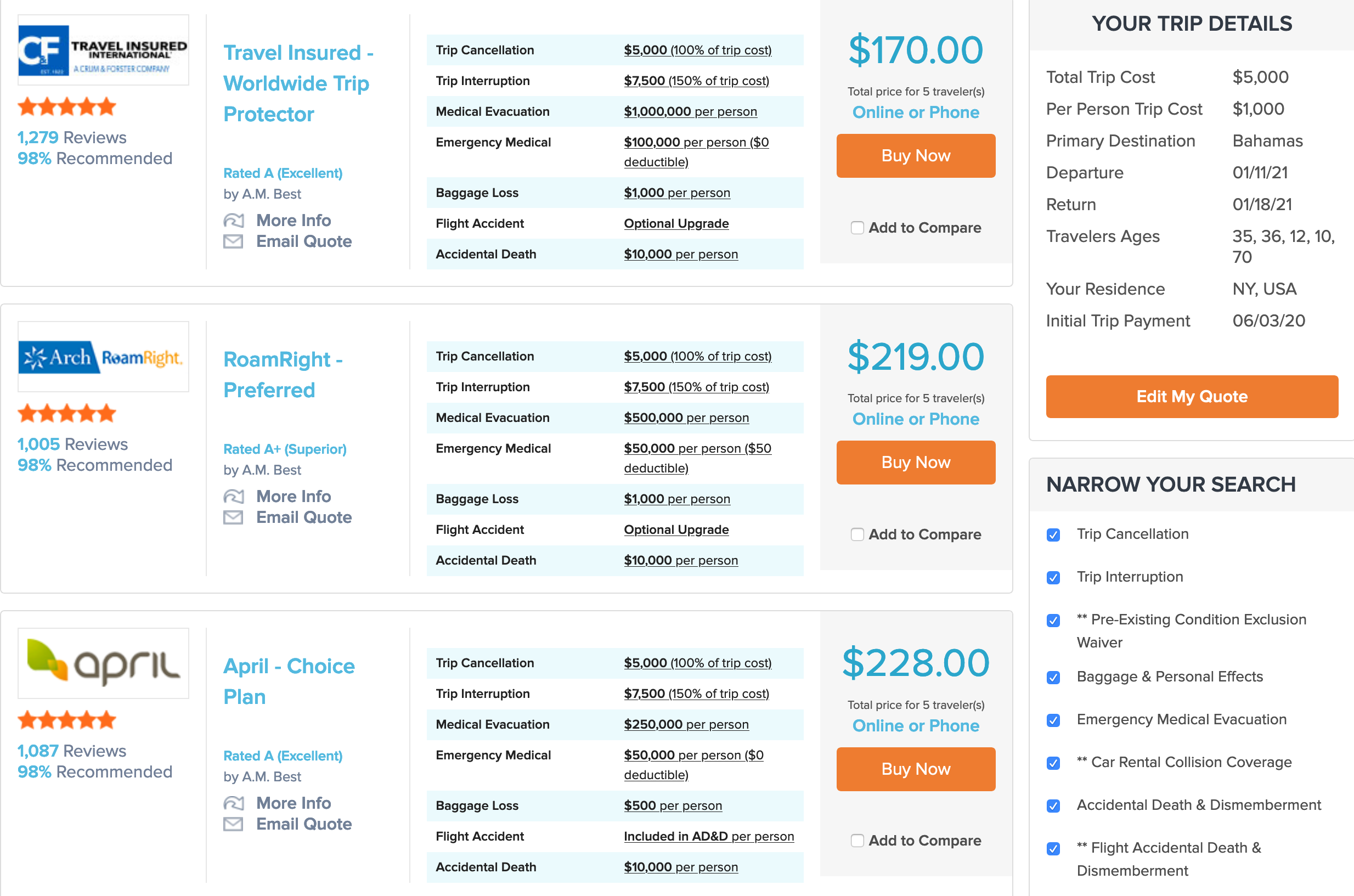
Mutal Life Insurance

Mutual life insurance is a unique and intriguing concept in the insurance industry, offering policyholders a range of benefits and a say in the company's operations. In an era where consumers are increasingly conscious of their financial choices, mutual life insurance presents an appealing alternative to traditional corporate policies. This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of mutual life insurance, exploring its history, structure, advantages, and how it stands out in the competitive insurance market.
