How Much Would Homeowners Insurance Cost
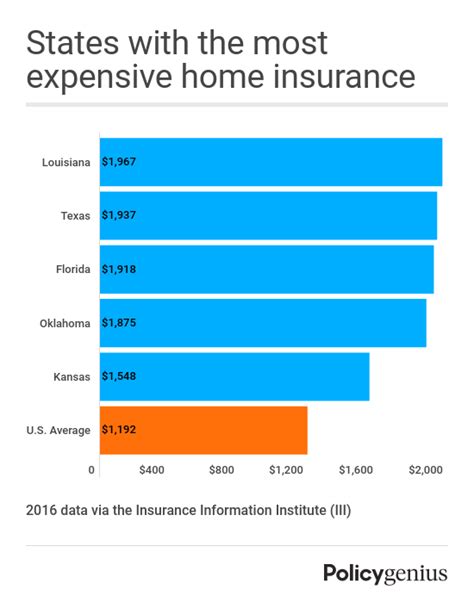
Homeowners insurance is an essential financial protection for homeowners, providing coverage for various risks and liabilities associated with owning a home. The cost of homeowners insurance can vary significantly depending on several factors, and understanding these variables is crucial for homeowners to make informed decisions about their insurance coverage. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the key aspects that influence homeowners insurance costs, explore real-world examples, and offer insights to help you navigate this complex landscape.
Understanding Homeowners Insurance Premiums

Homeowners insurance premiums, or the cost of coverage, are determined by a combination of factors that insurance companies use to assess the risk associated with insuring a particular home. These factors can vary depending on the location, the type of home, and the specific coverage needs of the homeowner. Let’s explore some of the primary influences on homeowners insurance costs.
1. Location and Regional Factors
One of the most significant determinants of homeowners insurance premiums is the location of the property. Insurance companies consider various regional factors when assessing risk, including the following:
- Natural Disasters: Areas prone to natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or wildfires typically face higher insurance premiums. For instance, coastal regions with a history of hurricanes may have elevated rates due to the increased risk of property damage.
- Crime Rates: Insurance companies also consider the crime rate in a particular area. Higher crime rates can lead to increased premiums, as homeowners may be more likely to file claims for theft or vandalism.
- Weather Patterns: Regions with extreme weather conditions, such as frequent hailstorms or heavy snowfall, can impact insurance costs. These events can cause damage to homes and increase the likelihood of insurance claims.
- Proximity to Fire Stations: The distance of a home from the nearest fire station can influence insurance rates. Homes located farther away from fire stations may face higher premiums, as response times could be slower in the event of a fire.
For example, let's consider two homes: one located in a suburban neighborhood with low crime rates and minimal natural disaster risks, and another situated in a coastal region prone to hurricanes. The insurance premium for the suburban home is likely to be lower due to the reduced risk factors, while the coastal home may face significantly higher premiums to account for the increased likelihood of hurricane-related damage.
2. Home Characteristics and Construction
The physical characteristics and construction of a home play a vital role in determining insurance costs. Here are some key factors insurance companies consider:
- Home Age: Older homes may require more extensive repairs and have outdated electrical or plumbing systems, leading to higher insurance premiums. Newer homes, built with modern materials and construction techniques, often have lower premiums.
- Building Materials: The type of materials used in a home's construction can impact insurance costs. Homes built with brick or stone may be more expensive to insure than those constructed with wood, as they are generally more resistant to fire and other types of damage.
- Roof Type and Age: The condition and age of a home's roof are important considerations. Older roofs, especially those with significant wear and tear, may increase insurance premiums. Metal roofs, which are more durable and resistant to weather damage, can sometimes result in lower premiums.
- Home Size: Larger homes generally have higher insurance premiums, as they typically involve more risk and may require more extensive coverage. The square footage and the number of rooms can influence the overall cost of insurance.
Imagine a scenario where we have two identical homes, except one is constructed with traditional wood framing and the other with steel framing. The home with steel framing, known for its durability and resistance to fire and wind damage, may qualify for lower insurance premiums compared to its wood-framed counterpart.
3. Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Homeowners have the flexibility to choose their coverage limits and deductibles, which directly impact insurance premiums. Here’s how these choices influence the cost of insurance:
- Coverage Limits: Higher coverage limits, which provide more extensive protection for the home and its contents, typically result in higher insurance premiums. Homeowners can opt for different levels of coverage based on their specific needs and the value of their property.
- Deductibles: Deductibles are the amount homeowners agree to pay out of pocket before their insurance coverage kicks in. Choosing a higher deductible can lead to lower insurance premiums, as it reduces the insurer's financial responsibility in the event of a claim. However, it's essential to ensure the deductible is affordable in the event of a loss.
Consider a homeowner who opts for a high-coverage policy with a low deductible. This choice provides comprehensive protection but comes with a higher premium. On the other hand, a homeowner who selects a lower-coverage policy with a higher deductible may pay a lower premium but would need to cover more out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim.
4. Additional Factors
Beyond the factors mentioned above, several other considerations can influence homeowners insurance costs. These include:
- Claims History: Insurance companies review a homeowner's claims history when determining premiums. A history of frequent claims may result in higher premiums or even policy non-renewal.
- Discounts and Bundling: Many insurance companies offer discounts for homeowners who bundle their policies (e.g., auto and home insurance). Additionally, safety features like smoke detectors, security systems, or fire-resistant roofing can qualify homeowners for reduced rates.
- Credit Score: In some cases, insurance companies may consider a homeowner's credit score when setting premiums. A higher credit score can sometimes lead to lower insurance rates.
For instance, a homeowner who has consistently maintained a high credit score and has never filed an insurance claim may be eligible for lower insurance rates compared to a homeowner with a lower credit score and a history of frequent claims.
Real-World Examples and Cost Estimates

