Medical Insurance Rates
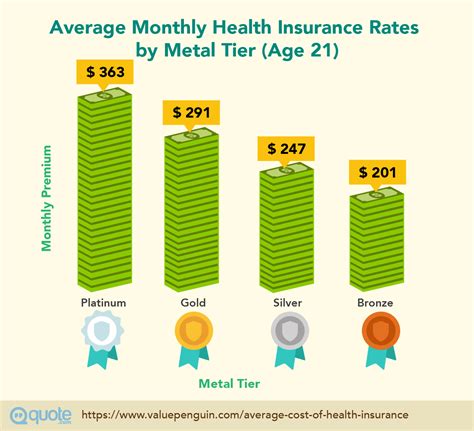
The world of medical insurance is a complex and often daunting one, with a myriad of factors influencing the rates and coverage offered to individuals and families. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about health insurance plans. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of medical insurance rates, exploring the key elements that impact them and providing valuable insights to navigate this essential aspect of healthcare.
Understanding the Basis of Medical Insurance Rates

Medical insurance rates are not arbitrary numbers; they are carefully calculated based on a comprehensive analysis of various risk factors. These factors can broadly be categorized into individual characteristics, lifestyle choices, and broader demographic and regional considerations.
Individual Factors
Each person’s health history and current health status play a significant role in determining insurance rates. Pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease, can lead to higher premiums, as they often require ongoing medical care and treatment. The age of the insured individual is another critical factor; younger individuals typically pay lower rates, as they are generally healthier and less likely to require extensive medical services. Gender can also influence rates, with some insurers charging different premiums for men and women based on historical health trends.
Furthermore, the occupation of the insured can impact rates. High-risk occupations, such as those involving heavy machinery or extreme sports, may result in higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of injuries or accidents. Similarly, tobacco use is a significant factor, as it is linked to various health issues and can lead to higher healthcare costs.
Lifestyle and Behavior
Lifestyle choices and behaviors also heavily influence medical insurance rates. Individuals who lead healthy lifestyles, incorporating regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoidance of risky behaviors, often enjoy lower premiums. On the other hand, those with unhealthy habits, such as excessive alcohol consumption or a sedentary lifestyle, may face higher rates.
Additionally, the use of preventive care services, such as regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, can impact rates. Insurers often reward individuals who proactively manage their health, as this reduces the likelihood of developing more serious and costly health issues.
Demographic and Regional Factors
Medical insurance rates are also influenced by broader demographic and regional considerations. The location of the insured individual can significantly impact rates, as healthcare costs vary across different regions. Urban areas, for instance, often have higher healthcare costs due to the concentration of specialized medical facilities and professionals.
The overall health of the community is another factor. Areas with a higher prevalence of certain health conditions or a higher rate of accidents and injuries may see increased insurance rates. This is because insurers must account for the potential costs of treating a larger number of individuals with specific health issues.
Moreover, the demographic composition of an area can influence rates. Insurers may consider factors such as the average age, gender distribution, and socioeconomic status of the population when setting rates for a particular region.
The Role of Insurance Companies in Rate Determination
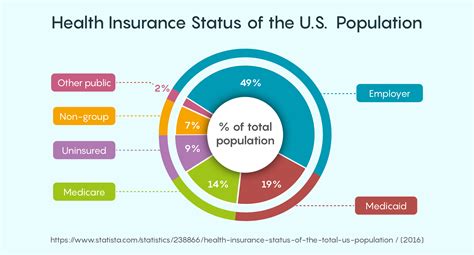
Insurance companies play a pivotal role in setting medical insurance rates. They employ a team of experts, including actuaries, who specialize in risk assessment and pricing. These professionals analyze vast amounts of data to determine the likelihood of individuals needing medical care and the associated costs.
Data Analysis and Rate Calculation
Actuaries utilize historical data, medical research, and statistical models to predict future healthcare needs and costs. They consider factors such as the average number of doctor visits, hospital admissions, and procedures required by individuals of different ages, genders, and health statuses. By analyzing this data, insurers can set rates that cover their expected costs while remaining competitive in the market.
Insurers also take into account the claims experience of their policyholders. If a particular group of individuals tends to utilize more healthcare services or have higher-than-average costs, insurers may adjust their rates accordingly. This ensures that the premiums collected are sufficient to cover the expected costs of providing healthcare services to that specific group.
Regulation and Oversight
The process of setting medical insurance rates is not without oversight. Government agencies and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring that insurers follow fair and transparent practices. They review proposed rate changes, investigate complaints, and enforce regulations to protect consumers from unfair practices.
For instance, in the United States, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced several reforms to the health insurance market, including the prohibition of insurers from denying coverage or charging higher rates based on pre-existing conditions. The ACA also introduced the concept of community rating, which limits the variation in premiums based on age and requires insurers to accept all applicants within a given geographic area.
The Impact of Medical Insurance Rates on Healthcare Access
Medical insurance rates are a critical determinant of healthcare access for individuals and families. Affordability is a significant factor in whether people can obtain and maintain health insurance coverage. High insurance rates can lead to individuals choosing to go without coverage, which can have serious consequences for their health and financial well-being.
