Hmo Or Ppo Health Insurance
When it comes to health insurance, understanding the different plan options is crucial to making an informed decision. Two popular types of health insurance plans are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). These plans offer distinct features and benefits, catering to various healthcare needs and preferences. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of HMOs and PPOs, helping you navigate the complex world of health insurance with clarity and confidence.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs)

Health Maintenance Organizations, or HMOs, are a type of managed care plan that emphasizes preventative care and a coordinated approach to healthcare. HMOs typically have a network of healthcare providers, including doctors, specialists, and hospitals, with whom they have negotiated discounted rates. By choosing an HMO, individuals gain access to this network and enjoy cost-effective healthcare services.
Key Features of HMOs
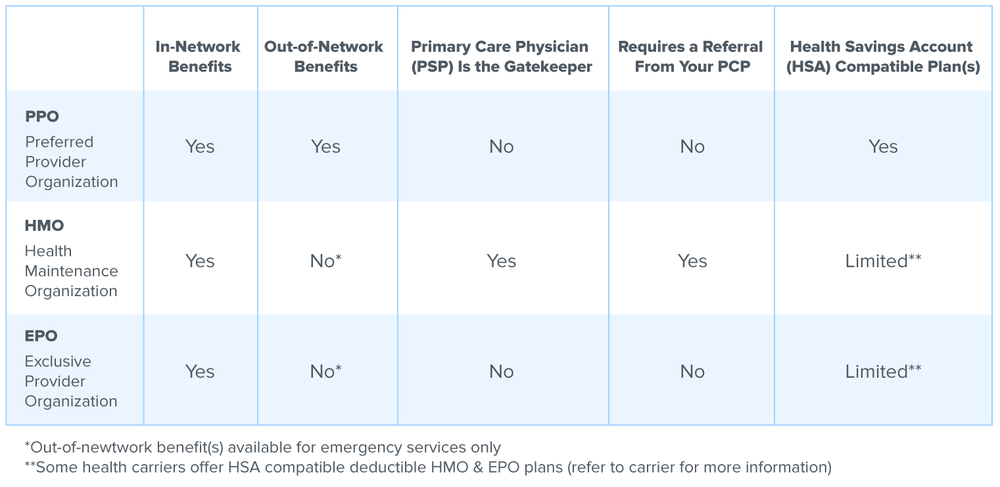
- Primary Care Physician (PCP): HMOs require individuals to select a PCP who serves as their primary point of contact for healthcare. The PCP acts as a gatekeeper, coordinating all medical care and referrals to specialists within the HMO network.
- Preauthorization and Referrals: In an HMO, preauthorization or referrals from the PCP are often necessary for certain services or procedures. This ensures that the healthcare received is cost-effective and within the network.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs: HMOs generally have lower deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses compared to other plan types. This makes them an attractive option for individuals seeking affordable healthcare.
- Network Restrictions: HMO members must receive care from providers within the HMO network. Out-of-network care is typically not covered, or it may incur significantly higher costs.
Advantages of HMOs
- Affordability: HMOs are known for their cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for individuals on a budget.
- Preventative Care Focus: HMOs prioritize preventative care, encouraging regular check-ups and early detection of health issues.
- Coordinated Care: With a PCP coordinating your care, HMOs provide a comprehensive and integrated approach to healthcare.
Disadvantages of HMOs
- Limited Network: HMO members are restricted to the plan’s network of providers, which may not include all desired specialists or healthcare facilities.
- Referral Requirements: The need for preauthorization and referrals can be seen as an administrative burden by some individuals.
- Limited Out-of-Network Coverage: Out-of-network care is often not covered, making it challenging to access certain providers or facilities.
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs)

