How Health Insurance Works
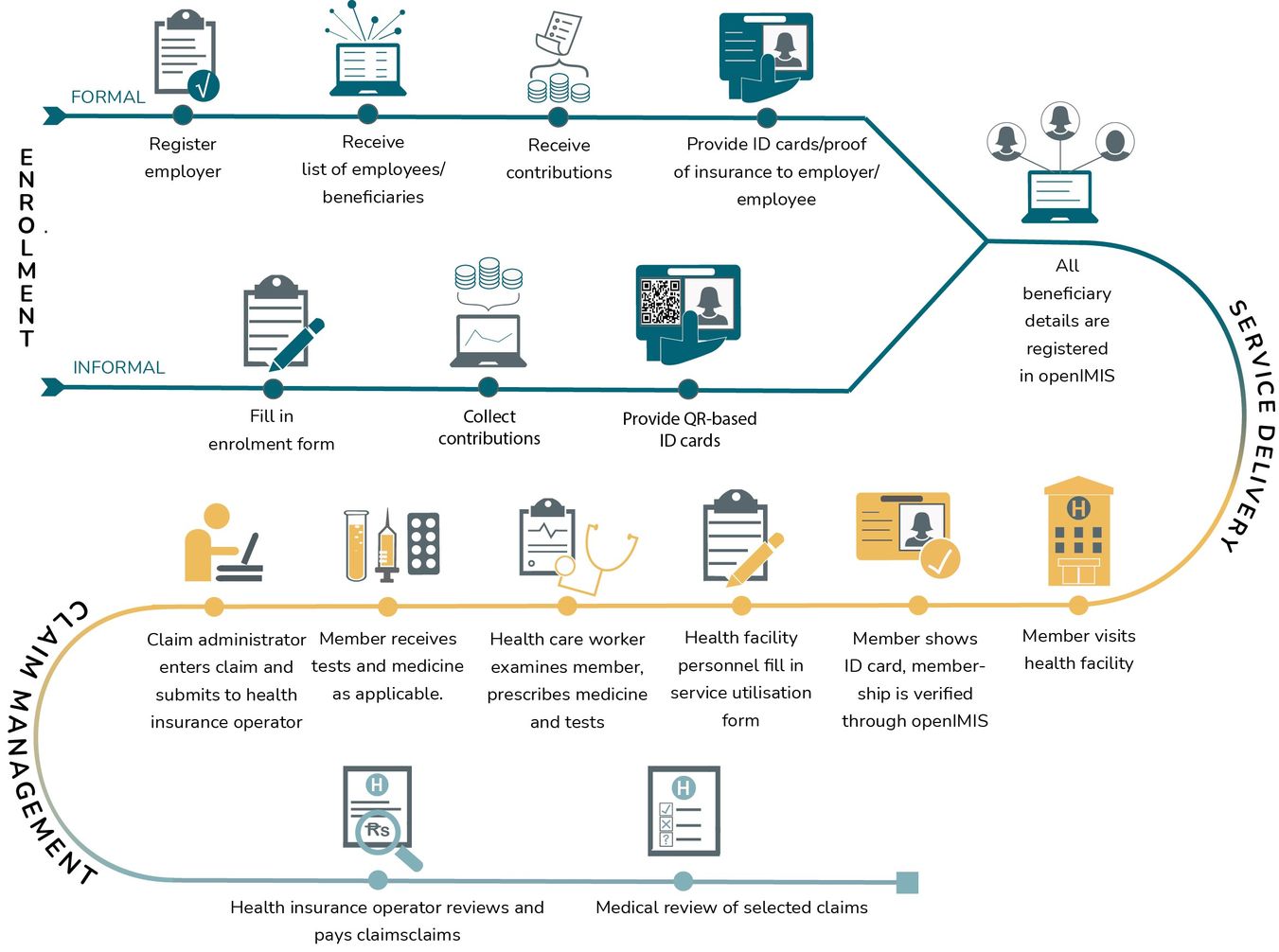
Health insurance is a vital aspect of modern healthcare systems, offering financial protection and access to essential medical services for individuals and families. In today's world, understanding how health insurance works is crucial, as it can significantly impact one's ability to receive timely and quality healthcare. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of health insurance, shedding light on its mechanisms, benefits, and implications.
