State By State Health Insurance Costs

Health insurance is a critical aspect of modern life, providing individuals and families with financial protection and access to essential healthcare services. With healthcare costs rising, understanding the state-by-state variations in insurance premiums is crucial for making informed decisions about coverage. This comprehensive guide will delve into the health insurance landscape across the United States, exploring the factors that influence insurance costs and providing insights to help individuals navigate the complex world of healthcare coverage.
Unraveling the Health Insurance Landscape
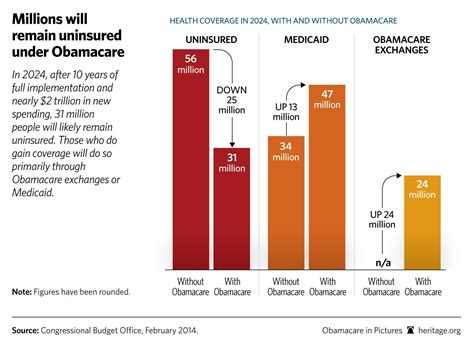
The United States healthcare system is a complex web of regulations, policies, and market dynamics, which collectively shape the cost of health insurance. While the Affordable Care Act (ACA) introduced standardization and reforms, the reality is that health insurance costs vary significantly from state to state. These variations are influenced by a myriad of factors, including population demographics, healthcare infrastructure, state regulations, and market competition.
Demographics and Population Health
One of the primary drivers of health insurance costs is the health profile of a state’s population. States with a higher proportion of elderly residents or individuals with chronic health conditions tend to have higher insurance premiums. For instance, Florida, with its large retiree population, often faces higher healthcare costs due to the higher prevalence of age-related health issues.
In contrast, states with younger populations and healthier demographics may enjoy lower insurance rates. For example, states like Utah and Colorado, known for their active lifestyles and outdoor cultures, often report lower rates of chronic diseases, leading to more affordable insurance options.
Healthcare Infrastructure and Provider Networks
The availability and cost of healthcare services within a state also significantly impact insurance premiums. States with robust healthcare infrastructure, including advanced medical facilities and a diverse range of healthcare providers, may experience higher insurance costs due to the increased demand for specialized care.
On the other hand, states with limited healthcare resources or a shortage of specialists may have lower insurance rates. However, this can also lead to longer wait times and reduced access to certain types of care.
State Regulations and Market Competition
State-level regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the health insurance market. Some states have implemented policies to control insurance costs, such as requiring insurers to justify rate increases or implementing risk adjustment programs. These regulatory interventions can help stabilize insurance premiums and protect consumers.
Additionally, the level of competition within a state's health insurance market influences costs. States with a more diverse range of insurers tend to have more competitive pricing, providing consumers with a wider array of coverage options at different price points.
State-by-State Breakdown: Health Insurance Costs
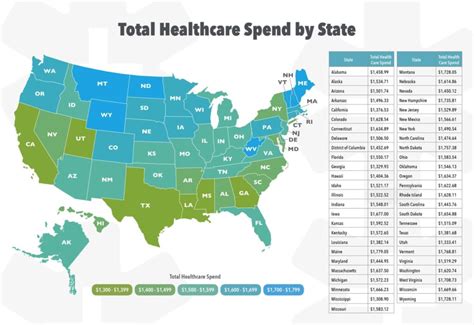
To provide a comprehensive overview, let’s examine the health insurance landscape in a few key states, highlighting the factors that contribute to their insurance costs.
California: A Diverse Market with Rising Costs
California boasts one of the most diverse populations in the United States, with a wide range of demographics and healthcare needs. This diversity, coupled with a robust healthcare infrastructure, contributes to relatively high insurance premiums.
| California Health Insurance Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Premium (Individual Plan) | $600/month |
| Number of Insurers | Over 20 |
| Population with Private Insurance | Over 12 million |
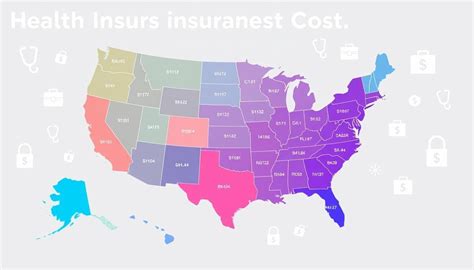
Despite the high costs, California's insurance market is highly competitive, offering a variety of plans and providers. The state's strong regulatory framework also helps protect consumers from excessive rate hikes.
