How Much Will Mortgage Insurance Cost
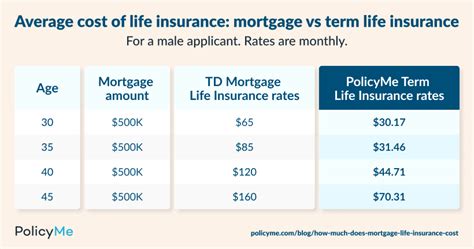
Understanding the costs associated with mortgage insurance is crucial for prospective homeowners, as it can significantly impact their overall financial commitments. Mortgage insurance, also known as private mortgage insurance (PMI) or mortgage guaranty insurance, is a protective measure for lenders that covers the risk of borrower default. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of mortgage insurance costs, exploring factors that influence them and offering insights to help individuals make informed decisions about their homeownership journey.
The Fundamentals of Mortgage Insurance

Mortgage insurance serves as a safety net for lenders, particularly in scenarios where borrowers put down less than a 20% down payment on their home purchase. This insurance policy protects the lender in case the borrower fails to make mortgage payments, ultimately reducing the lender’s financial risk. The cost of mortgage insurance is typically expressed as a percentage of the loan amount, and it can vary based on several critical factors.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Insurance Costs
The expense of mortgage insurance is determined by a range of variables, including:
- Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV): This is the proportion of the home's purchase price that the borrower finances. Lenders typically require mortgage insurance if the LTV exceeds a certain threshold, often 80%.
- Credit Score: A borrower's creditworthiness, as reflected in their credit score, plays a significant role. Borrowers with higher credit scores may qualify for lower mortgage insurance premiums.
- Loan Type: Different loan programs have varying mortgage insurance requirements and costs. For instance, FHA loans typically require both upfront and annual mortgage insurance premiums, while conventional loans may offer PMI cancellation options.
- Down Payment Amount: The size of the borrower's down payment can impact the duration and cost of mortgage insurance. Making a larger down payment can reduce the need for mortgage insurance or shorten the time it's required.
- Mortgage Term: The length of the mortgage term can affect insurance costs. Shorter-term loans may result in lower insurance premiums.
- Property Type: The type of property being purchased can influence insurance rates. For example, mortgage insurance for condominiums may have different rates compared to single-family homes.
| Factor | Impact on Mortgage Insurance Cost |
|---|---|
| Loan-to-Value Ratio | Higher LTVs often result in higher insurance premiums. |
| Credit Score | Stronger credit scores can lead to reduced insurance costs. |
| Loan Type | Different loan programs have unique insurance requirements and costs. |
| Down Payment | Larger down payments can lower or eliminate the need for insurance. |
| Mortgage Term | Shorter terms may result in lower insurance premiums. |
| Property Type | Insurance rates can vary based on the type of property. |

