Map Out Several Locations
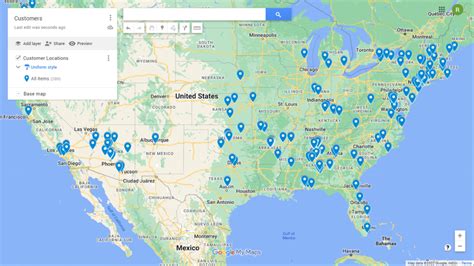
Embarking on an exploration of various geographical locations, we delve into the diverse world of mapping, a crucial tool for navigation, understanding spatial relationships, and discovering the intricacies of our planet. From ancient cartographic practices to modern digital mapping technologies, the evolution of mapping has revolutionized how we perceive and interact with our environment. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complexities and nuances of mapping, providing an in-depth analysis of its applications, methodologies, and future directions.
Unveiling the Art of Mapping: Ancient to Modern Times

The art of mapping has evolved significantly since its inception, progressing from rudimentary sketches on animal hides to intricate digital representations. Early civilizations, such as the Babylonians and Egyptians, pioneered mapping techniques to navigate their territories and record astronomical observations. These initial attempts at mapping laid the foundation for more sophisticated cartographic practices that would emerge in later centuries.
The Middle Ages witnessed a resurgence of mapping, with monks and scholars meticulously crafting detailed maps, often adorned with intricate illustrations. These maps served as navigational aids and were also used to depict religious concepts and mythical creatures, reflecting the cultural and spiritual beliefs of the time.
The Renaissance era brought about a revolution in mapping, with the introduction of scientific principles and the development of advanced instruments like the astrolabe and the sextant. Cartographers like Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius revolutionized map-making, creating maps that were not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly accurate representations of the Earth's surface. Their work paved the way for modern mapping techniques, influencing the development of nautical charts and land maps that aided exploration and colonization.
Digital Mapping: A Revolution in Geographic Representation
The advent of digital technology marked a significant turning point in the history of mapping. Digital mapping, or Geographic Information Systems (GIS), has transformed how we perceive and interact with geographical information. GIS allows for the collection, storage, analysis, and visualization of spatial data, offering unprecedented capabilities for mapping and understanding the world around us.
One of the key advantages of digital mapping is its ability to integrate diverse data sources, including satellite imagery, GPS data, and statistical information. This integration allows for the creation of dynamic and interactive maps that can be easily updated and shared. Digital mapping tools have revolutionized fields such as urban planning, environmental management, and disaster response, providing valuable insights and facilitating informed decision-making.
Additionally, the rise of citizen science and crowdsourcing has further enhanced the capabilities of digital mapping. With the proliferation of smartphones and GPS-enabled devices, individuals can contribute to mapping efforts, providing real-time data on various aspects of their environment. This collaborative approach has led to the creation of detailed and up-to-date maps, especially in regions where traditional mapping methods may be challenging or costly.
Applications of Digital Mapping
Digital mapping has a wide range of applications across various sectors:
- Urban Planning and Development: Digital maps provide valuable insights into land use, infrastructure, and demographic patterns, aiding in the efficient planning and development of urban areas.
- Environmental Management: GIS is instrumental in monitoring and managing natural resources, tracking wildlife populations, and assessing the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Disaster Response and Management: Digital mapping plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery. It enables the visualization of affected areas, facilitates the allocation of resources, and aids in the coordination of relief efforts.
- Transportation and Logistics: GIS-based maps are used to optimize transportation networks, route planning, and fleet management, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs.
- Health and Epidemiology: Digital mapping is utilized to track and analyze disease outbreaks, identify at-risk populations, and plan public health interventions.
| Mapping Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Topographic Mapping | Focuses on natural and man-made features, including elevation, landforms, and infrastructure. |
| Thematic Mapping | Displays specific themes or topics, such as population density, climate patterns, or soil types. |
| Choropleth Mapping | Uses shading or color patterns to represent statistical data across geographical areas. |
| Isoline Mapping | Illustrates data that varies continuously over an area, such as temperature or precipitation. |

The Future of Mapping: Exploring Emerging Trends
As we look ahead, the future of mapping holds exciting possibilities and challenges. Emerging trends in mapping are poised to further revolutionize our understanding and interaction with the world.
3D Mapping and Augmented Reality
3D mapping and augmented reality (AR) are rapidly gaining traction in the mapping domain. 3D mapping involves the creation of detailed, three-dimensional representations of geographical features, providing a more immersive and realistic view of the landscape. This technology is particularly useful in urban planning, architecture, and virtual tourism, offering a new level of spatial awareness.
AR, on the other hand, overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception of the environment. AR-enabled mapping applications can provide real-time information about buildings, landmarks, and other points of interest, transforming the way we explore and interact with our surroundings.
Crowdsourced and Participatory Mapping
The concept of crowdsourced mapping, where individuals contribute to the creation and updating of maps, has gained significant momentum. With the widespread use of smartphones and GPS-enabled devices, anyone can become a citizen cartographer, providing valuable data on local areas, roads, and landmarks. This approach not only improves the accuracy and detail of maps but also fosters a sense of community and ownership.
Participatory mapping, another emerging trend, involves engaging local communities in the mapping process. This approach ensures that maps are culturally sensitive and reflect the unique characteristics of a region. By involving local knowledge holders and stakeholders, participatory mapping promotes sustainable development, preserves cultural heritage, and empowers communities.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are set to play a pivotal role in the future of mapping. These technologies can automate various mapping tasks, such as image analysis, feature extraction, and map generalization. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling more efficient and accurate mapping.
Additionally, AI can enhance the interpretation of spatial data, providing valuable insights into complex phenomena such as climate change, urbanization, and natural resource management. By combining AI with advanced mapping techniques, we can unlock new possibilities for research, urban planning, and environmental conservation.
FAQ
How has mapping evolved over time?
+Mapping has evolved from ancient sketches on animal hides to intricate digital representations. The Renaissance era marked a significant turning point with the introduction of scientific principles and advanced instruments. The advent of digital technology further revolutionized mapping, leading to the development of GIS and other digital mapping tools.
What are the main applications of digital mapping?
+Digital mapping has diverse applications, including urban planning, environmental management, disaster response, transportation, and health. It provides valuable insights and facilitates informed decision-making across various sectors.
How does crowdsourced mapping work?
+Crowdsourced mapping involves individuals contributing to the creation and updating of maps using GPS-enabled devices. This approach improves map accuracy and detail while fostering a sense of community and ownership.
What role does AI play in the future of mapping?
+AI and machine learning are set to automate various mapping tasks, enhance data analysis, and provide valuable insights. They can improve the efficiency and accuracy of mapping, particularly in complex phenomena like climate change and urbanization.



