Insurance Rates By State
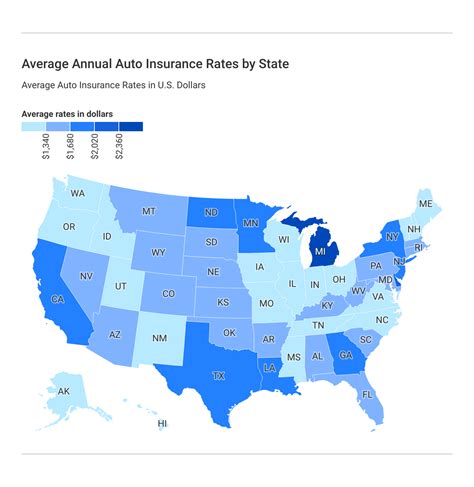
Insurance rates are a complex and dynamic aspect of personal finance, and they can vary significantly from one state to another. This article aims to delve into the factors influencing these variations and provide an in-depth analysis of insurance costs across the United States. By exploring the unique characteristics of each state, we can better understand the reasons behind these differences and make more informed decisions about our insurance coverage.
The Impact of Geographic and Demographic Factors

Insurance rates are not distributed evenly across the country, and this disparity can be attributed to a multitude of geographic and demographic influences. For instance, states with higher population densities often experience more frequent claims due to increased traffic and a higher likelihood of accidents. This is particularly evident in metropolitan areas, where the cost of living and, consequently, insurance rates, tend to be higher.
Additionally, the climate and weather patterns of a state can play a significant role. States prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or earthquakes, typically have higher insurance premiums to account for the increased risk of property damage. For instance, residents of Florida often face higher homeowners' insurance rates due to the state's vulnerability to hurricanes.
Population Density and Urban Centers
States with major metropolitan areas often have higher insurance rates, primarily due to the increased risk of accidents and claims. For instance, New York, with its dense population and heavy traffic, has some of the highest auto insurance rates in the nation. On the other hand, states with lower population densities, like Wyoming or North Dakota, tend to have lower insurance costs.
In urban centers, the cost of living is generally higher, which can also impact insurance rates. This is particularly true for cities with high real estate values, as homeowners' insurance premiums are often tied to the replacement cost of a home.
Climate and Natural Disaster Risk
The climate of a state is a significant factor in determining insurance rates, especially for property insurance. States that are prone to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, or wildfires, often have higher insurance premiums. For example, Florida, with its frequent hurricanes, has some of the highest homeowners' insurance rates in the country.
Similarly, states with a high risk of earthquakes, like California, also see increased insurance costs. In such cases, insurance providers often offer specific earthquake coverage, which can further elevate the overall insurance premium.
Legal and Regulatory Influences

Each state has its own set of laws and regulations that govern the insurance industry, which can significantly impact insurance rates. These regulations cover various aspects, including minimum coverage requirements, rate-setting guidelines, and insurance company operations.
Minimum Coverage Requirements
The level of insurance coverage mandated by each state can vary considerably. For instance, while some states require only liability coverage for auto insurance, others may mandate additional coverages like personal injury protection (PIP) or uninsured/underinsured motorist coverage. These differences in minimum requirements can directly affect insurance rates, as policyholders in states with more comprehensive requirements may pay higher premiums.
Rate-Setting Guidelines
Insurance rates are often determined based on actuarial data, which considers historical loss experience and other factors. However, states can impose regulations on how insurance companies set their rates. Some states employ prior approval systems, where insurance companies must seek approval from the state's insurance department before implementing rate changes. In contrast, other states allow more flexibility, enabling insurance companies to adjust rates based on market conditions.
| State | Rating System |
|---|---|
| California | Competitive Rating |
| Texas | Prior Approval |
| New York | File and Use |
| Florida | Prior Approval with Modifications |