Financial Implications
For those who can afford it, higher insurance rates may not be a significant barrier to obtaining coverage. However, for many individuals and families, especially those with low or moderate incomes, high insurance rates can be prohibitive. This can lead to underinsurance, where individuals have some form of coverage but it is inadequate to cover their healthcare needs, or uninsurance, where they lack coverage altogether.
Underinsurance and uninsurance can result in delayed or forgone healthcare, leading to poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run. Individuals may forego necessary medical care, such as screenings, vaccinations, or treatment for chronic conditions, which can exacerbate their health issues and lead to more complex and costly health problems later on.
Improving Access and Affordability
Efforts to improve access to healthcare often focus on addressing the issue of insurance affordability. This can involve subsidies and tax credits to help individuals and families afford insurance premiums. In the U.S., for example, the Health Insurance Marketplace, established under the ACA, offers financial assistance to help people pay for their insurance plans.
Additionally, community-based initiatives and public health programs can play a role in improving healthcare access. These programs often provide preventive care services, health education, and access to discounted or free healthcare services for those who cannot afford insurance or who have inadequate coverage.
The Future of Medical Insurance Rates
The landscape of medical insurance rates is constantly evolving, influenced by advancements in medical technology, changes in healthcare delivery models, and shifts in societal trends and demographics. As the healthcare industry adapts to these changes, the way insurance rates are determined and the factors that influence them are also likely to evolve.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in medical technology, such as telemedicine and digital health tools, are expected to play an increasingly significant role in the future of medical insurance rates. These technologies can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery, potentially reducing costs and impacting insurance rates.
For instance, telemedicine can provide convenient and cost-effective access to healthcare services, particularly for individuals in rural or remote areas. This can lead to lower healthcare utilization rates and, consequently, reduced insurance costs. Additionally, digital health tools, such as fitness trackers and health monitoring apps, can encourage healthier lifestyles and better disease management, which may also impact insurance rates over time.
Changing Healthcare Models
The shift towards value-based healthcare models, which focus on the quality and outcomes of care rather than the quantity of services provided, is another trend that may influence future insurance rates. Under value-based models, providers are incentivized to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care, which can lead to reduced healthcare costs and potentially lower insurance premiums.
Moreover, the growing popularity of direct primary care (DPC) models, where patients pay a monthly fee for unlimited primary care services, could also impact insurance rates. DPC models can provide cost savings for both patients and insurers, as they reduce the need for costly emergency room visits and hospitalizations.
Societal and Demographic Changes
Shifts in societal trends and demographics are also likely to shape the future of medical insurance rates. For instance, the aging population in many countries is expected to put increased pressure on healthcare systems, potentially leading to higher healthcare costs and insurance rates. However, this trend may also spur innovation in healthcare delivery and financing, which could help mitigate some of these cost increases.
Additionally, changes in lifestyle and health behaviors, such as increased focus on wellness and preventive care, could lead to a healthier population overall. This could result in reduced demand for healthcare services and, consequently, lower insurance rates over time.
Conclusion
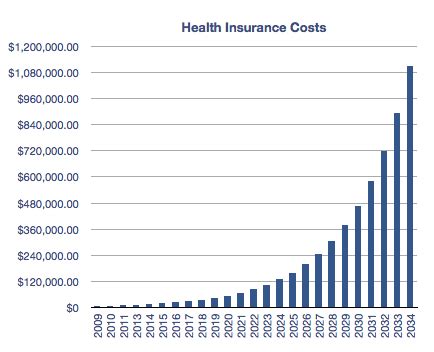
Medical insurance rates are a complex interplay of individual characteristics, lifestyle choices, demographic factors, and regional considerations. Understanding these factors is crucial for both insurers and consumers alike. For insurers, setting rates that accurately reflect the expected costs of providing healthcare services is essential for financial sustainability. For consumers, understanding how rates are determined can help them make informed choices about their healthcare coverage and advocate for policies that improve access and affordability.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so too will the factors influencing medical insurance rates. By staying informed about these changes and their potential impacts, both insurers and consumers can navigate the complex world of medical insurance with greater confidence and understanding.
How often do medical insurance rates change?
+Insurance rates can change annually or even more frequently, depending on various factors such as changes in healthcare costs, the insurer’s claims experience, and regulatory requirements. Insurers typically review and adjust their rates to ensure they can adequately cover the costs of providing healthcare services to their policyholders.
Are there ways to lower my medical insurance rates?
+Yes, there are several strategies you can employ to potentially lower your medical insurance rates. These include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which can lead to lower premiums; comparing quotes from different insurers to find the most competitive rates; and considering high-deductible health plans, which often have lower premiums but require you to pay more out-of-pocket before insurance coverage kicks in.
What factors do insurance companies consider when determining rates for group plans?
+For group plans, insurance companies typically consider the overall health and claims experience of the group, as well as factors such as the average age and gender distribution of the group members. They may also take into account the industry and size of the employer, as these can influence healthcare utilization and costs. It’s important to note that group plans often have more stable and predictable rates compared to individual plans.