Texas: A Complex Landscape
Texas presents a unique challenge in the health insurance landscape. With a large population and a diverse range of healthcare needs, the state’s insurance market is highly fragmented. This fragmentation often leads to wide variations in insurance costs, making it difficult for consumers to navigate.
| Texas Health Insurance Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Premium (Individual Plan) | $550/month |
| Number of Insurers | Over 15 |
| Population with Private Insurance | Over 11 million |
Texas has implemented various measures to stabilize its insurance market, including risk pools and reinsurance programs. However, the state's large uninsured population and limited access to healthcare services in certain regions contribute to the complexity of its insurance landscape.
New York: Balancing High Costs with Comprehensive Coverage
New York is known for its robust healthcare system and comprehensive insurance regulations. This state’s insurance market is characterized by high premiums, but it offers a wide range of benefits and protections to consumers.
| New York Health Insurance Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Premium (Individual Plan) | $700/month |
| Number of Insurers | Over 10 |
| Population with Private Insurance | Over 8 million |
New York's stringent regulations ensure that insurance plans provide a comprehensive set of benefits, including mental health coverage and substance abuse treatment. While the costs are high, consumers benefit from a strong safety net and access to a wide range of healthcare services.
Florida: Managing Healthcare Costs in a Retirement Haven
Florida’s unique demographic profile, with a large retiree population, presents specific challenges in the health insurance market. The state’s healthcare costs are influenced by the higher healthcare needs of its older residents.
| Florida Health Insurance Metrics | Data |
|---|---|
| Average Premium (Individual Plan) | $580/month |
| Number of Insurers | Over 12 |
| Population with Private Insurance | Over 7 million |
To manage costs, Florida has implemented various programs, including Medicare Advantage plans tailored to the needs of retirees. Additionally, the state's insurance market offers a range of options, providing flexibility for consumers to choose plans that fit their specific healthcare needs.
Navigating the Health Insurance Maze: Tips for Consumers
Understanding the state-by-state variations in health insurance costs is just the first step in making informed decisions. Here are some practical tips to help consumers navigate the complex world of healthcare coverage:
- Research Multiple Insurers: Compare plans and premiums from different insurers to find the best value for your needs.
- Utilize State-Specific Resources: Many states offer consumer guides and resources to help individuals understand their insurance options and rights.
- Consider Alternative Plans: Explore alternatives like short-term plans or health sharing ministries, especially if you're healthy and looking for more affordable coverage.
- Understand Your Healthcare Needs: Assess your current and potential future healthcare needs to choose a plan that provides adequate coverage.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with healthcare policy changes and insurance reforms that may impact your coverage and costs.
Conclusion: A Complex, Yet Navigable Landscape
The state-by-state variations in health insurance costs reflect the intricate interplay of demographics, healthcare infrastructure, regulations, and market dynamics. While these factors can make the insurance landscape complex, consumers can make informed decisions by understanding these nuances and leveraging available resources.
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive is key to ensuring access to quality healthcare at a reasonable cost. Whether you're a resident of California, Texas, New York, Florida, or any other state, understanding the unique characteristics of your state's insurance market can empower you to make choices that align with your health and financial needs.
FAQ
How do state regulations impact health insurance costs?
+
State regulations play a crucial role in shaping the health insurance market. Some states have implemented policies to control insurance costs, such as requiring insurers to justify rate increases or implementing risk adjustment programs. These regulatory interventions can help stabilize insurance premiums and protect consumers from excessive costs.
What factors contribute to the high insurance costs in certain states like California and New York?
+
The high insurance costs in states like California and New York can be attributed to a combination of factors. These states have diverse populations with varying healthcare needs, robust healthcare infrastructure, and stringent insurance regulations. The comprehensive coverage mandated by these regulations often leads to higher premiums, but it also provides consumers with a strong safety net and access to a wide range of healthcare services.
How can consumers in states with high uninsured rates, like Texas, access affordable healthcare?
+
In states like Texas with a high uninsured rate, consumers can explore alternative insurance options such as short-term plans or health sharing ministries. Additionally, these states often have programs and resources to assist low-income individuals in obtaining coverage. It’s essential for consumers to research and understand their options, including potential subsidies and assistance programs, to access affordable healthcare.