The Basics of Health Insurance

At its core, health insurance is a contractual agreement between an individual (or a group, such as a family or an employer) and an insurance provider. This agreement, known as a health insurance policy, outlines the terms and conditions under which the insurance company will provide financial coverage for various medical expenses.
The concept of health insurance revolves around the idea of risk pooling, where a large group of individuals contribute premiums to a common fund. This fund is then used to cover the healthcare costs of those who require medical treatment. By spreading the financial risk across a diverse population, health insurance aims to ensure that everyone has access to healthcare, regardless of their current health status or financial situation.
Key Components of a Health Insurance Policy
A health insurance policy typically includes several essential components, each playing a crucial role in determining the coverage and benefits provided.
- Premiums: The amount an individual or group pays regularly (usually monthly or annually) to maintain their health insurance coverage. Premiums are the primary source of income for insurance companies and are often influenced by factors such as age, location, and the level of coverage desired.
- Deductibles: This is the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance company starts covering their medical expenses. Deductibles can vary widely and are often negotiated as part of the insurance policy.
- Copayments (Co-pays): Co-pays are fixed amounts an insured person pays for a covered medical service at the time of receiving the service. For example, a co-pay for a doctor's visit might be $20, regardless of the actual cost of the visit.
- Coinsurance: Coinsurance refers to the percentage of medical costs that an insured individual must pay after meeting their deductible. For instance, if the coinsurance is 20%, the insured person pays 20% of the medical bill, and the insurance company covers the remaining 80%.
- Coverage Limits: Health insurance policies often have limits on the total amount of coverage provided within a specific period, such as a year. These limits can include individual or family maximums, as well as lifetime maximums.
- Network of Providers: Many health insurance plans have a network of preferred healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and specialists. Using in-network providers typically results in lower out-of-pocket costs compared to using out-of-network providers.
- Pre-authorization and Prior Approval: Certain medical procedures or treatments may require pre-authorization from the insurance company before they can be covered. This process ensures that the procedure is medically necessary and aligns with the insurance plan's coverage guidelines.
Types of Health Insurance Plans

Health insurance plans come in various forms, each designed to cater to different needs and preferences. Understanding the different types of plans can help individuals make informed choices about their healthcare coverage.
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
An HMO is a type of health insurance plan that typically requires members to select a primary care physician (PCP) within the HMO’s network. The PCP acts as a gatekeeper, coordinating and authorizing all healthcare services for the member. HMO plans often have lower out-of-pocket costs but may have more restrictive networks of providers.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
A PPO plan offers members more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Members can visit in-network providers without a referral and still receive discounted rates. Out-of-network providers are also an option, but at a higher cost. PPO plans often have higher premiums but provide greater freedom of choice.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
EPO plans are similar to PPO plans in that they offer a network of preferred providers. However, unlike PPOs, EPOs do not cover out-of-network services unless it’s an emergency. EPO plans can be a cost-effective option for those who prefer a limited but high-quality network of providers.
Point-of-Service (POS) Plans
POS plans combine elements of both HMO and PPO plans. Members typically choose a primary care physician and receive discounted rates for in-network services. However, they also have the option to see out-of-network providers, although at a higher cost. POS plans offer a balance between network flexibility and cost savings.
High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHP)
HDHPs are health insurance plans with higher deductibles compared to traditional plans. These plans are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), allowing individuals to save money tax-free for medical expenses. HDHPs can be a cost-effective option for those who are generally healthy and do not anticipate frequent medical needs.
| Plan Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| HMO | Requires a primary care physician; Lower out-of-pocket costs; More restrictive network. |
| PPO | Flexibility in choosing providers; Higher premiums; Access to both in-network and out-of-network providers. |
| EPO | Preferred provider network; No out-of-network coverage except in emergencies. |
| POS | Primary care physician required; Flexibility to choose in-network or out-of-network providers; Balanced cost structure. |
| HDHP | Higher deductibles; Paired with Health Savings Accounts; Cost-effective for healthy individuals. |

The Role of Insurance Companies
Insurance companies play a pivotal role in the health insurance ecosystem. They are responsible for managing the risk associated with providing healthcare coverage to their policyholders.
