Term Of Insurance
In the realm of financial planning and security, the term of insurance plays a pivotal role. It is an essential component of any comprehensive insurance strategy, offering a defined period of coverage and protection. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of insurance terms, providing an in-depth analysis and insights to help individuals make informed decisions about their financial future.
Understanding the Term of Insurance
The term of insurance refers to the specific duration for which an insurance policy is active and provides coverage. It is a predetermined timeframe, agreed upon by the policyholder and the insurance provider, during which the insured individual or entity is protected against specified risks. This period can vary significantly, depending on the type of insurance, the needs of the policyholder, and the nature of the risks being insured against.
For instance, in the case of life insurance, the term could range from a few years to several decades, ensuring that the policyholder's loved ones are financially protected throughout their lifetime. On the other hand, short-term policies like travel insurance typically have much briefer terms, covering the duration of a specific trip or event.
The concept of the term of insurance is fundamental to understanding the nature and scope of insurance coverage. It defines the boundaries within which the policy is valid and sets the expectations for both the policyholder and the insurance company. A clear understanding of the term helps individuals tailor their insurance plans to their unique needs and circumstances.
Types of Insurance Terms
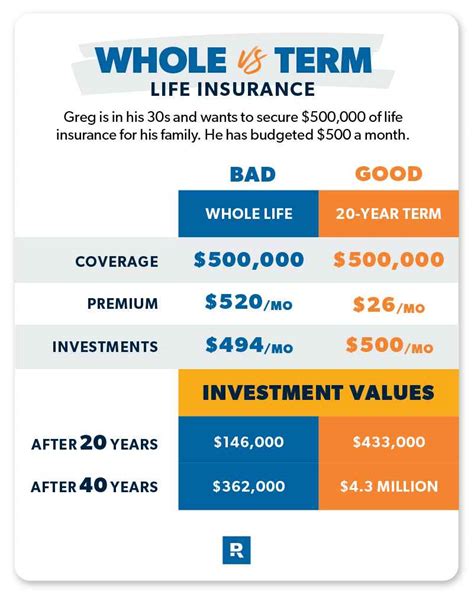
Insurance terms can be broadly categorized into two main types: fixed-term and renewable.
Fixed-Term Insurance
Fixed-term insurance, as the name suggests, offers coverage for a specified period, after which the policy expires. This type of insurance is often chosen for its affordability and simplicity. During the term, the policyholder pays a fixed premium, and in return, receives coverage for the defined risks. Fixed-term policies are commonly used for life insurance, where the term can be tailored to match the policyholder’s financial goals or the duration they wish to provide financial protection for their dependents.
For example, a parent might opt for a 20-year term life insurance policy to ensure their children's financial security until they reach adulthood. Once the term is over, the policy expires, and the policyholder would need to decide whether to renew the policy or explore other options.
Renewable Insurance
Renewable insurance policies, on the other hand, offer more flexibility. These policies can be renewed at the end of the term, often at a higher premium, to extend the coverage period. This type of insurance is particularly beneficial for individuals whose needs or circumstances may change over time. By allowing for renewal, these policies provide ongoing protection without the need for a new application or medical examination, which can be especially advantageous as individuals age or their health status changes.
An example of renewable insurance is a health insurance policy. Many health insurance plans are renewable annually, allowing individuals to maintain coverage year after year, even as their healthcare needs evolve.
Factors Influencing Insurance Terms
The term of an insurance policy is influenced by a multitude of factors, each playing a crucial role in determining the duration and cost of coverage.
Risk Profile
The risk profile of the policyholder is a significant factor. Insurance companies assess the risks associated with insuring an individual or entity, taking into account factors such as age, health status, occupation, and lifestyle. A higher-risk profile typically results in shorter terms or higher premiums, as the insurance company assumes more risk in providing coverage.
Financial Goals
The financial goals of the policyholder also impact the term of insurance. For instance, a young professional might opt for a longer term life insurance policy to provide financial protection for their family over a more extended period. Conversely, a retiree might choose a shorter term policy to cover their immediate financial needs.
