Medicare.gov/Medigapsupplementalinsuranceplans
In the complex landscape of healthcare coverage, Medigap stands out as a crucial component for individuals seeking comprehensive protection. This article delves into the intricacies of Medigap Supplemental Insurance Plans, exploring their purpose, benefits, and how they integrate with the Medicare system to provide essential healthcare support.
Understanding Medigap: A Supplemental Solution
Medigap, or Medicare Supplement Insurance, is a collection of standardized plans designed to fill the coverage gaps left by original Medicare (Parts A and B). These gaps often include deductibles, co-insurance, and co-payments, which can be significant financial burdens for many Medicare beneficiaries.
The importance of Medigap lies in its ability to provide a safety net, ensuring individuals have the financial security to access necessary medical services without facing excessive out-of-pocket expenses. This is particularly critical for those with chronic conditions or high healthcare needs.
Standardization and Variety
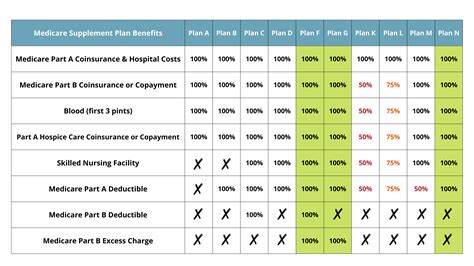
Medigap plans are standardized by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), ensuring that each plan type offers the same benefits regardless of the insurance company providing it. This standardization simplifies the process of comparing plans and understanding coverage.