Preferred Provider Organizations, or PPOs, offer a more flexible approach to healthcare. PPOs maintain a network of healthcare providers, similar to HMOs, but with a broader range of options. PPOs allow individuals to choose from a larger network of providers, including both in-network and out-of-network options.
Key Features of PPOs
- Freedom of Choice: PPO members have the flexibility to choose any healthcare provider, whether in-network or out-of-network, without needing referrals.
- Lower Costs with In-Network Providers: PPOs offer discounted rates for services received from in-network providers, making it more cost-effective to stay within the network.
- Partial Coverage for Out-of-Network Providers: PPOs typically provide some coverage for out-of-network care, although at a higher cost compared to in-network services.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: PPOs often have higher deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses compared to HMOs.
Advantages of PPOs
- Flexibility: PPOs offer the freedom to choose any healthcare provider, providing greater flexibility and control over your healthcare decisions.
- Wider Network: PPOs typically have a more extensive network of providers, giving individuals access to a broader range of healthcare options.
- Partial Out-of-Network Coverage: While out-of-network care may be more expensive, PPOs provide some coverage, offering peace of mind in emergency situations.
Disadvantages of PPOs
- Higher Costs: PPOs generally have higher out-of-pocket expenses, making them less cost-effective for individuals on a tight budget.
- Less Coordinated Care: Without a PCP coordinating care, PPOs may not provide the same level of integrated healthcare as HMOs.
- Potential for Higher Out-of-Network Costs: While partial coverage is provided, out-of-network care can still be significantly more expensive.
Comparing HMOs and PPOs
When deciding between an HMO and a PPO, it’s essential to consider your healthcare needs and preferences. HMOs offer affordability, a focus on preventative care, and coordinated healthcare through a PCP. On the other hand, PPOs provide flexibility, a wider network of providers, and partial coverage for out-of-network care. The choice ultimately depends on whether you prioritize cost-effectiveness, a comprehensive healthcare approach, or the freedom to choose your healthcare providers.
Performance Analysis
HMOs and PPOs have distinct performance characteristics. HMOs tend to perform well for individuals seeking affordable, coordinated healthcare with a strong emphasis on preventative care. PPOs, with their flexible nature and wider network, cater to those who value the freedom to choose their providers and are willing to pay slightly higher costs for that freedom.
| Category | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Network Size | Smaller, restricted | Larger, more extensive |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Lower | Higher |
| Provider Flexibility | Limited to network | Freedom to choose |
| Preauthorization | Often required | Not required |
| Coverage for Out-of-Network Care | Limited or none | Partial coverage |

Future Implications
The healthcare industry is constantly evolving, and the landscape of health insurance plans is no exception. While HMOs and PPOs remain popular options, new plan types and innovations are emerging to meet the diverse needs of individuals. Here are some key trends and future implications to consider:
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
High-Deductible Health Plans, often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), are gaining popularity. These plans have higher deductibles but offer tax advantages and the ability to save for future healthcare expenses. They provide flexibility and control over healthcare decisions, making them an attractive option for certain individuals.
Value-Based Care Models
Value-based care models are becoming increasingly prevalent, focusing on outcomes and patient satisfaction rather than solely on the volume of services provided. This shift encourages healthcare providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care, aligning with the goals of both HMOs and PPOs.
Telehealth and Digital Health Solutions
The integration of telehealth and digital health solutions is transforming the way healthcare is delivered. With the rise of remote consultations and digital health platforms, individuals can access healthcare services more conveniently and efficiently. This trend is particularly beneficial for individuals with HMOs, as it enhances the accessibility and coordination of care.
Consumer-Directed Health Plans
Consumer-directed health plans, such as Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRAs) and Health Reimbursement Accounts (HRAs), are gaining traction. These plans give individuals more control over their healthcare spending, encouraging cost-conscious decisions. They align well with the flexibility offered by PPOs, allowing individuals to make informed choices about their healthcare expenses.
Evidence-Based Medicine
The healthcare industry is increasingly focusing on evidence-based medicine, utilizing scientific research and data to guide treatment decisions. This approach ensures that patients receive the most effective and efficient care, regardless of their insurance plan. Both HMOs and PPOs can benefit from evidence-based practices, improving the quality of healthcare delivered.
FAQs
Can I change my HMO or PPO plan mid-year?
+
Yes, you can typically change your health insurance plan during open enrollment periods or due to certain qualifying life events. Check with your insurance provider for specific guidelines.
What happens if I need emergency care while traveling and I’m not within my HMO or PPO network?
+
In emergency situations, your health insurance plan typically covers emergency care, regardless of whether the provider is in-network or not. However, it’s essential to review your specific plan’s coverage details.
Do HMOs or PPOs cover pre-existing conditions?
+
Yes, both HMOs and PPOs are required by law to cover pre-existing conditions. This ensures that individuals with prior health issues can access necessary healthcare without discrimination.



