Medicare And Supplemental Health Insurance
Navigating the complexities of health insurance is a crucial aspect of planning for one's future, especially for individuals approaching retirement age. Medicare, the federal health insurance program for people aged 65 and older, and those under 65 with certain disabilities or end-stage renal disease, plays a pivotal role in ensuring access to healthcare services. However, Medicare alone may not cover all medical expenses, which is where supplemental health insurance steps in to bridge the gaps.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding Medicare and the supplemental health insurance options available, empowering readers to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
Medicare: A Comprehensive Overview

Medicare is a federal health insurance program in the United States that provides healthcare coverage to individuals aged 65 and older, as well as younger individuals with certain disabilities or specific health conditions. It is divided into several parts, each covering different aspects of healthcare.
Medicare Part A
Medicare Part A, also known as hospital insurance, covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home healthcare services. It is typically premium-free for those who have worked and paid Medicare taxes for a minimum of 10 years. Part A helps cover the cost of medically necessary care received during an inpatient hospital stay, including room and board, nursing care, and other related services.
| Coverage | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Inpatient Hospital Care | Covers room and board, nursing care, and other services. |
| Skilled Nursing Facility Care | Provides coverage for a limited time after a hospital stay. |
| Hospice Care | Offers support for terminally ill individuals and their families. |
| Home Healthcare | Covers certain services, such as nursing care and therapy, received at home. |

Medicare Part B
Medicare Part B, or medical insurance, covers a wide range of outpatient services and preventive care. This includes doctor visits, outpatient hospital care, durable medical equipment, and certain home healthcare services. Part B is generally available to individuals upon turning 65, and a monthly premium is usually required.
| Coverage | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Doctor Visits | Covers visits to primary care physicians and specialists. |
| Outpatient Care | Provides coverage for services received outside of a hospital stay. |
| Durable Medical Equipment | Offers support for the purchase of equipment like wheelchairs and oxygen tanks. |
| Preventive Care | Covers various screenings and vaccinations to maintain health. |
Medicare Part C
Medicare Part C, also known as Medicare Advantage plans, is an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits. These plans are offered by private insurance companies and must cover everything that Original Medicare (Part A and B) covers. Part C plans often include additional benefits, such as prescription drug coverage and vision or dental care.
Medicare Part D
Medicare Part D is a voluntary program that helps cover the cost of prescription medications. It is available to those enrolled in Original Medicare (Part A and/or Part B) and is offered through private insurance companies. Part D plans can vary significantly in terms of the medications they cover and the costs associated with them.
Understanding the Gaps in Medicare Coverage