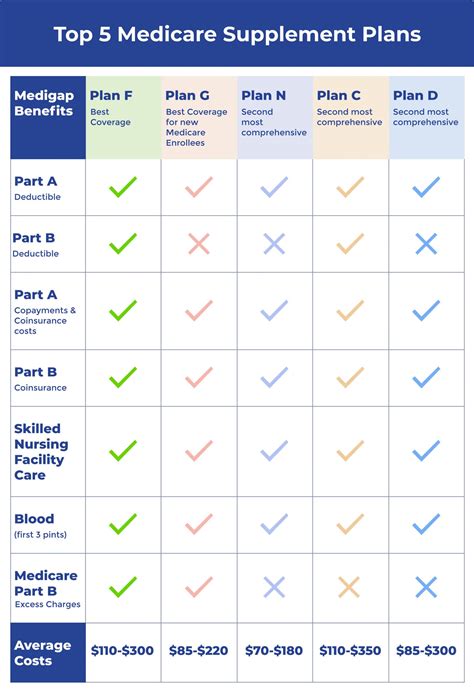
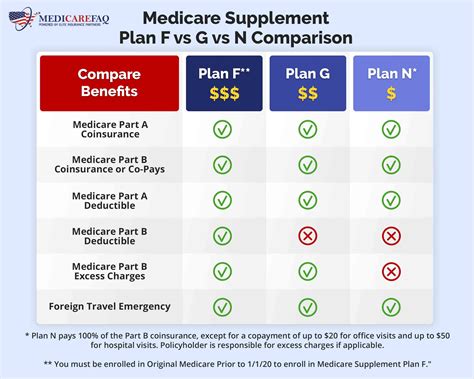
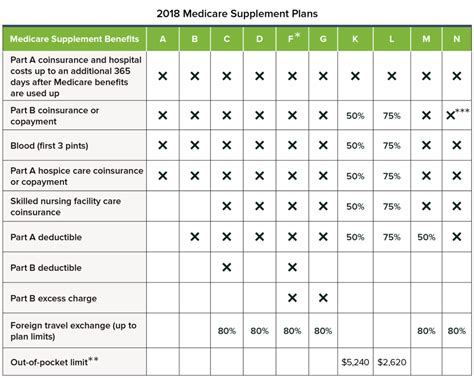
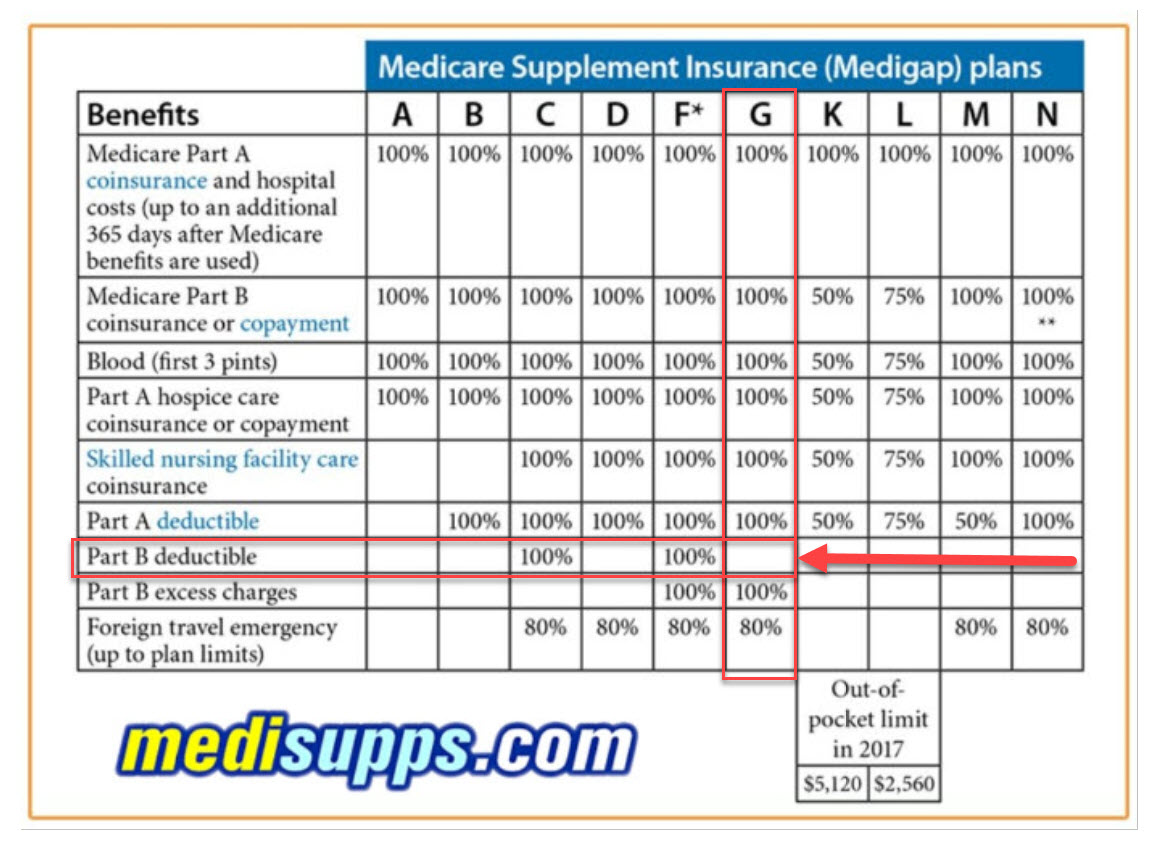
There are ten standard Medigap plan types, labeled A through N, with each plan offering a unique set of benefits. For example, Plan A provides the most basic coverage, while Plan F (offered only to those who were eligible for Medicare before 2020) offers the most comprehensive coverage, including foreign travel emergency coverage.
| Plan | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Plan A | Basic coverage, including Part A coinsurance and hospital costs. |
| Plan F | Comprehensive coverage, including foreign travel emergency coverage. |
| Plan G | Similar to Plan F, but without the Part B deductible. |
| Plan N | Offers lower premiums but with some cost-sharing, like copays for office visits. |
Integration with Medicare
Medigap plans are designed to work hand-in-hand with original Medicare. When a beneficiary has both Medicare and a Medigap plan, the Medigap plan typically covers the costs that original Medicare does not, ensuring a more complete coverage picture.