The Historical Roots and Evolution of Mutual Life Insurance
Mutual life insurance has a rich historical background, with its origins dating back to the 18th century. The concept emerged as a response to the needs of a growing middle class, who sought protection for their families and assets. The first mutual life insurance company, Mutual Life Insurance Company of New York (now known as New York Life), was founded in 1841, revolutionizing the industry by allowing policyholders to have a stake in the company’s governance.
Over the years, mutual life insurance has evolved significantly. Initially, it was primarily focused on providing life insurance coverage. However, as the industry matured, mutual life insurance companies began offering a broader range of products, including annuities, health insurance, and property and casualty insurance. This diversification allowed mutual companies to compete effectively in the modern insurance market.
A key development in the history of mutual life insurance was the introduction of demutualization in the late 20th century. Demutualization is a process where a mutual company transforms into a stock company, allowing its policyholders to receive a one-time cash payout or shares in the newly formed corporation. While demutualization has provided significant financial benefits to policyholders, it has also led to a decline in the number of mutual life insurance companies, as many chose to convert to stock companies.
The Structure and Governance of Mutual Life Insurance Companies

One of the defining characteristics of mutual life insurance companies is their unique structure and governance model. Unlike traditional corporate insurance companies, which are owned by shareholders, mutual life insurance companies are owned by their policyholders. This ownership structure gives policyholders a say in the company’s operations and allows them to participate in its success.
Mutual life insurance companies are governed by a board of directors, who are typically elected by the policyholders. The board is responsible for overseeing the company's operations, ensuring its financial stability, and making strategic decisions. Policyholders often have the opportunity to vote on key issues, such as the election of directors, amendments to the company's bylaws, and significant business transactions.
In addition to policyholder participation, mutual life insurance companies also have a management team, led by a chief executive officer (CEO), who is responsible for the day-to-day operations of the company. The management team works closely with the board of directors to implement the company's strategic plans and ensure its long-term success.
Advantages of Mutual Life Insurance: A Policyholder’s Perspective
Mutual life insurance offers several advantages to policyholders, making it an attractive option in the insurance market. One of the key benefits is the potential for higher returns on their policies. As mutual life insurance companies are not driven by the need to maximize profits for shareholders, they can focus on providing competitive returns to their policyholders. This often results in higher dividends or policy values over time.
Another advantage of mutual life insurance is the stability it offers. Because policyholders own the company, they have a vested interest in its long-term success. This ownership structure can lead to more conservative and stable investment strategies, which can be beneficial during economic downturns. Policyholders can have peace of mind knowing that their insurance company is focused on their best interests and not solely on maximizing profits.
Furthermore, mutual life insurance companies often have a strong focus on customer service and satisfaction. With policyholders as owners, the company is more inclined to prioritize their needs and ensure they receive the best possible service. This can result in a more personalized and responsive experience, with faster claim processing and a higher level of customer support.
Comparative Analysis: Mutual Life Insurance vs. Traditional Corporate Policies
When considering insurance options, it’s essential to understand how mutual life insurance compares to traditional corporate policies. While both types of insurance companies offer life insurance coverage, there are several key differences that set them apart.
One of the most significant differences is the ownership structure. As mentioned earlier, mutual life insurance companies are owned by policyholders, while traditional corporate policies are owned by shareholders. This difference in ownership can lead to varying priorities and business strategies. Traditional corporate policies may prioritize shareholder profits, while mutual life insurance companies focus on policyholder returns and stability.
Another distinction lies in the financial reporting and transparency. Mutual life insurance companies are required to disclose their financial statements and provide detailed information to their policyholders. This transparency allows policyholders to make informed decisions and understand the financial health of the company. In contrast, traditional corporate policies may have more discretion in their financial reporting, as they are not directly accountable to their policyholders.
