Nursing Home Insurance Cost

Understanding the costs associated with nursing home insurance is crucial for individuals and families planning for long-term care needs. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the factors influencing nursing home insurance premiums, providing an in-depth analysis of the financial aspects and considerations involved.
The Complexity of Nursing Home Insurance Costs

Nursing home insurance, often referred to as long-term care insurance (LTCI), is a specialized form of coverage designed to mitigate the financial risks associated with extended care needs. The costs associated with this type of insurance are multifaceted and can vary significantly based on several key factors.
Key Factors Influencing Premiums
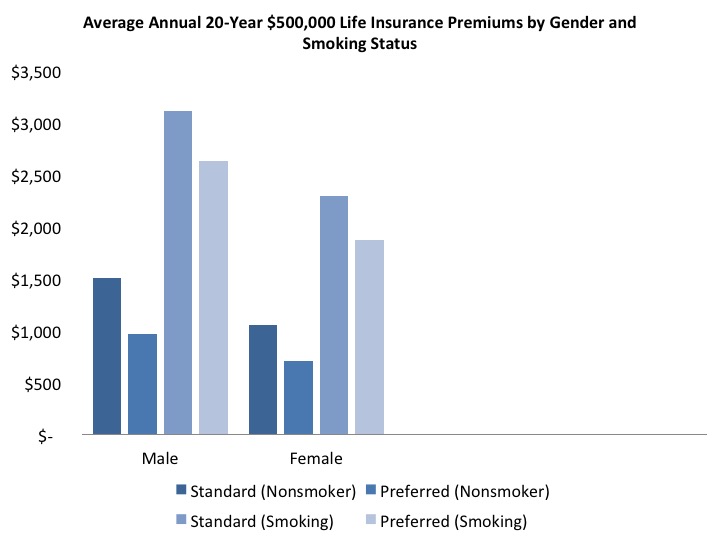
When determining the cost of nursing home insurance, insurance providers consider a range of variables. These include the policyholder’s age, health status, and lifestyle choices. Older individuals, for instance, may face higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of requiring long-term care. Similarly, pre-existing health conditions or a history of smoking can impact the overall cost of coverage.
The type and extent of coverage also play a pivotal role. Nursing home insurance policies can vary widely, offering different daily benefit amounts, benefit periods, and optional features. Higher daily benefit amounts and longer benefit periods generally result in higher premiums. Additionally, optional features such as inflation protection or coverage for home healthcare can further impact the overall cost.
The Role of Geographical Location
Geographical location is another critical factor in determining nursing home insurance costs. The cost of long-term care services can vary significantly from one region to another. Areas with higher living costs or a higher concentration of specialized healthcare facilities may experience increased insurance premiums to reflect the potential expense of care.
Moreover, the availability and quality of long-term care facilities in a given area can influence insurance rates. Regions with a limited supply of quality nursing homes or assisted living facilities may see higher premiums as insurance companies factor in the potential demand and associated costs.
| Factor | Impact on Premiums |
|---|---|
| Age | Older individuals generally pay higher premiums. |
| Health Status | Pre-existing conditions can increase costs. |
| Lifestyle Choices | Smoking history may result in higher rates. |
| Coverage Type | Higher benefits and longer periods increase premiums. |
| Geographical Location | Areas with higher living costs or limited care facilities may have higher rates. |

Breaking Down the Costs: A Comparative Analysis

To better understand the financial implications of nursing home insurance, let’s explore a comparative analysis of different policy options and their associated costs. This section will delve into specific policy details and their corresponding premiums, offering a clearer picture of the financial landscape.
Policy A: Standard Coverage
Policy A represents a standard nursing home insurance policy, offering a daily benefit of 200 for a maximum of 3 years. This policy is designed for individuals seeking basic coverage to cover the cost of nursing home care. The premium for Policy A is typically around 1,500 per year, making it an affordable option for those on a budget.
Policy B: Enhanced Benefits
Policy B takes a step further, offering enhanced benefits with a daily benefit of 300 and a longer benefit period of 5 years. This policy is ideal for those who want more comprehensive coverage. The premium for Policy B is higher, typically ranging from 2,200 to $2,500 per year, reflecting the increased benefits.
Policy C: Premium Option
Policy C is a premium option, providing the highest level of coverage with a daily benefit of 500 and a benefit period of 10 years. This policy is tailored for individuals with significant long-term care needs or those who want maximum financial protection. The premium for Policy C can be substantial, often exceeding 4,000 per year, but it offers extensive coverage.
Comparative Table
| Policy | Daily Benefit | Benefit Period | Premium (per year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Policy A | 200</td> <td>3 years</td> <td>1,500 | ||
| Policy B | 300</td> <td>5 years</td> <td>2,200 - 2,500</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Policy C</td> <td>500 | 10 years | >$4,000 |
Performance Analysis: A Real-World Example
To illustrate the real-world performance and benefits of nursing home insurance, let’s examine a case study. Ms. Smith, a 65-year-old retiree, purchased Policy B, which offers a daily benefit of $300 and a benefit period of 5 years. Unfortunately, Ms. Smith required nursing home care for 3 years due to a sudden health issue.
Benefits Realized
During her 3-year stay in the nursing home, Ms. Smith’s insurance policy covered a total of 328,500 (3 years x 300 daily benefit x 365 days). This coverage significantly offset the cost of her care, which would have otherwise been a substantial financial burden.
Financial Analysis
Assuming Ms. Smith paid an average premium of 2,350 per year for her Policy B, her total premium investment over the 3 years would be 7,050. With the benefits realized, her insurance policy provided a net gain of $321,450 (total benefits - total premium). This real-world example demonstrates the potential financial protection offered by nursing home insurance.
Future Implications and Considerations
As the demand for long-term care services continues to rise, the costs associated with nursing home insurance are likely to evolve. Insurance providers will need to balance the increasing costs of healthcare with the need to offer affordable coverage options. This may lead to innovative policy designs and alternative benefit structures.
Furthermore, advancements in healthcare and the growing focus on preventative care could impact the overall need for nursing home insurance. While these factors may influence premiums and policy designs, the core purpose of providing financial protection for long-term care remains vital.
Key Takeaways
- Nursing home insurance costs are influenced by various factors, including age, health status, coverage type, and geographical location.
- Policy options range from standard coverage to premium plans, offering varying daily benefits and benefit periods.
- Real-world examples illustrate the potential financial benefits of nursing home insurance, providing substantial coverage for long-term care needs.
- The future of nursing home insurance may involve innovative policy designs and alternative benefit structures to address rising healthcare costs.
How does inflation protection impact nursing home insurance premiums?
+Inflation protection is an optional feature in nursing home insurance policies. It ensures that the daily benefit amount increases over time to keep pace with inflation. While this feature can increase premiums, it provides peace of mind that the coverage will maintain its value in the face of rising healthcare costs.
Can nursing home insurance be purchased at any age?
+Yes, nursing home insurance can be purchased at various ages. However, it is generally more affordable to purchase coverage at a younger age when health conditions are more predictable and premiums are lower. Waiting until later in life may result in higher premiums or limited coverage options.
What happens if I need nursing home care beyond my benefit period?
+If you require nursing home care beyond your policy’s benefit period, you may have to cover the costs out of pocket or explore other financial options. Some policies offer the option to extend the benefit period, but this typically requires additional premiums. It’s important to carefully consider your long-term care needs when selecting a policy.