Hsa And Health Insurance

The relationship between Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and health insurance is a complex and evolving topic in the healthcare industry. HSAs have become an increasingly popular financial tool for individuals to manage their healthcare expenses and save for future medical needs. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the interplay between HSAs and health insurance, offering insights into their benefits, eligibility criteria, and potential impact on healthcare affordability and accessibility.
Understanding Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)

Health Savings Accounts are tax-advantaged savings accounts designed to help individuals pay for qualified medical expenses. HSAs are often paired with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs), offering a unique opportunity for individuals to take control of their healthcare finances. Here’s a closer look at how HSAs work and their key features:
HSA Eligibility and HDHPs
To be eligible for an HSA, an individual must be enrolled in a qualifying high-deductible health plan. HDHPs are insurance plans with higher deductibles than traditional plans, typically exceeding 1,400 for individuals and 2,800 for families. These plans offer lower premiums, making them an attractive option for those who anticipate minimal medical expenses. However, the high deductible can be a challenge for unexpected or more extensive healthcare needs.
HSAs are designed to complement HDHPs by providing a savings mechanism to cover those deductibles and other qualified medical expenses. The funds in an HSA roll over year to year and can accumulate interest tax-free, offering long-term financial benefits.
Tax Benefits of HSAs
One of the primary advantages of HSAs is their tax efficiency. Contributions to HSAs are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing taxable income and providing an immediate tax savings. Additionally, the funds grow tax-free within the account, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free as well. This triple tax advantage makes HSAs an attractive option for individuals seeking to minimize their tax liability while preparing for future healthcare costs.
Qualified Medical Expenses
HSAs can be used to pay for a wide range of qualified medical expenses, including doctor visits, prescription medications, dental care, vision care, and even some over-the-counter medications with a prescription. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides a comprehensive list of eligible expenses, ensuring individuals can use their HSA funds for a variety of healthcare needs. This flexibility is a significant benefit, allowing individuals to manage their healthcare expenses effectively.
| HSA Contributions Limits (2023) | Amount |
|---|---|
| Individual Coverage | $3,700 |
| Family Coverage | $7,400 |
| Catch-up Contributions (Age 55+) | $1,000 |

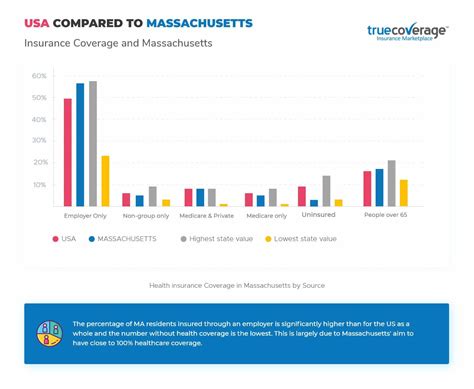
The Role of Health Insurance in HSA Compatibility

