and reducing the burden of chronic diseases. This proactive approach to healthcare aligns with the HMO philosophy of prioritizing health maintenance over reactive treatment.
3. Coordinated Care and Referral Management
Coordinated care is a cornerstone of HMO insurance, ensuring that members receive comprehensive and well-managed healthcare. The HMO network, consisting of hospitals, clinics, and a wide range of healthcare providers, works collaboratively to provide integrated care.
When a member requires specialized care, the PCP is responsible for providing a referral to an in-network specialist. This referral process ensures that the member's care is well-coordinated, reducing the risk of duplicate services and improving overall healthcare efficiency. The HMO model thus promotes a seamless healthcare experience, where different providers work together to meet the member's healthcare needs.
4. Cost-Effectiveness and Managed Care
HMO insurance plans are renowned for their cost-effectiveness, offering comprehensive healthcare coverage at a relatively affordable price. This is achieved through the HMO’s managed care approach, which involves careful selection and contracting of healthcare providers to deliver quality services at competitive rates.
By negotiating favorable rates with providers and implementing strategies to reduce unnecessary healthcare utilization, HMO plans are able to control costs while still providing high-quality care. This managed care model not only benefits the HMO and its members but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the healthcare system.
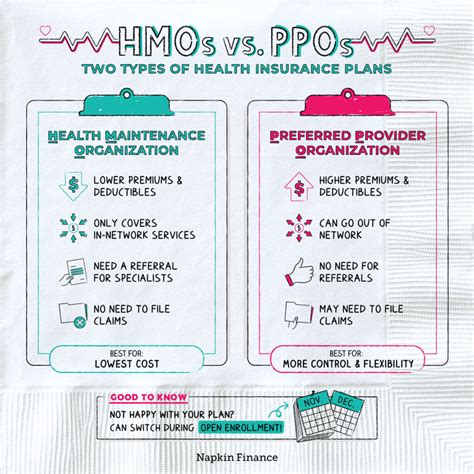
The Benefits and Drawbacks of HMO Insurance
Like any healthcare model, HMO insurance comes with its own set of advantages and limitations, which are essential to consider when choosing a healthcare plan.
Benefits of HMO Insurance
HMO plans offer several notable benefits that can make them an attractive choice for many individuals and families.
Firstly, the emphasis on preventative care and coordinated services can lead to improved health outcomes and a higher quality of life. By catching health issues early and providing timely interventions, HMO plans can help prevent more serious health complications down the line.
Secondly, the cost-effectiveness of HMO plans is a significant advantage. With lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other insurance models, HMO plans can provide substantial savings, especially for those with limited healthcare needs.
Lastly, the HMO model often provides access to a broad network of healthcare providers, ensuring that members have a range of options for their healthcare needs. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who require specialized care or who prefer a particular type of provider.
Drawbacks of HMO Insurance
While HMO plans offer many benefits, there are also potential drawbacks that should be considered.
One common concern with HMO plans is the requirement to select a PCP and the need for referrals to see specialists. This process can sometimes be seen as cumbersome or restrictive, especially for those who prefer to have more freedom in choosing their healthcare providers.
Additionally, while HMO plans are generally cost-effective, there may be certain services or treatments that are not covered or have limited coverage. This can result in unexpected out-of-pocket expenses, particularly for those with more complex healthcare needs.
Lastly, the HMO model may not be well-suited for individuals who require frequent emergency care or who have health conditions that require specialized, ongoing treatment. In such cases, the managed care approach of HMO plans may not provide the flexibility or coverage needed.
HMO Insurance in Practice: Real-World Examples
To better understand how HMO insurance works in practice, let’s explore some real-world examples of HMO plans and their impact on healthcare delivery.
1. HMO Plan for a Family with Young Children
A family with young children may opt for an HMO plan due to its emphasis on preventative care and the potential for cost savings. The HMO plan can provide coverage for annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings, ensuring that the children receive the necessary preventative care to maintain good health.
In this scenario, the family would select a PCP who would act as the primary point of contact for all their healthcare needs. The PCP would coordinate any necessary referrals to specialists, such as pediatricians or allergists, ensuring that the children receive comprehensive and well-managed care.
The cost-effectiveness of the HMO plan can be particularly beneficial for this family, as they may have limited healthcare needs and can therefore save on premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other insurance models.
2. HMO Plan for an Individual with Chronic Health Conditions
An individual with chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, may choose an HMO plan for the coordinated care and specialized services it offers. The HMO network can provide access to a range of healthcare providers, including specialists and support services, to manage the individual’s complex healthcare needs.
In this case, the individual would select a PCP who would oversee their care and ensure that they receive the necessary treatments and interventions. The PCP would coordinate with specialists, such as endocrinologists or cardiologists, to develop a comprehensive care plan and manage the individual's health effectively.
