How Much Does It Cost For Health Insurance Per Month
Health insurance is an essential aspect of financial planning and healthcare access, and understanding the associated costs is crucial for individuals and families. The cost of health insurance varies significantly based on numerous factors, including the type of plan, location, age, and coverage options. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the factors influencing health insurance costs and provide an in-depth analysis of the expenses involved, offering valuable insights for those seeking affordable and comprehensive healthcare coverage.
The Complexity of Health Insurance Costs

Determining the exact cost of health insurance is a complex endeavor due to the multitude of variables at play. Insurance premiums, the amount paid monthly to maintain coverage, are influenced by a range of factors, each contributing to the overall cost structure.
Key Factors Affecting Insurance Premiums
Several key factors significantly impact the cost of health insurance premiums. These include:
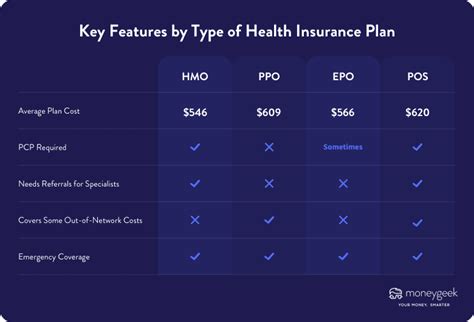
- Plan Type: Different types of health insurance plans, such as Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs), offer varying levels of coverage and flexibility. The choice of plan type directly influences premium costs.
- Location: Health insurance costs can vary significantly from one state to another and even within different regions of the same state. Factors like the cost of living, healthcare infrastructure, and state regulations all contribute to these variations.
- Age: Insurance providers often base their premiums on an individual’s age. Typically, older individuals tend to have higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of requiring medical services. However, under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), age-based rating factors are limited to a 3:1 ratio, ensuring that premiums for older individuals are not excessively high.
- Coverage Options: The level of coverage desired plays a crucial role in determining insurance premiums. Plans with extensive coverage, including a wide range of services and lower out-of-pocket costs, generally come with higher premiums. On the other hand, more basic plans with limited coverage may have lower monthly costs.
Understanding the Cost Structure
To gain a comprehensive understanding of health insurance costs, it’s essential to break down the various components that make up the overall premium. These include:
- Premium: The monthly payment made to the insurance provider to maintain coverage. This is the primary cost associated with health insurance.
- Deductible: The amount an individual must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles often result in lower premiums.
- Copayment (Copay): A fixed amount paid by the insured individual at the time of receiving medical services. Copays vary based on the type of service and are typically a predetermined amount set by the insurance provider.
- Coinsurance: This is the percentage of the total cost of a medical service that the insured individual is responsible for paying. For instance, if the coinsurance is 20%, the individual pays 20% of the service cost, while the insurance provider covers the remaining 80%.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount an individual is required to pay out of pocket for covered services in a given year. Once this limit is reached, the insurance provider covers 100% of the costs for covered services for the remainder of the year.
Analyzing Real-World Examples