To illustrate the variability in homeowners insurance costs, let’s explore some real-world examples and provide cost estimates based on different scenarios.
Example 1: Suburban Homeowner
John, a homeowner in a low-risk suburban area, has a 2,500 square foot home built with traditional wood framing. He opts for a standard coverage policy with a 1,000 deductible. Given the low-risk nature of his location and the standard construction of his home, John's annual homeowners insurance premium is estimated to be around 1,200.
Example 2: Coastal Property Owner
Sarah owns a beachfront property in a hurricane-prone coastal region. Her home, a 3,000 square foot residence built with reinforced concrete, has a high-coverage policy with a 2,000 deductible. Due to the increased risk of natural disasters, Sarah's annual homeowners insurance premium is estimated to be approximately 3,500.
Example 3: Urban Condo Owner
Mike, a resident of an urban condo building, has a 1,200 square foot unit on the 10th floor. His building has robust security measures, and Mike opts for a basic coverage policy with a 1,500 deductible. Given the relatively low risk of natural disasters and the security features of the building, Mike's annual homeowners insurance premium is estimated to be around 800.
| Example | Location | Home Characteristics | Coverage & Deductible | Estimated Annual Premium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suburban Homeowner | Low-risk suburban area | 2,500 sq. ft., wood framing | Standard coverage, $1,000 deductible | $1,200 |
| Coastal Property Owner | Hurricane-prone coastal region | 3,000 sq. ft., reinforced concrete | High coverage, $2,000 deductible | $3,500 |
| Urban Condo Owner | Urban area | 1,200 sq. ft. condo, 10th floor | Basic coverage, $1,500 deductible | $800 |

Strategies for Lowering Homeowners Insurance Costs
While homeowners insurance is essential, there are strategies to potentially reduce the cost of coverage. Here are some tips to consider:
- Shop Around: Compare quotes from multiple insurance companies. Rates can vary significantly, so obtaining multiple quotes can help you find the most competitive option.
- Increase Deductibles: Choosing a higher deductible can lead to lower premiums. However, ensure the deductible is manageable in the event of a claim.
- Bundle Policies: If you have multiple insurance needs, consider bundling your policies (e.g., auto and home insurance) with the same provider to potentially qualify for discounts.
- Enhance Home Security: Installing security systems, smoke detectors, and fire-resistant features can make your home a lower risk for insurers, potentially resulting in lower premiums.
- Review Coverage Regularly: As your home and personal circumstances change, review your insurance coverage to ensure it aligns with your needs. You may be able to adjust your policy to save money without compromising protection.
Conclusion
Understanding the factors that influence homeowners insurance costs is crucial for making informed decisions about your coverage. From location-based risks to home characteristics and coverage choices, each factor plays a role in determining the price you pay for insurance. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, you can navigate the homeowners insurance landscape with confidence and find the right coverage for your needs at a competitive price.
FAQ

What is the average cost of homeowners insurance in the United States?
+The average cost of homeowners insurance in the U.S. varies by state and can range from around 700 to over 2,000 per year. Factors like location, home value, and coverage limits influence these averages.
How often should I review my homeowners insurance policy?
+It’s recommended to review your homeowners insurance policy annually, especially if your home value or personal circumstances have changed. This ensures your coverage remains adequate and up-to-date.
Can I negotiate my homeowners insurance premiums?
+While insurance premiums are primarily based on risk assessments, it doesn’t hurt to ask your insurance provider if they offer any discounts or if there are ways to lower your premiums. Negotiation may not always be possible, but it’s worth exploring.


