Us Medical Insurance Cost
Unraveling the Complexity: Understanding US Medical Insurance Costs

In the United States, medical insurance is a vital component of healthcare access and financial security. However, navigating the intricate world of healthcare costs can be daunting. The price of medical insurance varies significantly, influenced by a multitude of factors. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the key elements that contribute to the cost of US medical insurance, offering clarity and insight to those seeking to understand this complex landscape.
The Multifaceted Nature of Medical Insurance Costs

Medical insurance costs in the US are shaped by a combination of personal, regional, and policy-related factors. Let's delve into these aspects to grasp the breadth of influences on insurance premiums.
Personal Factors: A Unique Mosaic
Individual characteristics play a pivotal role in determining insurance costs. Age is a primary consideration, with younger individuals generally enjoying lower premiums due to their lower risk profile. In contrast, older adults often face higher costs as their healthcare needs tend to increase with age. Gender is another factor, with women often paying more due to their higher utilization of healthcare services. Pre-existing medical conditions can also significantly impact costs, as insurers may charge higher premiums to cover the potential costs associated with these conditions.
Lifestyle choices also come into play. For instance, smokers may face higher premiums due to the increased health risks associated with tobacco use. Similarly, individuals with hazardous hobbies or occupations might see their insurance costs rise, as their activities carry a higher risk of injury or illness.
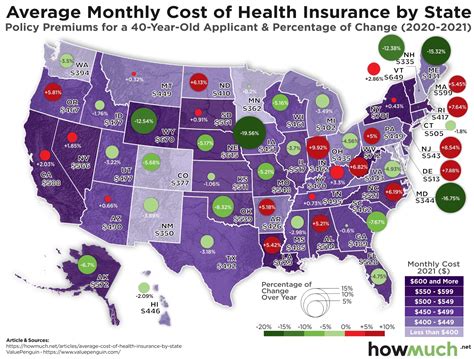
Regional Variations: A Tale of Two Cities
The cost of medical insurance can vary dramatically across different regions of the US. This disparity is influenced by a range of factors, including the cost of living, the availability of healthcare services, and the demographic composition of an area. For example, urban areas with a high cost of living and a dense population often have higher insurance premiums due to the concentration of healthcare facilities and the associated expenses.
Regional variations can also be driven by state-specific regulations and policies. Some states mandate that certain healthcare services or treatments be covered by insurance plans, which can impact the overall cost. Additionally, the competitive landscape of insurance providers within a state can affect the prices consumers pay for coverage.
Policy Features: The Fine Print Matters
The features and benefits of a medical insurance policy are a significant determinant of its cost. Policies with a broader range of covered services, lower deductibles, and higher maximum benefit limits tend to be more expensive. On the other hand, plans with narrower coverage, higher deductibles, and lower maximum benefits can be more affordable, but they may leave policyholders vulnerable to higher out-of-pocket costs if they require extensive medical care.
The network of healthcare providers a plan covers also influences its cost. In-network providers, who have negotiated rates with the insurance company, generally result in lower costs for policyholders. Out-of-network providers, however, can lead to higher expenses, as the insurance company may not have negotiated rates with these providers, leaving policyholders to pay more out of pocket.
| Policy Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Covered Services | The range of medical services and treatments included in the plan. |
| Deductibles | The amount a policyholder must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage begins. |
| Maximum Benefits | The maximum amount the insurance company will pay towards covered medical expenses in a given period. |
| Network of Providers | The healthcare providers who have negotiated rates with the insurance company. |

Analyzing Performance and Trends
Understanding the current landscape of medical insurance costs is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike. By examining recent trends and performance indicators, we can gain insights into the state of the industry and identify areas for improvement.
The Rising Tide of Insurance Costs
Over the past decade, medical insurance costs have experienced a steady upward trend. According to the Kaiser Family Foundation, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family coverage rose from $15,733 in 2010 to $21,342 in 2020, an increase of 35.6%. For single coverage, the rise was from $5,429 to $7,470, an increase of 37.6%. These figures highlight the significant financial burden that medical insurance imposes on individuals and families.
Performance Indicators: A Closer Look
- Deductibles: The average deductible for single coverage has increased by 99% over the last decade, from $1,077 in 2010 to $2,133 in 2020. This shift means that individuals are paying more out of pocket before their insurance coverage kicks in.
- Maximum Out-of-Pocket Limits: The maximum amount individuals can be expected to pay for covered services has also risen. In 2020, the average maximum out-of-pocket limit for single coverage was $7,470, up from $5,356 in 2010.
- In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Costs: The difference in costs between in-network and out-of-network providers has widened. In 2020, the average out-of-pocket cost for an emergency room visit was $768 with in-network providers and $1,573 with out-of-network providers, a difference of $805.
The Future of Medical Insurance Costs: Projections and Implications
Looking ahead, several factors suggest that medical insurance costs will continue to rise. The aging population, advancements in medical technology, and increasing healthcare utilization are expected to drive up costs. Additionally, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of healthcare access and may lead to policy changes that could impact insurance premiums.
Policy Changes on the Horizon
Proposed policies aimed at enhancing healthcare access and affordability could significantly impact insurance costs. For instance, the expansion of Medicaid coverage or the implementation of a public option could increase competition and drive down prices. Conversely, the repeal of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) or the introduction of more restrictive policies could limit access to insurance and potentially drive up costs for those who remain insured.
Implications for Consumers
The rising cost of medical insurance has significant implications for consumers. For many, the financial burden of insurance premiums can be a significant challenge, particularly for those with limited income or resources. This can lead to difficult choices, such as deciding between maintaining insurance coverage or forgoing it to save money in the short term. However, the potential long-term costs of going without insurance, such as high medical bills in the event of an accident or illness, can be even more devastating.
Conclusion: A Complex Equation

The cost of medical insurance in the US is influenced by a complex interplay of personal, regional, and policy-related factors. Understanding these influences is essential for consumers, policymakers, and healthcare providers alike. By staying informed about the trends and performance indicators in the medical insurance landscape, we can work towards developing solutions that enhance access to affordable, quality healthcare for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average cost of medical insurance in the US?
+
The average cost of medical insurance varies depending on the type of coverage and the individual’s circumstances. As of 2020, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family coverage was 21,342, while for single coverage it was 7,470. However, these averages can vary significantly based on factors such as age, location, and the specific plan features.
How do deductibles impact insurance costs?
+
Deductibles are the amount an insured individual must pay out of pocket before their insurance coverage begins. Higher deductibles generally mean lower premiums, as the individual is responsible for a larger portion of their healthcare costs upfront. However, this can result in higher out-of-pocket expenses if the individual requires significant medical care.
What are some ways to reduce the cost of medical insurance?
+
There are several strategies to potentially reduce insurance costs. These include comparing plans and providers to find the best value, considering high-deductible plans paired with a health savings account (HSA), and taking advantage of employer-provided wellness programs or discounts. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing costly medical conditions, which may lead to lower premiums.
How does the Affordable Care Act (ACA) impact insurance costs?
+
The ACA, also known as Obamacare, has had a significant impact on insurance costs. It introduced measures to make insurance more accessible and affordable, such as prohibiting insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions and offering subsidies to lower-income individuals. However, the law has also faced criticism for potentially driving up costs for certain demographics, such as younger, healthier individuals.
What are the potential future trends in medical insurance costs?
+
Several factors suggest that medical insurance costs will continue to rise. These include an aging population, increasing healthcare utilization, and advancements in medical technology. Additionally, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic may lead to policy changes that could impact insurance premiums. However, proposed policies aimed at enhancing healthcare access and affordability could also drive down costs.