To illustrate the variations in health insurance costs, let’s examine a few real-world examples. These scenarios will provide a tangible understanding of the factors at play and the resulting costs.
Scenario 1: Young Adult in a Large City
Consider a 25-year-old individual residing in New York City. Given the high cost of living and advanced healthcare infrastructure in this metropolitan area, health insurance premiums are likely to be on the higher end. Let’s assume this individual opts for a PPO plan with moderate coverage, including a network of preferred providers and some flexibility in choosing healthcare professionals.
| Plan Type | Premium (per month) |
|---|---|
| PPO | $450 |
Scenario 2: Family in a Suburban Area
Now, let’s consider a family of four living in a suburban area outside a major city. The cost of living in this region is moderate, and the family opts for a HMO plan with a narrower network of providers but lower out-of-pocket costs.
| Plan Type | Premium (per month) |
|---|---|
| HMO | $1,200 |
Scenario 3: Elderly Individual with Pre-Existing Conditions
Imagine an elderly individual, aged 70, with pre-existing health conditions residing in a rural area. This individual requires comprehensive coverage and has opted for a PPO plan with a broad network of providers and specialists.
| Plan Type | Premium (per month) |
|---|---|
| PPO | $1,500 |
Performance Analysis and Future Implications
The analysis of health insurance costs reveals a complex interplay of factors, with significant variations based on individual circumstances and regional differences. While the examples provided offer a glimpse into the cost structure, it’s essential to note that these are just snapshots and may not reflect the complete picture for every individual.
Performance Analysis
When analyzing the performance of health insurance plans, it’s crucial to assess not only the upfront costs but also the long-term financial implications. This includes evaluating the out-of-pocket expenses, such as deductibles, copays, and coinsurance, which can vary significantly based on the plan’s design and the individual’s healthcare needs.
Additionally, the choice of plan type and provider network can impact the availability and cost of healthcare services. For instance, while HMO plans may offer lower premiums, they often have a more restricted network of providers, which can limit an individual's choices for healthcare services. On the other hand, PPO and EPO plans typically offer a broader network, providing more flexibility but potentially at a higher cost.
Future Implications
The landscape of health insurance is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as healthcare policy changes, advancements in medical technology, and shifts in demographic trends. These changes can significantly impact the cost and availability of insurance coverage, making it crucial for individuals to stay informed and adapt their insurance choices accordingly.
Furthermore, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of health insurance and the need for comprehensive coverage. As the healthcare system navigates the challenges posed by the pandemic, it's likely that insurance providers will continue to adapt their offerings, potentially leading to changes in premiums and coverage options.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost of health insurance is a critical aspect of financial planning and healthcare access. The factors influencing these costs are diverse and complex, ranging from individual demographics to regional variations and plan design. By breaking down the cost structure and analyzing real-world examples, individuals can make more informed decisions about their healthcare coverage, balancing the need for affordability with the desire for comprehensive protection.
FAQ

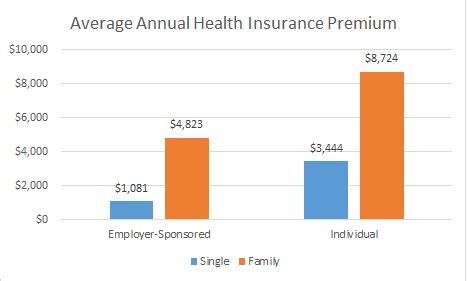
What is the average monthly cost of health insurance in the United States?
+
The average monthly cost of health insurance in the U.S. varies significantly based on numerous factors. According to recent data, the national average premium for an individual plan is around 450 per month, while family plans can range from 1,100 to $1,800 per month. However, these averages can fluctuate based on regional differences, plan types, and individual circumstances.
Are there any ways to reduce the cost of health insurance premiums?
+
Yes, there are several strategies to potentially reduce health insurance premiums. These include opting for plans with higher deductibles, considering Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) or Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) to offset out-of-pocket expenses, and exploring employer-sponsored plans, which often come with lower premiums due to group discounts.
What are the penalties for not having health insurance under the Affordable Care Act (ACA)?
+
Under the ACA, individuals without qualifying health insurance coverage may face a penalty, also known as the Individual Shared Responsibility Payment. However, this penalty was eliminated starting from 2019. Nevertheless, it’s important to note that some states may have their own requirements and penalties for lacking health insurance coverage.
Can I get health insurance if I have a pre-existing condition?
+
Yes, thanks to the ACA, insurance providers cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based solely on pre-existing conditions. However, the cost of insurance for individuals with pre-existing conditions can still be higher, depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen plan’s coverage.
Are there any government programs that offer free or low-cost health insurance?
+
Yes, several government programs provide free or low-cost health insurance options. These include Medicaid, which offers coverage to eligible low-income individuals and families, and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), which provides coverage for children from low-income families. Additionally, some states offer their own health insurance programs for specific populations.