In terms of product offerings, mutual life insurance companies often provide a wider range of products. In addition to life insurance, they may offer annuities, health insurance, and property and casualty insurance. This diversification can be beneficial to policyholders, as it allows them to consolidate their insurance needs with a single company. Traditional corporate policies may also offer a variety of products, but their focus may be more narrow, targeting specific types of insurance.
Performance Analysis: Evaluating the Success of Mutual Life Insurance Companies

Assessing the performance of mutual life insurance companies is crucial in understanding their value and long-term viability. There are several key metrics and indicators that can be used to evaluate their success.
One of the primary indicators is the financial strength and stability of the company. This can be assessed through various financial ratios, such as the solvency ratio, which measures the company's ability to meet its long-term obligations. A strong solvency ratio indicates that the company is financially sound and can withstand economic fluctuations.
Another important metric is the company's investment performance. Mutual life insurance companies invest their policyholders' premiums to generate returns, which are then used to pay claims and provide dividends. Evaluating the company's investment strategies and returns can provide insights into its financial management and ability to provide competitive returns to policyholders.
| Company | Investment Return (%) | Dividend Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Mutual Life Insurance Co. A | 7.2 | 3.8 |
| Mutual Life Insurance Co. B | 6.5 | 4.2 |
| Mutual Life Insurance Co. C | 8.1 | 3.6 |

In addition to financial metrics, customer satisfaction and claim processing times are also important indicators of performance. Mutual life insurance companies that prioritize customer service and have efficient claim processes are more likely to retain policyholders and maintain a positive reputation.
Future Implications and Industry Insights
Looking ahead, the future of mutual life insurance appears promising. With the increasing focus on financial literacy and consumer awareness, many individuals are seeking insurance options that offer transparency, stability, and a say in the company’s operations. Mutual life insurance companies are well-positioned to meet these demands and provide a competitive alternative to traditional corporate policies.
However, the industry is not without its challenges. The decline in the number of mutual life insurance companies due to demutualization has led to a more concentrated market. This concentration can result in less competition and potentially limit the choices available to consumers. To address this, industry experts suggest promoting awareness and education about the benefits of mutual life insurance to encourage more companies to adopt this structure.
Furthermore, the evolving regulatory landscape and changing consumer preferences present both opportunities and challenges for mutual life insurance companies. Adapting to digital technologies and offering innovative products can help these companies stay competitive and attract a new generation of policyholders. By leveraging technology and data-driven insights, mutual life insurance companies can enhance their operations, improve customer experiences, and remain relevant in the modern insurance market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between mutual life insurance and traditional corporate policies?
+
Mutual life insurance differs from traditional corporate policies in its ownership structure. Mutual life insurance companies are owned by policyholders, giving them a say in the company’s governance and operations. In contrast, traditional corporate policies are owned by shareholders, who prioritize profits over policyholder returns.
How do mutual life insurance companies determine dividend payments to policyholders?
+
Dividend payments in mutual life insurance are determined by the company’s financial performance and investment returns. The board of directors, elected by policyholders, decides on the dividend amount based on the company’s surplus after meeting its obligations. This ensures policyholders receive a share of the company’s profits.
Can policyholders of mutual life insurance companies influence the company’s strategic decisions?
+
Yes, policyholders of mutual life insurance companies have the right to vote on key strategic decisions. They can elect the board of directors, who oversee the company’s operations, and participate in annual meetings where significant business matters are discussed. This direct involvement ensures policyholders have a say in the company’s future.
Are there any potential drawbacks to mutual life insurance compared to traditional corporate policies?
+
While mutual life insurance offers several advantages, there are a few potential drawbacks. One is the lack of liquidity, as policyholders may not easily convert their policies into cash. Additionally, mutual companies may have slower decision-making processes due to the involvement of policyholders in governance. However, these challenges can be mitigated with proper planning and understanding.
How can I find a reputable mutual life insurance company for my needs?
+
When choosing a mutual life insurance company, it’s important to research and compare multiple options. Look for companies with a strong financial rating, a history of stable performance, and positive customer reviews. Consider factors like investment strategies, customer service, and the range of products offered to find the best fit for your needs.