What Is The Average Cost Of Health Insurance
Understanding the average cost of health insurance is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it impacts financial planning and access to essential healthcare services. While the exact figures can vary greatly depending on numerous factors, this article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the average health insurance costs, offering insights into the key variables that influence these expenses and strategies to navigate the healthcare insurance landscape effectively.
The Variability of Health Insurance Costs

Health insurance costs are notoriously variable, influenced by a multitude of factors that can significantly impact the average premiums. Age is a primary determinant, with younger individuals generally enjoying lower premiums due to their relatively lower risk of requiring extensive medical care. In contrast, older adults often face higher costs, as they are more likely to need medical attention.
Geographical location also plays a substantial role. Healthcare expenses can vary significantly from one region to another, influenced by factors such as the cost of living, the availability of healthcare services, and local regulations. For instance, urban areas with advanced medical facilities and a high cost of living often command higher insurance premiums compared to rural regions.
The type of insurance plan chosen is another critical factor. Plans offering comprehensive coverage with low deductibles and copayments will naturally carry higher premiums. On the other hand, plans with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket expenses may be more affordable but require individuals to pay more when utilizing healthcare services.
Average Health Insurance Costs by Plan Type
Health insurance plans can be broadly categorized into several types, each with its own average cost range. Here’s a breakdown of some common plan types and their associated expenses:
Employer-Sponsored Plans
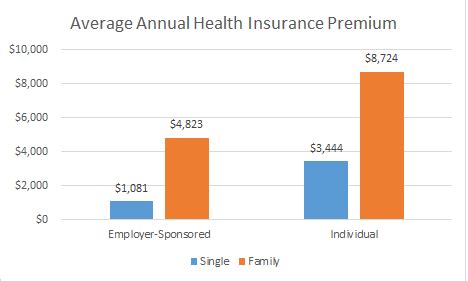
These plans are often the most cost-effective option for employees, as employers typically contribute a significant portion of the premium. The average cost for an employee-only plan under employer-sponsored coverage is approximately 7,700 annually, while family plans average around 22,200 per year. These costs are shared between the employer and the employee, with the latter typically contributing a fixed amount or a percentage of the premium.
Individual Market Plans
Individuals purchasing health insurance on their own in the individual market face higher costs. The average premium for an individual plan in the individual market is around 450 per month, or 5,400 annually. Family plans in this market can cost significantly more, with averages approaching 1,500 per month, or 18,000 annually.
Government-Sponsored Plans
Government-sponsored plans, such as Medicaid and Medicare, offer healthcare coverage to eligible individuals based on specific criteria. Medicaid, which provides coverage for low-income individuals and families, has varying costs depending on the state, with some states requiring no premiums. Medicare, primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, has Part B premiums averaging around $145 per month, though this can increase based on income.
| Plan Type | Average Annual Cost (Individual) | Average Annual Cost (Family) |
|---|---|---|
| Employer-Sponsored | $7,700 | $22,200 |
| Individual Market | $5,400 | $18,000 |
| Government-Sponsored (Medicaid) | Varies by State | Varies by State |
| Government-Sponsored (Medicare Part B) | $1,740 | N/A |

Factors Influencing Health Insurance Costs
Beyond the type of plan, several other factors contribute to the variability in health insurance costs. These include:
- Health Status: Pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses can lead to higher premiums, as they increase the likelihood of costly medical treatments.
- Tobacco Use: Smokers often face higher insurance premiums, as tobacco use is associated with various health complications.
- Number of Family Members: Family plans cover multiple individuals, leading to higher premiums compared to individual plans.
- Plan Network: In-network providers are often more cost-effective than out-of-network options, as insurance companies negotiate lower rates with in-network healthcare providers.
- Deductibles and Copayments: Plans with higher deductibles and copayments may have lower monthly premiums, but individuals pay more out of pocket when utilizing healthcare services.
Navigating Health Insurance Costs
Given the variability of health insurance costs, it’s essential to approach the selection process strategically. Here are some tips to help navigate the landscape:
Assess Your Needs
Determine your healthcare needs and prioritize the aspects most important to you. If you require frequent medical attention, a plan with lower deductibles and copayments might be more suitable, even if it comes with a higher premium. Conversely, if you’re generally healthy and don’t anticipate frequent medical expenses, a plan with higher deductibles and lower premiums could be a cost-effective choice.
Shop Around
Don’t settle for the first plan you encounter. Compare options from different insurers to find the best fit for your needs and budget. Online marketplaces, like healthcare.gov in the U.S., can provide a comprehensive view of available plans and their costs.
Consider Subsidies
If you’re purchasing insurance on the individual market, you might be eligible for subsidies to help lower your premiums. These subsidies, available through the Affordable Care Act, are based on income and can significantly reduce the cost of insurance.
Employer Benefits
If you’re employed, take advantage of your employer’s health insurance benefits. These plans are often more cost-effective due to the employer’s contribution, and they can provide additional perks like wellness programs and discounts on healthcare services.
Stay Informed
Keep yourself updated on healthcare reforms and changes in the insurance market. These changes can impact your coverage and costs, so staying informed can help you make the best decisions for your healthcare needs.
The Future of Health Insurance Costs

Predicting the future of health insurance costs is challenging due to the dynamic nature of the healthcare industry. However, several trends and factors can provide some insights into potential cost trajectories.
Technological Advancements
The integration of technology in healthcare, such as telemedicine and electronic health records, has the potential to reduce costs by improving efficiency and reducing administrative burdens. Additionally, wearable technology and health monitoring devices can empower individuals to take a more proactive approach to their health, potentially leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare expenses.
Healthcare Reform
Healthcare reform efforts, both at the federal and state levels, can significantly impact insurance costs. The Affordable Care Act, for instance, introduced subsidies and reforms that have helped make insurance more affordable for many. Future reforms could continue to shape the landscape, potentially reducing costs further or introducing new challenges.
Demographic Shifts
Changes in the demographic composition of the population, such as an aging population or shifts in the prevalence of chronic diseases, can influence insurance costs. An aging population, for example, may lead to higher costs as older adults generally require more healthcare services.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions, such as inflation and wage growth, can impact insurance costs. Inflation can drive up healthcare expenses, leading to higher premiums. Conversely, economic downturns can result in reduced healthcare utilization, potentially lowering costs.
Conclusion
Health insurance costs are a complex and ever-changing landscape, influenced by a myriad of factors. While understanding the average costs is a valuable starting point, it’s crucial to delve deeper into the specific variables that apply to your unique situation. By staying informed and making strategic choices, individuals and businesses can navigate the healthcare insurance landscape effectively, ensuring access to essential healthcare services while managing financial considerations.
What is the average cost of health insurance for a family of four?
+The average cost of health insurance for a family of four can vary significantly depending on the type of plan and other factors. In the individual market, family plans can cost upwards of 1,500 per month or 18,000 annually. Employer-sponsored family plans, which are often more cost-effective due to employer contributions, average around $22,200 per year.
Are there ways to reduce health insurance costs?
+Yes, there are several strategies to reduce health insurance costs. These include assessing your healthcare needs and choosing a plan that aligns with those needs, shopping around for the best rates, considering subsidies if eligible, taking advantage of employer-sponsored plans, and staying informed about healthcare reforms and economic trends that can impact costs.
How do deductibles and copayments impact insurance costs?
+Deductibles and copayments are cost-sharing mechanisms in health insurance plans. Plans with higher deductibles and copayments typically have lower monthly premiums, as the insured individual pays more out of pocket when utilizing healthcare services. On the other hand, plans with lower deductibles and copayments have higher monthly premiums but require less out-of-pocket expenses when accessing healthcare.



