Money Market Fdic Insured

The money market, an integral part of the financial system, plays a crucial role in facilitating short-term borrowing and lending, often for periods ranging from overnight to a year. This market is characterized by its focus on highly liquid assets and short-term financial instruments. For investors, the money market offers a safe haven for their funds, particularly in times of economic uncertainty.
One of the key advantages of the money market is the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) insurance it provides. FDIC insurance offers crucial protection to depositors, ensuring the safety of their funds up to a specified limit. This insurance plays a pivotal role in fostering confidence in the financial system, encouraging individuals and businesses to park their funds in these short-term investments.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the money market, exploring its various components, and the significance of FDIC insurance. By understanding these concepts, investors can make informed decisions about their short-term investments, leveraging the security and liquidity offered by the money market.
Understanding the Money Market
The money market is a highly liquid segment of the financial market that specializes in short-term borrowing and lending, typically for periods of less than a year. It facilitates the trading of financial instruments with high liquidity and low default risk, such as Treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit (CDs), and repurchase agreements (repos). These instruments are often used by entities like governments, banks, and large corporations to manage their short-term cash flow needs and excess liquidity.
The money market serves as a critical intermediary between borrowers and lenders, providing a platform for the exchange of short-term funds. It offers a range of benefits, including liquidity, safety, and short-term returns. Investors can quickly access their funds, ensuring their capital remains secure and generating modest returns in the process.
Despite its focus on short-term instruments, the money market has a significant impact on the overall financial landscape. It influences interest rates, affecting the cost of credit for borrowers and the returns for lenders. Additionally, the money market plays a vital role in maintaining the stability of the financial system by providing a ready source of funds for short-term needs, thus reducing the risk of liquidity crises.
Key Components of the Money Market
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills): Short-term debt obligations issued by governments, typically maturing in less than a year. They are considered one of the safest investments due to the backing of the government.
- Commercial Paper: Unsecured promissory notes issued by corporations to finance their short-term debt obligations, often maturing in less than 270 days. It’s a way for companies to access short-term funds directly from investors.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): A time deposit with a fixed maturity date and interest rate issued by banks. CDs are insured by the FDIC, making them a safe investment option.
- Repurchase Agreements (Repos): A form of short-term borrowing for dealers in government securities. It involves selling securities to investors with an agreement to repurchase them later at a specified price and date.
- Money Market Mutual Funds (MMMFs): These are mutual funds that invest in short-term debt securities, such as those mentioned above. MMMFs aim to maintain a stable net asset value (NAV) of $1 per share and are a popular choice for investors seeking liquidity and safety.
The Role of FDIC Insurance
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a U.S. government corporation providing deposit insurance to banks and thrift institutions. FDIC insurance is a critical safeguard for depositors, protecting their funds in the event of a bank failure. This insurance fosters confidence in the banking system, encouraging individuals and businesses to use banks as a secure place to keep their money.
FDIC insurance covers various deposit products, including checking accounts, savings accounts, money market deposit accounts (MMDAs), and certificates of deposit (CDs). The coverage extends to both interest and principal, offering comprehensive protection to depositors.
FDIC Insurance Coverage
As of 2023, FDIC insurance covers deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank. This coverage limit applies to each ownership category, including single accounts, joint accounts, trusts, and certain retirement accounts. The FDIC provides separate coverage for different categories of ownership, ensuring that individuals can maximize their protection by diversifying their accounts across multiple categories.
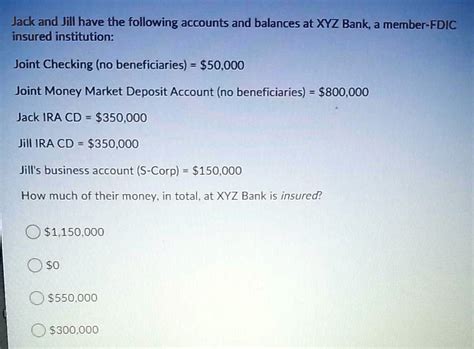
For example, a depositor with $300,000 in a single account would have $250,000 covered by FDIC insurance, leaving $50,000 uninsured. However, if this depositor had $250,000 in a single account and $50,000 in a joint account with a spouse, both accounts would be fully insured, as they fall under different ownership categories.
| Ownership Category | FDIC Insurance Coverage |
|---|---|
| Single Account | $250,000 |
| Joint Account | $250,000 per co-owner |
| Trust Account | Varies based on trust structure |
| Retirement Account (e.g., IRA) | $250,000 |