While Medicare provides comprehensive coverage, there are certain gaps and limitations that individuals should be aware of. These gaps can result in significant out-of-pocket expenses, especially for those with chronic health conditions or frequent medical needs.
Deductibles and Coinsurance
Medicare typically requires individuals to pay a deductible, which is a set amount that must be paid out of pocket before Medicare coverage begins. Additionally, coinsurance, which is a percentage of the Medicare-approved amount for a service, may also be required. For example, a 20% coinsurance means the individual pays 20% of the approved amount, and Medicare pays the remaining 80%.
Limitations on Certain Services
Medicare may have limitations on the frequency or duration of certain services. For instance, skilled nursing facility care is generally covered for up to 100 days, with a daily coinsurance rate after the first 20 days. Similarly, home healthcare services are typically limited to a specific number of visits or hours per year.
Non-Covered Services
Medicare does not cover all healthcare services. Some examples of non-covered services include long-term care (such as assisted living facilities), routine foot care, acupuncture, and certain dental procedures. It’s important for individuals to understand what is and isn’t covered by Medicare to avoid unexpected costs.
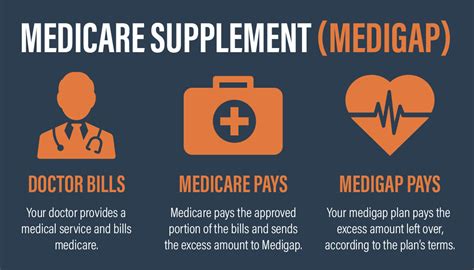
The Role of Supplemental Health Insurance
Supplemental health insurance, often referred to as Medigap insurance, is designed to fill the gaps left by Original Medicare (Part A and Part B). These policies are offered by private insurance companies and are intended to cover costs such as deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments, ensuring that individuals have more comprehensive coverage and fewer out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of Supplemental Health Insurance
There are ten standardized Medigap plans (Plans A through N) available, each with a unique set of benefits. The specific plan an individual chooses will depend on their healthcare needs and budget. Some plans cover only the basic gaps in Medicare, while others offer more comprehensive coverage.
| Plan | Coverage Highlights |
|---|---|
| Plan A | Covers basic Medicare gaps like deductibles and coinsurance for Part A and Part B. |
| Plan F | Offers the most comprehensive coverage, including Part B deductible and excess charges. |
| Plan G | Similar to Plan F but does not cover the Part B deductible. |
| Plan N | Covers Part A deductible, copayments, and excess charges; has some cost-sharing. |
Enrolling in Supplemental Health Insurance
The enrollment process for supplemental health insurance can vary depending on the state and the insurance company. Generally, individuals can enroll during their Medigap Open Enrollment Period, which is a six-month period starting the month they turn 65 and are enrolled in Medicare Part B. During this time, insurance companies cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums based on an individual’s health status.
Considerations for Choosing Supplemental Health Insurance
When selecting a supplemental health insurance plan, it’s important to consider factors such as the individual’s health needs, the cost of premiums, and the potential for future rate increases. It’s also crucial to compare plans from different insurance companies to find the best fit. Some plans may offer additional benefits, such as coverage for foreign travel, which can be beneficial for those who frequently travel outside the United States.
The Future of Medicare and Supplemental Health Insurance
As healthcare continues to evolve, so do the options for Medicare and supplemental health insurance. With the aging population and advancements in medical technology, it’s essential to stay informed about changes to these programs. Here are some key considerations for the future:
Changes in Medicare Coverage
Medicare coverage and benefits can change from year to year. It’s important to stay updated on any changes to ensure that one’s coverage remains adequate. This includes keeping track of any modifications to deductibles, coinsurance rates, and covered services.
Advancements in Healthcare Technology
The integration of technology in healthcare is rapidly advancing. From telemedicine to wearable health devices, these innovations can improve access to care and potentially reduce costs. As these technologies become more widespread, they may influence the way Medicare and supplemental insurance plans operate and the benefits they offer.
The Impact of Healthcare Policy Changes
Healthcare policy is subject to change, and any alterations to federal or state laws can have a significant impact on Medicare and supplemental insurance. It’s crucial to stay informed about these changes, as they can affect eligibility, coverage, and costs.
The Role of Preventive Care
Preventive care is an essential aspect of maintaining health and well-being. Medicare already covers many preventive services, and this trend is likely to continue and even expand. As more emphasis is placed on preventive care, individuals can expect to see an increase in covered services and potentially lower out-of-pocket costs.
Conclusion

Understanding Medicare and supplemental health insurance is a crucial step towards ensuring comprehensive healthcare coverage as one ages. By familiarizing oneself with the different parts of Medicare, the gaps in coverage, and the benefits of supplemental insurance, individuals can make informed decisions to protect their health and financial well-being. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, staying informed and adaptable is key to navigating the complex world of health insurance.
What is the difference between Original Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans?
+
Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) is the traditional fee-for-service Medicare program, while Medicare Advantage plans (Part C) are offered by private insurance companies and provide an alternative way to receive Medicare benefits. Medicare Advantage plans often include additional benefits, such as prescription drug coverage and vision or dental care.
Are there any limitations on enrolling in supplemental health insurance (Medigap)?
+
Yes, there are specific enrollment periods and eligibility requirements for Medigap plans. Generally, individuals can enroll during their Medigap Open Enrollment Period, which is a six-month period starting the month they turn 65 and are enrolled in Medicare Part B. It’s important to note that certain conditions may apply, and individuals should consult with their insurance provider or a Medicare expert for more details.
How do I choose the right supplemental health insurance plan for my needs?
+
Choosing the right supplemental health insurance plan involves considering factors such as your health needs, the cost of premiums, and potential for future rate increases. It’s beneficial to compare plans from different insurance companies and assess which plan offers the most comprehensive coverage for your specific requirements. Consulting with a healthcare or insurance professional can also provide valuable guidance in this decision-making process.