Premium Costs
The cost of premiums is a critical factor in determining the term of insurance. Longer terms often result in higher overall premiums, as the insurance company assumes more extended risk coverage. Policyholders must balance their financial capacity with their desired level of protection when choosing an insurance term.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, including economic trends and the insurance industry’s overall health, can also influence insurance terms. During periods of economic downturn or when the insurance market is highly competitive, insurance companies may offer more extended terms or lower premiums to attract customers.
Performance Analysis of Different Insurance Terms
The performance of insurance policies can vary significantly depending on the term chosen. Fixed-term policies often provide more straightforward cost structures, with predictable premiums over the policy’s duration. This can be advantageous for individuals on a tight budget or those seeking long-term financial planning.
Renewable policies, while offering more flexibility, may result in higher overall costs due to the potential for premium increases at renewal. However, they provide the benefit of ongoing coverage without the need for a new application process, which can be particularly valuable for individuals with changing health or lifestyle factors.
The performance of an insurance policy also depends on the type of coverage and the specific risks being insured against. For instance, a life insurance policy with a longer term may provide more extensive financial protection for beneficiaries, while a shorter term policy might be more cost-effective for individuals with fewer financial dependents.
| Insurance Type | Fixed-Term | Renewable |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | Predictable premiums over the term | Potential for premium increases at renewal |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, policy expires at the end of the term | More flexible, can be renewed for ongoing coverage |
| Benefits | Straightforward cost structure, suitable for long-term planning | Ongoing coverage without new application, beneficial for changing circumstances |
The Future of Insurance Terms
As the insurance industry continues to evolve, the concept of insurance terms is also likely to undergo significant changes. With advancements in technology and data analytics, insurance companies are increasingly able to personalize insurance policies based on individual risk profiles and needs. This could lead to more tailored insurance terms, offering greater flexibility and precision in coverage.
Additionally, the growing trend of insurance as a service, where insurance is offered as a subscription-based model, could further revolutionize insurance terms. This model would allow policyholders to pay for coverage on a monthly or yearly basis, with the option to adjust the term and coverage as their needs change. This would provide unprecedented flexibility and control over insurance coverage.
Furthermore, the rise of parametric insurance, which pays out based on the occurrence of a specific event rather than the extent of the loss, could also impact insurance terms. This type of insurance, often used in agriculture and natural disaster coverage, offers a new approach to risk management and could potentially lead to more innovative insurance term structures.
Conclusion
Understanding the term of insurance is crucial for anyone seeking financial security and peace of mind. Whether it’s life insurance, health insurance, or any other type of coverage, the term of insurance defines the scope and duration of protection. By carefully considering factors such as risk profile, financial goals, and premium costs, individuals can make informed decisions about the length and type of insurance term that best suits their needs.
As the insurance landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and innovations in insurance terms will be essential. With the right knowledge and a proactive approach to financial planning, individuals can ensure they have the coverage they need to protect their financial well-being and that of their loved ones.
What happens if I outlive my life insurance term?
+
If you outlive your life insurance term, the policy will typically expire, and no benefits will be payable. However, some policies offer the option to renew or convert to a permanent policy, allowing you to continue coverage. It’s important to review your policy and discuss options with your insurance provider before the term ends.
Can I change the term of my insurance policy after it has started?
+
In most cases, it’s not possible to change the term of an insurance policy once it has started. Insurance terms are typically agreed upon at the beginning of the policy, and changing them can be complex and may require a new application. However, some policies offer the option to renew or extend the term, which should be discussed with the insurance provider.
How does the insurance term impact the overall cost of my policy?
+
The insurance term can significantly impact the overall cost of your policy. Longer terms generally result in higher premiums, as the insurance company assumes more extended risk coverage. On the other hand, shorter terms may be more affordable but offer less protection over time. It’s essential to balance your financial capacity with your desired level of protection when choosing an insurance term.