Estimating Mortgage Insurance Costs

The cost of mortgage insurance can be estimated using a combination of factors, including the loan amount, down payment, loan term, and credit score. While these estimates provide a starting point, it’s crucial to obtain quotes from multiple lenders to get an accurate picture of your insurance costs.
Calculating Monthly Premiums
Monthly mortgage insurance premiums are typically expressed as a percentage of the loan balance. For example, a borrower with a loan amount of 200,000 and a 5% down payment might expect to pay around 0.5% to 1% of the loan balance annually for mortgage insurance. This translates to a monthly premium of approximately 83 to $167.
Upfront Costs and Annual Premiums
Some mortgage programs, like FHA loans, require both upfront and annual mortgage insurance premiums. Upfront premiums are typically financed into the loan amount, while annual premiums are paid monthly along with the mortgage payment. The cost of upfront premiums can range from 1.75% to 3.00% of the loan amount, depending on the loan-to-value ratio and other factors.
Cancelling Mortgage Insurance
The ability to cancel mortgage insurance varies depending on the loan program and the borrower’s circumstances. For conventional loans, mortgage insurance can often be cancelled once the loan-to-value ratio reaches 78%, while for FHA loans, it may require refinancing or paying off a significant portion of the loan balance.
Strategies to Minimize Mortgage Insurance Costs
Homebuyers have several strategies at their disposal to reduce the financial burden of mortgage insurance. These include:
- Increasing Down Payment: Making a larger down payment can reduce the loan-to-value ratio, which often leads to lower insurance premiums or the ability to avoid insurance altogether.
- Improving Credit Score: A higher credit score can qualify borrowers for lower insurance rates. Taking steps to improve credit, such as paying bills on time and reducing debt, can significantly impact insurance costs.
- Exploring Alternative Loan Programs: Different loan programs have varying insurance requirements. Researching and comparing loan options can help borrowers find programs that better suit their financial situation and potentially offer more favorable insurance terms.
- Refinancing: For existing homeowners, refinancing can be a strategy to reduce or eliminate mortgage insurance. By refinancing into a new loan with a lower loan-to-value ratio, borrowers may be able to cancel insurance or secure a lower premium.
The Impact of Mortgage Insurance on Homeownership
Mortgage insurance plays a critical role in the homeownership process, particularly for first-time buyers or those with limited savings for a down payment. While it adds to the overall cost of homeownership, it also provides an opportunity for individuals to achieve their dream of homeownership sooner by requiring a smaller down payment.
The Benefits of Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance offers several advantages, including:
- Lower Barrier to Entry: By allowing borrowers to purchase a home with a smaller down payment, mortgage insurance makes homeownership more accessible for a broader range of individuals.
- Risk Mitigation: Mortgage insurance provides a safety net for lenders, which in turn makes it possible for more borrowers to secure financing. This risk mitigation encourages lending and supports a healthy housing market.
- Building Equity: With a lower down payment, borrowers can start building equity in their home sooner, which can be advantageous in a rising housing market.
The Trade-Offs of Mortgage Insurance
However, mortgage insurance also comes with certain trade-offs that prospective homeowners should consider:
- Additional Costs: Mortgage insurance adds an extra expense to the monthly mortgage payment, which can impact a borrower's budget and overall financial planning.
- Limited Flexibility: Some loan programs with mortgage insurance may have restrictions on how the loan can be used or refinanced, impacting the borrower's future financial decisions.
- Potential for Cancellation: The ability to cancel mortgage insurance can be limited, and borrowers may need to meet specific criteria or refinance to achieve cancellation.
The Future of Mortgage Insurance

The landscape of mortgage insurance is constantly evolving, influenced by factors such as economic conditions, housing market trends, and regulatory changes. While the exact future of mortgage insurance is uncertain, several potential developments could impact its role in the homeownership process.
Potential Changes and Innovations
Here are some potential scenarios that could shape the future of mortgage insurance:
- Increased Use of Alternative Credit Scoring: As lenders explore new ways to assess creditworthiness, alternative credit scoring methods could become more prevalent. This shift may lead to more accurate risk assessments and potentially reduce the need for mortgage insurance in certain cases.
- Integration of Technology: Technological advancements in the mortgage industry, such as digital lending platforms and data analytics, could streamline the mortgage insurance process and potentially reduce costs.
- Regulatory Adjustments: Government policies and regulations can significantly impact mortgage insurance requirements. Changes in regulations could lead to more flexible cancellation criteria or even the elimination of mortgage insurance for certain loan programs.
How can I estimate my monthly mortgage insurance premium?
+Estimating your monthly mortgage insurance premium involves considering factors like your loan amount, down payment, loan term, and credit score. Online mortgage calculators can provide rough estimates, but for a more accurate assessment, it’s best to obtain quotes from multiple lenders.
Are there ways to avoid paying mortgage insurance?
+Yes, there are strategies to avoid paying mortgage insurance. Making a larger down payment of 20% or more can eliminate the need for mortgage insurance. Additionally, exploring loan programs like VA loans, which are available to eligible military members and veterans, often do not require mortgage insurance.
Can I cancel my mortgage insurance once it’s in place?
+The ability to cancel mortgage insurance depends on the loan program and your circumstances. For conventional loans, mortgage insurance can often be cancelled once the loan-to-value ratio reaches 78%. For FHA loans, it may require refinancing or paying off a significant portion of the loan balance.