For instance, if a Medicare beneficiary has a Medigap plan that covers the Part A deductible, they won't have to pay that deductible out of pocket when admitted to the hospital. This integration simplifies the billing process and reduces the financial stress often associated with medical care.
Eligibility and Enrollment
Eligibility for Medigap plans is tied to enrollment in original Medicare. Specifically, individuals must be enrolled in Medicare Part B to be eligible for a Medigap plan. This alignment ensures that Medigap provides supplemental coverage for the services covered by Part B.
The enrollment process often involves a medical underwriting period, where insurance companies assess an individual's health status before offering a policy. However, during certain open enrollment periods, individuals can enroll in Medigap plans without undergoing medical underwriting, ensuring access to coverage regardless of health status.
Choosing the Right Medigap Plan
Selecting the appropriate Medigap plan involves careful consideration of one’s healthcare needs and financial situation. While more comprehensive plans offer wider coverage, they often come with higher premiums.
Individuals should evaluate their healthcare history and future needs, assessing the likelihood of requiring extensive medical services. Those with more predictable and manageable healthcare needs might opt for a plan with lower premiums, whereas those with unpredictable or complex health issues may benefit from a more comprehensive plan.
Cost Considerations
Medigap plans can vary significantly in cost, with premiums influenced by factors such as the plan type, the insurance company, and the beneficiary’s age, location, and health status.
It's important to shop around and compare rates from different insurance providers. While the benefits of each plan type are standardized, the premiums can vary considerably, offering opportunities to find the best value for one's specific needs.
The Future of Medigap
The landscape of Medigap insurance is evolving, with ongoing debates and policy changes shaping its future. One notable development is the introduction of Medicare Advantage plans, which offer an alternative to original Medicare and often include additional benefits like vision, dental, and hearing coverage.
However, Medigap plans remain a crucial option for those seeking to supplement original Medicare, offering a straightforward and reliable approach to healthcare coverage. As the healthcare industry continues to innovate, Medigap's role in providing financial security and access to care will likely remain a key focus.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I have both a Medigap plan and a Medicare Advantage plan?
+
No, you cannot have both a Medigap plan and a Medicare Advantage plan simultaneously. Medigap plans are designed to supplement original Medicare (Parts A and B), while Medicare Advantage plans are an alternative to original Medicare. Enrolling in a Medicare Advantage plan automatically replaces your original Medicare coverage, making a Medigap plan redundant.
Are Medigap plans available in all states?
+
Yes, Medigap plans are available in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. However, the specific plans offered and their costs can vary by state due to differences in state regulations and the insurance market.
What is the difference between a Medigap plan and a Part D prescription drug plan?
+
A Medigap plan and a Part D prescription drug plan serve different purposes within the Medicare system. Medigap plans are designed to cover the gaps in original Medicare (Parts A and B) coverage, including deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments. In contrast, a Part D prescription drug plan provides coverage specifically for prescription medications. While some Medigap plans may offer limited prescription drug coverage, a Part D plan is typically required for comprehensive prescription drug coverage.
Can I change my Medigap plan if I find a better option?
+
Yes, you have the flexibility to switch Medigap plans during specific enrollment periods. These periods include the initial Medigap enrollment period (when you first become eligible for Medicare Part B), the annual Medigap open enrollment period (from January 1 to June 30 each year), and special enrollment periods triggered by certain life events (such as moving or losing other health coverage).
Do Medigap plans cover long-term care services?
+
No, Medigap plans do not cover long-term care services, which include assistance with activities of daily living like bathing, dressing, and eating. These services are typically provided in a nursing home, assisted living facility, or at home. Medicare does offer some limited coverage for skilled nursing care and home health care, but it does not cover custodial or personal care services, which are often needed for long-term care.