Risk Assessment and Underwriting
Insurance companies assess the risk of insuring individuals or groups by evaluating various factors, including age, health status, medical history, and lifestyle. This process, known as underwriting, helps insurance companies determine the premiums and coverage limits for each policyholder.
Claims Processing
When an insured individual receives medical treatment, they or their healthcare provider submits a claim to the insurance company. The insurance company then reviews the claim to ensure it meets the criteria for coverage as outlined in the policy. If the claim is approved, the insurance company pays the healthcare provider or reimburses the insured individual for their expenses.
Network Negotiations
Insurance companies negotiate contracts with healthcare providers to establish their network of preferred providers. These negotiations involve setting rates for various medical services, which can impact the out-of-pocket costs for insured individuals.
The Impact of Health Insurance on Healthcare Access
Health insurance plays a critical role in ensuring that individuals have access to essential healthcare services. Here’s how it influences healthcare access:
Financial Protection
One of the primary benefits of health insurance is financial protection. It helps individuals and families manage the potentially high costs of medical care, including hospital stays, surgeries, prescription medications, and specialist visits. By spreading the financial risk, health insurance makes healthcare more affordable and accessible.
Preventive Care
Many health insurance plans cover preventive care services, such as annual check-ups, immunizations, and screenings for various health conditions. These services are often provided at little to no cost to the insured, encouraging individuals to prioritize their health and detect potential issues early on.
Specialist Access
Health insurance plans typically provide access to a network of specialists, including cardiologists, oncologists, and other medical experts. This access is crucial for individuals with complex or chronic health conditions, ensuring they receive specialized care and treatment when needed.
Emergency Care
In emergency situations, health insurance ensures that individuals can receive timely and appropriate care without worrying about the financial burden. Whether it’s a sudden illness or an accident, health insurance covers the costs associated with emergency room visits and necessary treatments.
Challenges and Future Outlook

While health insurance has made significant strides in improving healthcare access, it is not without its challenges. Here are some key considerations for the future of health insurance:
Cost of Healthcare
The rising cost of healthcare is a significant concern for both individuals and insurance companies. As medical treatments and technologies advance, the cost of healthcare services continues to increase. This can lead to higher premiums and out-of-pocket expenses for insured individuals.
Access to Care
Ensuring that all individuals have access to quality healthcare remains a challenge. While health insurance provides a safety net, there are still barriers to accessing care, such as limited provider networks, geographic restrictions, and complex enrollment processes.
Innovation and Technology
The healthcare industry is experiencing rapid technological advancements, from telemedicine to electronic health records. These innovations have the potential to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. Health insurance companies will need to adapt to these changes to provide coverage for emerging technologies and treatment options.
Regulatory and Policy Changes
Health insurance is subject to various regulations and policies at the federal, state, and local levels. Changes in healthcare legislation can significantly impact the insurance industry, affecting coverage options, premium rates, and provider networks. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for both insurers and policyholders.
How does health insurance impact my overall healthcare expenses?
+Health insurance significantly reduces your out-of-pocket healthcare expenses by covering a portion or all of your medical costs. This can include hospital stays, surgeries, specialist visits, and prescription medications. However, it’s important to consider factors like deductibles, copays, and coinsurance when estimating your potential costs.
What happens if I need medical treatment while traveling abroad with my health insurance plan?
+The coverage for medical treatment while traveling abroad depends on your specific health insurance plan. Some plans may offer limited international coverage, while others may require you to purchase additional travel insurance. It’s essential to review your policy’s terms and conditions or consult your insurance provider before traveling.
Can I switch health insurance plans during the year?
+In most cases, you can only switch health insurance plans during designated open enrollment periods or if you experience a qualifying life event, such as getting married, having a baby, or losing your current coverage. However, certain states and regions may have additional enrollment options. It’s best to check with your insurance provider or local healthcare authorities for specific guidelines.
Related Terms:
- How health insurance works pdf
- How health insurance works NGPF
- Health insurance 101 training