While HMO plans may have certain limitations in coverage for specialized treatments, the managed care approach can still provide cost savings and ensure that the individual receives high-quality, coordinated care.
3. HMO Plan for a Large Employer
Large employers often choose to offer HMO plans to their employees due to the cost-effectiveness and comprehensive coverage these plans provide. By negotiating favorable rates with the HMO and leveraging the managed care approach, employers can offer competitive healthcare benefits to their workforce.
The HMO plan can provide access to a broad network of healthcare providers, ensuring that employees have a range of options for their healthcare needs. This can be particularly beneficial for a diverse workforce with varying healthcare requirements.
Additionally, the emphasis on preventative care and coordinated services can help employers promote a culture of health and wellness among their employees, leading to improved productivity and reduced absenteeism.
The Future of HMO Insurance: Trends and Innovations
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, HMO insurance is also adapting and innovating to meet the changing needs of its members and the healthcare system as a whole.
1. Focus on Value-Based Care
There is a growing trend towards value-based care in the healthcare industry, and HMO plans are no exception. Value-based care emphasizes the delivery of high-quality, cost-effective healthcare that is centered on the needs of the patient.
HMO plans are increasingly adopting value-based care models, which focus on improving health outcomes and patient satisfaction while reducing unnecessary healthcare utilization and costs. This shift towards value-based care aligns with the HMO philosophy of promoting preventative care and coordinated services.
2. Integration of Technology
Technology is playing an increasingly significant role in the healthcare industry, and HMO plans are leveraging technology to enhance their operations and improve the member experience.
HMO plans are adopting digital tools and platforms to facilitate communication between healthcare providers and members, improve referral management, and enhance overall care coordination. Telehealth services, for example, are becoming more prevalent, allowing members to access healthcare services remotely, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
Additionally, HMO plans are utilizing data analytics and artificial intelligence to identify trends, predict healthcare needs, and improve the efficiency of their healthcare delivery systems.
3. Emphasis on Wellness and Prevention
The focus on wellness and prevention is gaining traction within the HMO industry, as plans recognize the importance of promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing disease.
HMO plans are developing initiatives and programs to encourage members to adopt healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management. These initiatives can include fitness challenges, nutrition counseling, and mental health support services.
By promoting wellness and prevention, HMO plans aim to not only improve the overall health of their members but also reduce the burden of chronic diseases and healthcare costs in the long term.
Conclusion: The Role of HMO Insurance in the Healthcare Landscape

HMO insurance plays a vital role in the U.S. healthcare landscape, offering a managed care approach that emphasizes preventative care, coordinated services, and cost-effectiveness. By selecting a primary care physician and utilizing the HMO network, members can access comprehensive healthcare services tailored to their needs.
While HMO plans come with certain limitations, such as the need for referrals and potential limitations in coverage, they remain a popular choice for many individuals and families due to their focus on wellness, cost-effectiveness, and access to a broad network of healthcare providers.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, HMO plans are adapting and innovating to meet the changing needs of their members. By embracing value-based care, integrating technology, and promoting wellness, HMO insurance is poised to continue playing a significant role in delivering high-quality, accessible healthcare in the years to come.
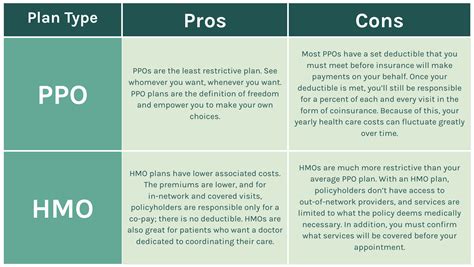
What is the difference between an HMO and a PPO insurance plan?
+An HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and a PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) are two different types of health insurance plans. The key difference lies in their approach to healthcare coverage and provider networks. HMO plans typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within their network and obtain referrals for specialist care. They emphasize preventative care and coordinated services. On the other hand, PPO plans offer more flexibility, allowing members to see any in-network provider without a referral. PPO plans often have a larger network of providers and may offer more coverage options, but they generally come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
How do I choose the right HMO plan for my needs?
+Choosing the right HMO plan involves considering several factors. First, assess your healthcare needs and preferences. If you value preventative care and coordinated services, an HMO plan may be a good fit. Evaluate the HMO network to ensure it includes providers and specialists you may need. Consider the cost of premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, as well as any potential limitations in coverage. It’s also beneficial to read reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources to get a better understanding of the HMO’s performance and member satisfaction.
Are there any disadvantages to choosing an HMO plan?
+While HMO plans offer many advantages, there are some potential disadvantages to consider. One common concern is the requirement to select a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals for specialist care, which may be seen as restrictive. Additionally, while HMO plans are generally cost-effective, there may be certain services or treatments that are not fully covered, leading to unexpected out-of-pocket expenses. Furthermore, the managed care approach of HMO plans may not be suitable for individuals with frequent emergency care needs or complex, ongoing health conditions.



