How Much Should I Charge For Delivery Per Mile
Determining the optimal pricing for delivery services, especially on a per-mile basis, is a crucial aspect of running a successful business in the logistics industry. This article aims to delve into the various factors that influence delivery pricing, provide real-world examples, and offer insights to help businesses establish a competitive and profitable pricing strategy.
Understanding the Delivery Pricing Landscape

The delivery industry is diverse, encompassing various sectors such as food delivery, e-commerce logistics, and freight transportation. Each sector has its own unique pricing models, influenced by factors like competition, market demand, and operational costs. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses aiming to establish a sustainable pricing strategy.
For instance, the food delivery sector often operates on slim margins, with pricing heavily influenced by competition and customer expectations. In contrast, e-commerce logistics may have higher pricing flexibility due to the nature of the products and the potential for higher-value orders.
Calculating Operational Costs
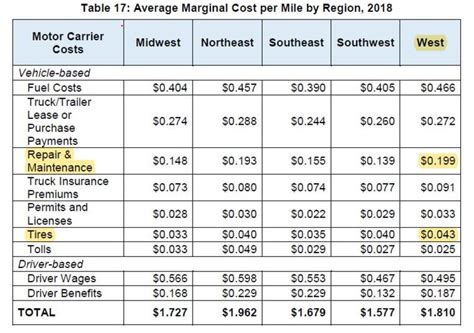
A key component in determining delivery pricing is the calculation of operational costs. These costs can vary significantly depending on the type of delivery service and the region in which the business operates. Some key cost components to consider include:
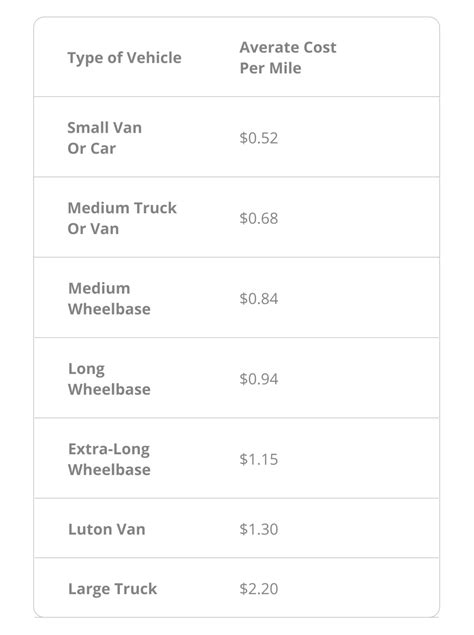
- Vehicle Maintenance and Fuel Costs: The cost of maintaining delivery vehicles, including fuel expenses, is a significant factor. These costs can fluctuate with the price of fuel and the efficiency of the vehicle fleet.
- Driver Salaries or Contractor Fees: The cost of hiring drivers or engaging independent contractors can vary based on the region and the nature of the delivery service. This cost may also include additional expenses like insurance and benefits.
- Insurance and Regulatory Costs: Delivery services often require specific insurance coverage, which can add to the overall operational costs. Additionally, compliance with local regulations may also incur additional expenses.
- Overhead Costs: These include office rent, administrative staff salaries, and other general business expenses that contribute to the overall cost of running the delivery service.
To illustrate, consider a hypothetical delivery service, "Swift Deliveries," operating in an urban setting. Their operational costs might include vehicle maintenance at $0.50 per mile, driver salaries at $15 per hour, insurance premiums at $0.10 per mile, and overhead costs of $2 per mile. Based on these figures, the total operational cost per mile would be $4.60.
| Cost Category | Cost Per Mile |
|---|---|
| Vehicle Maintenance | $0.50 |
| Driver Salaries | $15 per hour (assuming 10 miles per hour) |
| Insurance | $0.10 |
| Overhead | $2.00 |
| Total Operational Cost | $4.60 per mile |
Competitive Pricing Strategies
Once operational costs are determined, the next step is to set a competitive pricing strategy. This involves understanding the pricing structure of competitors and identifying opportunities to differentiate your service.
For example, if competitors in the same region are charging an average of $5 per mile for delivery, a business could consider offering a slightly lower price of $4.50 per mile to attract cost-conscious customers. Alternatively, a business could focus on providing additional services, such as faster delivery times or specialized packaging, to justify a higher price point.
Maximizing Profitability with Dynamic Pricing

To optimize profitability, many delivery businesses are turning to dynamic pricing strategies. This approach involves adjusting prices based on various factors, such as time of day, day of the week, or even real-time demand.
For instance, a delivery service might charge a higher rate during peak hours or on weekends when demand is typically higher. Conversely, off-peak hours or less busy days could see a reduction in pricing to encourage more orders.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing Strategies
Successfully implementing dynamic pricing requires a robust understanding of customer behavior and market trends. Businesses can utilize historical data and analytics to identify patterns in demand and adjust pricing accordingly.
Additionally, leveraging technology can be advantageous. Delivery management software, for example, can automate the process of adjusting prices based on predefined rules, ensuring a seamless and efficient pricing strategy.
Conclusion: Tailoring Your Delivery Pricing Strategy
Determining the optimal price for delivery services per mile is a nuanced process that requires a deep understanding of operational costs, market dynamics, and customer expectations. By carefully calculating costs, analyzing competitor pricing, and considering dynamic pricing strategies, businesses can establish a sustainable and profitable pricing model.
It's crucial to remember that pricing is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each delivery business must tailor its pricing strategy to its unique circumstances, taking into account the specific needs of its customers, the nature of its operations, and the competitive landscape in which it operates.
How often should I review and adjust my delivery pricing strategy?
+It’s advisable to review your pricing strategy periodically, ideally every quarter or whenever there are significant changes in operational costs, market conditions, or customer behavior. Regular reviews ensure your pricing remains competitive and aligned with your business goals.
What if I want to offer discounts or promotions? How should I factor that into my pricing strategy?
+Discounts and promotions are powerful tools to attract new customers and retain existing ones. When incorporating discounts, ensure that they are strategically placed to attract the right audience and that they don’t erode your profit margins. Consider offering promotional prices for specific time periods or target audiences to manage their impact on overall profitability.
How can I ensure my pricing strategy remains competitive without compromising profitability?
+Staying competitive while maintaining profitability requires a delicate balance. Regularly monitor your competitors’ pricing and adjust your strategy accordingly. Consider the value proposition you offer customers and ensure your prices reflect this. Additionally, continuous improvement in operational efficiency can help reduce costs, allowing you to offer competitive prices while maintaining profitability.