Insurance Company Operations
State regulations can also impact the operational costs of insurance companies, which can be reflected in insurance rates. For instance, some states impose stricter guidelines on insurance companies' investment activities, while others may have specific requirements for maintaining reserves or paying taxes. These operational costs can vary significantly from state to state, affecting the overall insurance rates.
The Role of Claims Frequency and Severity
The frequency and severity of insurance claims in a particular state are key factors that influence insurance rates. States with a higher number of claims, especially those involving costly repairs or settlements, often see higher insurance premiums.
Claims Frequency
The number of insurance claims filed in a state can significantly impact insurance rates. States with higher population densities or those that experience severe weather events often see a higher frequency of claims. For instance, states like Florida and Texas, which are prone to hurricanes and tornadoes, tend to have a higher number of property insurance claims, leading to increased insurance rates.
Claims Severity
In addition to the frequency of claims, the severity of those claims is also a critical factor. Claims involving significant property damage or high medical costs can lead to increased insurance premiums. For instance, states with a high number of severe car accidents or states that experience frequent natural disasters often see higher auto and homeowners' insurance rates, respectively.
| State | Average Auto Insurance Claims Severity |
|---|---|
| California | $12,500 |
| Texas | $15,000 |
| Florida | $18,000 |
| New York | $14,000 |
Competitive Landscape and Market Share
The insurance industry in the United States is highly competitive, with a variety of insurers offering different types of coverage. The competitive landscape and market share of insurance companies can also influence insurance rates.
Market Concentration
In some states, the insurance market may be dominated by a few large insurance companies, leading to a more concentrated market. In such cases, these dominant insurers may have more control over pricing, which can result in higher insurance rates. On the other hand, states with a more diverse insurance market, where a larger number of insurers compete for customers, often see more competitive pricing and lower insurance rates.
Market Share of Insurance Companies
The market share of insurance companies can vary significantly from state to state. For instance, a particular insurer may have a large market share in one state but a much smaller share in another. This variation can be due to a number of factors, including the insurer's historical presence in the state, its reputation, and the specific products and services it offers. Insurers with a larger market share often have more negotiating power with customers, which can lead to higher insurance rates.
| State | Top Insurance Company Market Share |
|---|---|
| California | State Farm (22%) |
| Texas | Geico (18%) |
| Florida | Progressive (16%) |
| New York | Allstate (14%) |
Driver and Vehicle Characteristics

The demographic and behavioral characteristics of drivers in a state can also impact insurance rates. These factors can include the average age of drivers, their driving records, and the types of vehicles they drive.
Driver Demographics
The age distribution of drivers in a state can influence insurance rates. States with a higher proportion of younger drivers, who are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents, often have higher insurance rates. Conversely, states with a larger percentage of experienced, mature drivers may see lower insurance rates.
Driving Records
The driving records of a state's residents are a critical factor in determining insurance rates. States with a higher incidence of traffic violations, such as speeding tickets or DUIs, often see increased insurance premiums. Insurance companies use these records to assess the risk associated with insuring a particular driver.
Vehicle Characteristics
The types of vehicles driven in a state can also impact insurance rates. States with a higher concentration of luxury or sports cars, which are more expensive to repair or replace, often see higher insurance premiums. Similarly, states with a higher proportion of older vehicles, which may have lower safety ratings, can also see increased insurance rates.
| State | Average Vehicle Age | Percentage of Luxury/Sports Cars |
|---|---|---|
| California | 6.5 years | 12% |
| Texas | 7.2 years | 9% |
| Florida | 6.8 years | 10% |
| New York | 6.3 years | 14% |
Conclusion: Understanding the Complexities of Insurance Rates
Insurance rates are influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from geographic and demographic considerations to legal and regulatory environments. By understanding these factors and their impact on insurance rates, individuals can make more informed decisions about their insurance coverage. It's important to note that insurance rates are not static and can change over time due to various economic, social, and environmental factors.
As we navigate the complex landscape of insurance rates, it's crucial to stay informed about the unique characteristics of our state and the factors that influence our insurance costs. By doing so, we can ensure that we're getting the best value for our insurance coverage and that we're adequately protected against the risks we face.
FAQ
How do insurance rates vary by state for homeowners’ insurance?
+Homeowners’ insurance rates can vary significantly by state due to a variety of factors, including the state’s climate and natural disaster risk, population density, and the cost of living. For instance, states prone to hurricanes, like Florida, often have higher homeowners’ insurance rates due to the increased risk of property damage. Similarly, states with higher population densities, like California, may have higher rates due to increased claims frequency.
What impact do state regulations have on insurance rates?
+State regulations can significantly influence insurance rates. These regulations cover various aspects, including minimum coverage requirements, rate-setting guidelines, and insurance company operations. For example, states with stricter minimum coverage requirements may have higher insurance rates, as policyholders are required to purchase more extensive coverage. Additionally, states with more stringent regulations on insurance company operations may see higher operational costs reflected in insurance rates.
How do driver demographics affect insurance rates?
+Driver demographics, such as the average age of drivers in a state, can impact insurance rates. States with a higher proportion of younger drivers, who are statistically more likely to be involved in accidents, often have higher insurance rates. Conversely, states with a larger percentage of experienced, mature drivers may see lower insurance rates. The driving records of a state’s residents are also a critical factor, with states with a higher incidence of traffic violations often seeing increased insurance premiums.
What role do vehicle characteristics play in determining insurance rates?
+Vehicle characteristics, such as the average age and type of vehicles driven in a state, can influence insurance rates. States with a higher concentration of luxury or sports cars, which are more expensive to repair or replace, often see higher insurance premiums. Similarly, states with a higher proportion of older vehicles, which may have lower safety ratings, can also see increased insurance rates. Insurance companies consider these factors when assessing the risk associated with insuring a particular vehicle.