It's important to note that FDIC insurance does not cover investments in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, life insurance policies, annuities, or municipal securities, even if these products are offered by an FDIC-insured bank. The insurance is specific to deposit products, ensuring the safety of funds held in these accounts.
Benefits of FDIC Insurance
FDIC insurance offers several key benefits to depositors:
- Safety: FDIC insurance provides a crucial layer of protection, ensuring that depositors’ funds are secure even if the bank fails.
- Peace of Mind: With FDIC insurance, depositors can have confidence in the safety of their funds, knowing they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
- Convenience: FDIC insurance allows depositors to keep their funds in insured banks without the need for complex strategies to protect their money.
- Liquidity: FDIC-insured deposit accounts offer easy access to funds, allowing depositors to withdraw their money as needed.
Money Market Instruments and FDIC Insurance
FDIC insurance plays a pivotal role in the money market, providing crucial protection to depositors investing in short-term financial instruments. While not all money market instruments are FDIC-insured, a significant portion of them, such as certificates of deposit (CDs) and money market deposit accounts (MMDAs), fall under FDIC coverage.
FDIC-Insured Money Market Instruments
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are a popular choice for investors seeking a safe and predictable return. FDIC insurance covers CDs, providing protection to depositors. Investors can choose from a range of CD terms, from a few months to several years, depending on their investment goals and liquidity needs.
- Money Market Deposit Accounts (MMDAs): MMDAs are similar to money market mutual funds but are offered by banks and are FDIC-insured. These accounts typically offer higher interest rates than standard savings accounts and provide check-writing privileges. MMDAs are a safe and liquid investment option for those seeking short-term returns.
- Savings Accounts: Basic savings accounts are FDIC-insured, offering a simple and secure way to save money. While the interest rates on savings accounts may be lower than other money market instruments, they provide easy access to funds and are a good option for emergency funds or short-term savings goals.
Non-FDIC-Insured Money Market Instruments
It’s important to note that not all money market instruments are FDIC-insured. Some common non-insured instruments include:
- Treasury Bills (T-Bills): T-Bills, despite being considered one of the safest investments due to their government backing, are not FDIC-insured. This is because they are not issued by banks, but rather by the government.
- Commercial Paper: Commercial paper, which is issued by corporations to finance their short-term debt obligations, is also not FDIC-insured. While it is considered a relatively safe investment due to its short-term nature, it carries more risk than FDIC-insured instruments.
- Money Market Mutual Funds (MMMFs): While MMMFs invest in short-term securities, they are not FDIC-insured. Instead, they aim to maintain a stable net asset value (NAV) of 1 per share, offering a level of security and liquidity. However, MMMFs are not guaranteed, and there is a risk of loss if the fund's NAV falls below 1.
When investing in money market instruments, it's crucial to understand the level of protection provided by FDIC insurance. While FDIC-insured instruments offer a high level of safety, non-insured instruments may provide higher returns but also carry more risk. Investors should carefully assess their risk tolerance and investment goals before choosing a money market instrument.
The Future of Money Market and FDIC Insurance
The money market and FDIC insurance have a symbiotic relationship, with each influencing the other’s development and direction. As the financial landscape evolves, so too do the money market and FDIC insurance, adapting to meet the changing needs of investors and the financial system.
Trends and Developments
Several trends and developments are shaping the future of the money market and FDIC insurance:
- Digital Transformation: The rise of digital banking and fintech has brought about significant changes in the money market. Online and mobile banking platforms now offer a wide range of money market instruments, making it easier for investors to access and manage their short-term investments.
- Increased Regulation: In the wake of the 2008 financial crisis, there has been a push for increased regulation in the money market. This includes measures to enhance transparency, mitigate risk, and protect investors. For example, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has implemented rules to improve the stability of money market funds, ensuring they maintain a stable NAV of 1 per share.</li> <li><strong>Expanding Coverage</strong>: FDIC insurance coverage has expanded over time, increasing from 100,000 to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank. This expansion provides greater protection to depositors, fostering confidence in the banking system.
- Innovation in Money Market Instruments: The money market is constantly evolving, with new instruments and strategies emerging. For instance, the development of money market funds with enhanced liquidity features and the introduction of short-term ETFs have provided investors with additional options for short-term investments.
Implications and Opportunities
The evolving landscape of the money market and FDIC insurance presents both implications and opportunities for investors and the financial industry:
- Enhanced Safety and Security: With increased regulation and expanded coverage, the money market and FDIC insurance offer greater safety and security to depositors. This fosters confidence in the financial system, encouraging individuals and businesses to invest in short-term instruments.
- Improved Accessibility: Digital transformation has made it easier for investors to access and manage their money market investments. Online platforms and mobile apps offer convenience and flexibility, allowing investors to monitor and adjust their portfolios quickly.
- Diversification Opportunities: The expansion of money market instruments provides investors with a broader range of options. This diversification can help mitigate risk and optimize returns, allowing investors to tailor their portfolios to their specific goals and risk tolerance.
- Innovative Strategies: The introduction of new money market instruments and strategies opens up opportunities for investors to explore innovative approaches. For instance, short-term ETFs and enhanced liquidity funds offer unique features that can be leveraged to meet specific investment objectives.
As the money market and FDIC insurance continue to evolve, investors can expect to see further enhancements in safety, accessibility, and investment options. By staying informed about these developments, investors can make strategic decisions to optimize their short-term investment strategies.
FAQs

What is the money market, and how does it work?
+The money market is a segment of the financial market focused on short-term borrowing and lending, typically for periods of less than a year. It facilitates the trading of highly liquid and low-risk financial instruments such as Treasury bills, commercial paper, certificates of deposit (CDs), and repurchase agreements (repos). The money market serves as an intermediary between borrowers and lenders, offering liquidity and short-term returns while playing a vital role in maintaining financial system stability.
What is FDIC insurance, and how does it protect depositors?
+FDIC insurance, provided by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, is a safeguard for depositors in case of bank failure. It covers various deposit products, including checking accounts, savings accounts, money market deposit accounts (MMDAs), and certificates of deposit (CDs). FDIC insurance offers protection to depositors, ensuring their funds are secure and providing peace of mind.
Which money market instruments are FDIC-insured, and which are not?
+FDIC-insured money market instruments include certificates of deposit (CDs), money market deposit accounts (MMDAs), and basic savings accounts. Non-insured instruments include Treasury bills (T-Bills), commercial paper, and money market mutual funds (MMMFs). It’s important to understand the level of protection provided by FDIC insurance when investing in money market instruments.
How has the money market evolved, and what are the implications for investors?
+The money market has evolved with digital transformation, increased regulation, and expanded FDIC insurance coverage. These developments have enhanced safety, accessibility, and diversification opportunities for investors. New money market instruments and strategies, such as short-term ETFs and enhanced liquidity funds, offer innovative approaches for investors to meet their specific investment objectives.