Health insurance plays a crucial role in the functionality and appeal of HSAs. While HSAs provide a means to save for healthcare expenses, health insurance offers financial protection against catastrophic medical events and ensures access to essential healthcare services. Here’s how health insurance interacts with HSAs:
HDHPs and Health Insurance Coverage
As mentioned earlier, HSAs are typically paired with high-deductible health plans. These plans offer lower premiums, making them affordable for individuals who are generally healthy and anticipate minimal medical expenses. However, HDHPs may not be suitable for those with chronic conditions or frequent healthcare needs, as the high deductibles can become a financial burden.
Health insurance, particularly comprehensive health plans, provides a safety net for individuals with higher healthcare needs. These plans typically have lower deductibles and offer more extensive coverage for a wider range of medical services. While the premiums may be higher, they provide peace of mind and financial protection for individuals facing significant medical challenges.
Coordinating HSAs with Health Insurance Plans
Individuals can choose to enroll in an HDHP with an HSA or opt for a more comprehensive health plan without an HSA. The decision often depends on personal healthcare needs and financial goals. Those who anticipate minimal medical expenses and want to maximize tax savings may prefer an HDHP with an HSA. On the other hand, individuals with higher healthcare needs or those seeking more comprehensive coverage may opt for a traditional health plan without an HSA.
It's important to note that HSAs can be used in conjunction with other types of health insurance, such as Medicare or Medicaid. However, the eligibility criteria and contribution limits may vary depending on the specific insurance program.
Health Insurance and HSA Eligibility
While HSAs are primarily associated with HDHPs, there are certain exceptions and considerations regarding health insurance and HSA eligibility. For instance, individuals with certain types of health coverage, such as Medicaid or TRICARE, may not be eligible for HSAs. Additionally, those with employer-sponsored health plans that provide comprehensive coverage may not meet the HSA eligibility criteria.
Understanding the specific requirements and limitations regarding health insurance and HSA eligibility is crucial for individuals seeking to maximize the benefits of both.
Benefits and Challenges of HSAs and Health Insurance
The integration of HSAs and health insurance offers several advantages, but it also presents certain challenges. Here’s a closer look at the benefits and potential drawbacks:
Benefits
- Tax Savings: HSAs provide significant tax advantages, allowing individuals to reduce their taxable income and grow their savings tax-free. This can result in substantial long-term financial benefits.
- Financial Control: HSAs empower individuals to take control of their healthcare finances. They can decide how and when to use their funds, providing flexibility and autonomy in managing medical expenses.
- Healthcare Accessibility: HSAs, when paired with HDHPs, can make healthcare more affordable for those with minimal medical needs. The lower premiums of HDHPs can make insurance more accessible to a broader range of individuals.
- Long-Term Savings: The ability to accumulate funds in an HSA tax-free makes it an attractive option for long-term healthcare planning. Individuals can save for future medical expenses or even retirement healthcare needs.
Challenges
- High Deductibles: HDHPs, which are necessary for HSA eligibility, come with high deductibles. This can be a challenge for individuals facing unexpected medical emergencies or those with chronic conditions, as they may need to pay substantial out-of-pocket costs before insurance coverage kicks in.
- Limited Coverage: HDHPs may not provide the same level of coverage as more comprehensive health plans. This can be a concern for individuals with specific healthcare needs or those who require specialized medical services.
- Complex Eligibility Criteria: The eligibility requirements for HSAs can be complex, and individuals must navigate a range of factors, including insurance plan types and other health coverage. This complexity may deter some individuals from exploring HSAs as an option.
- Limited Flexibility: While HSAs offer flexibility in using funds for qualified medical expenses, they may not cover all healthcare-related costs. Some expenses, such as certain alternative therapies or non-prescription items, may not be eligible for HSA funds.
Maximizing the Benefits of HSAs and Health Insurance
To make the most of the advantages offered by HSAs and health insurance, individuals should consider the following strategies:
Understanding Eligibility and Coverage
It’s essential to thoroughly understand the eligibility criteria for HSAs and the specific coverage provided by one’s health insurance plan. This includes knowing the plan’s deductibles, out-of-pocket maximums, and the range of services covered. Being informed about these details can help individuals make more informed decisions about their healthcare finances.
Strategic Planning
Individuals should develop a strategic plan for their healthcare finances. This includes estimating annual medical expenses, understanding the potential for unexpected medical events, and determining the appropriate level of coverage and savings. Regularly reviewing and adjusting this plan based on life changes and healthcare needs is crucial.
Utilizing HSA Funds Effectively
HSAs offer flexibility in using funds for qualified medical expenses. Individuals should explore the full range of eligible expenses and consider how their HSA funds can best support their healthcare needs. This may include using HSA funds for preventive care, prescription medications, or even investing in health-related equipment or services.
Staying Informed
The healthcare industry and insurance landscape are constantly evolving. Staying informed about changes in regulations, tax laws, and insurance options can help individuals make the most of their healthcare finances. Regularly reviewing and comparing insurance plans and HSA options can ensure individuals are getting the best value for their healthcare needs.
The Future of HSAs and Health Insurance

The relationship between HSAs and health insurance is likely to evolve further as healthcare policies and consumer needs change. Here are some potential future developments and their implications:
Expanding HSA Eligibility
There is a growing movement to expand HSA eligibility beyond HDHPs. Some experts advocate for allowing individuals with more comprehensive health plans to open HSAs, potentially with lower contribution limits. This could make HSAs more accessible to a broader range of individuals and encourage more people to save for healthcare expenses.
Increased Flexibility in HSA Funds Usage
There are ongoing discussions about expanding the range of eligible expenses for HSA funds. Some proposals suggest allowing HSA funds to be used for a wider range of healthcare-related services, including certain alternative therapies and wellness programs. This could enhance the flexibility and attractiveness of HSAs for individuals seeking comprehensive healthcare planning.
Integration with Digital Health Technologies
The rise of digital health technologies, such as telemedicine and health tracking apps, presents opportunities for HSAs to integrate with these platforms. This could simplify the process of using HSA funds for eligible expenses and provide individuals with more convenient and accessible healthcare options.
Impact on Healthcare Affordability
The combination of HSAs and health insurance has the potential to make healthcare more affordable for a wider range of individuals. By offering tax-advantaged savings and flexible spending options, HSAs can reduce the financial burden of healthcare expenses. This could encourage more people to seek preventive care and manage their health proactively.
Can I have an HSA if I’m not enrolled in an HDHP?
+No, to be eligible for an HSA, you must be enrolled in a qualifying high-deductible health plan (HDHP). These plans have specific deductible and out-of-pocket maximum requirements. However, there are other health savings options, such as Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs), that may be available to you.
Are there any age restrictions for opening an HSA?
+No, there are no age restrictions for opening an HSA. Individuals of all ages, including minors with qualifying HDHP coverage, can open and contribute to an HSA.
Can I use my HSA funds for non-medical expenses?
+No, HSA funds are intended for qualified medical expenses only. Withdrawing funds for non-medical purposes may result in taxes and penalties. However, there are certain exceptions, such as using HSA funds for eligible retirement expenses after reaching age 65.