Private Health Care Insurance

Private health care insurance is a vital aspect of modern healthcare systems, offering individuals and families peace of mind and access to specialized medical services. With rising healthcare costs and evolving medical needs, understanding the nuances of private health insurance is essential for making informed decisions about your well-being and financial security. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the world of private health care insurance, shedding light on its benefits, coverage options, and implications.
The Rise of Private Health Insurance: A Global Perspective

Private health insurance has become increasingly prevalent worldwide, complementing and sometimes competing with public healthcare systems. While public healthcare aims to provide universal coverage, private insurance offers additional benefits and personalized care. The global demand for private healthcare is driven by factors such as faster access to specialized treatments, enhanced privacy, and the desire for more control over one’s medical choices.
In countries with well-established private healthcare sectors, like the United States and the United Kingdom, private insurance plays a significant role in shaping the overall healthcare landscape. These systems often offer a wide range of plans, catering to diverse needs and budgets. For instance, in the US, private insurance covers over 65% of the population, with various options like employer-sponsored plans, individual market policies, and Medicare Advantage.
Similarly, in countries with robust public healthcare systems, like the Netherlands and Switzerland, private insurance provides an additional layer of coverage, offering faster access to certain treatments and more luxurious amenities. These countries often employ a mixed system, where private insurance can complement public healthcare, providing an option for those seeking more personalized or specialized care.
Understanding Private Health Insurance Coverage

Private health insurance coverage can vary significantly depending on the plan and the healthcare system it operates within. Here’s a detailed look at the key aspects of private health insurance coverage:
Types of Plans
Private health insurance plans come in various forms, each designed to meet different needs and budgets. Some common types include:
- Indemnity Plans: These traditional plans allow you to choose any doctor or hospital and reimburse you for covered services. They offer flexibility but may have higher premiums.
- Managed Care Plans: This category includes Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). HMOs typically have a network of providers and require referrals for specialists, while PPOs offer more flexibility but may have higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Exclusive Provider Organizations (EPOs): EPOs are similar to PPOs but typically do not cover out-of-network care, except in emergencies.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs, allowing members to choose between in-network and out-of-network care, often with varying cost structures.
Coverage Options
Private health insurance coverage can include a wide range of medical services and treatments. Here are some key areas typically covered:
- Inpatient Care: Coverage for hospital stays, including surgery, intensive care, and post-operative recovery.
- Outpatient Care: Services received outside a hospital setting, such as doctor visits, diagnostic tests, and certain therapies.
- Prescription Drugs: Coverage for medications, with plans often offering preferred drug lists and varying cost-sharing structures.
- Preventive Care: Services aimed at preventing illness and detecting health issues early, including vaccinations, screenings, and wellness programs.
- Specialist Care: Access to specialists like cardiologists, oncologists, and mental health professionals.
- Maternity and Newborn Care: Coverage for pregnancy, childbirth, and newborn care, including prenatal visits, delivery, and postpartum care.
- Mental Health and Substance Abuse Treatment: Coverage for therapy, counseling, and residential treatment for mental health conditions and substance abuse.
Benefits and Perks
Private health insurance plans often come with additional benefits and perks to enhance member experience and provide added value. These can include:
- Telehealth Services: Access to virtual doctor visits and consultations, offering convenience and reducing travel time.
- Wellness Programs: Incentives and resources to promote healthy lifestyles, such as gym memberships, nutrition counseling, and smoking cessation programs.
- Chronic Condition Management: Support and resources for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and asthma, including educational materials and access to specialized care teams.
- Travel Insurance: Coverage for emergency medical care while traveling, ensuring access to necessary treatments regardless of location.
- Discounts and Rewards: Plans may offer discounts on health-related products and services, or reward members for achieving certain health milestones.
Choosing the Right Private Health Insurance Plan
Selecting the right private health insurance plan is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your healthcare experience and financial well-being. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed choice:
Assess Your Needs
Start by evaluating your personal and family healthcare needs. Consider factors such as:
- Current health status and any ongoing medical conditions.
- The frequency of doctor visits and the types of specialists you may require.
- Prescription drug needs and the cost of medications.
- Whether you anticipate major medical procedures or surgeries in the near future.
- The importance of access to specific hospitals or healthcare providers.
Understand Your Options
Research the various private health insurance plans available in your region. Compare plans based on coverage, cost, and provider networks. Consider the following:
- Deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums.
- Coverage limits and exclusions.
- Network size and the inclusion of your preferred providers.
- Any additional benefits or perks that align with your health goals.
Evaluate Cost vs. Coverage
Weigh the cost of premiums against the level of coverage and benefits offered. While it’s tempting to opt for the lowest premium, consider the potential costs of out-of-pocket expenses, especially if you anticipate significant medical needs.
Consider Your Employer’s Plans
If you’re employed, explore the private health insurance options offered by your employer. These plans often provide cost-effective coverage with additional benefits tailored to employees. However, always review the coverage and terms carefully, as they may not suit your specific needs.
Read the Fine Print
Thoroughly review the policy documents and understand the terms and conditions. Pay attention to any exclusions, limitations, and waiting periods. Ensure you understand the process for filing claims and accessing benefits.
Seek Professional Advice
Consider consulting an insurance broker or financial advisor who specializes in healthcare. They can provide personalized guidance based on your needs and help you navigate the complex world of private health insurance.
The Impact of Private Health Insurance on Healthcare Systems
Private health insurance plays a significant role in shaping healthcare systems worldwide. Its impact extends beyond individual coverage, influencing the overall structure and accessibility of healthcare services. Here’s a closer look at how private health insurance affects healthcare systems:
Access to Specialized Care
Private health insurance often provides faster access to specialized medical services. With the right coverage, individuals can bypass long waiting times associated with public healthcare systems, especially for non-emergency procedures. This is particularly beneficial for those requiring urgent or complex treatments.
Healthcare Innovation
The competition between private insurers drives innovation in healthcare. Insurers invest in new technologies, treatments, and healthcare delivery models to attract customers. This can lead to improved patient outcomes, enhanced efficiency, and the development of specialized medical centers.
Financial Stability for Healthcare Providers
Private health insurance can provide a stable revenue stream for healthcare providers, ensuring their financial sustainability. This stability allows healthcare facilities to invest in infrastructure, research, and the latest medical technologies, ultimately benefiting patients.
Patient Empowerment
Private health insurance empowers patients by giving them more control over their healthcare choices. With a private plan, individuals can choose their healthcare providers, often opting for those with a strong reputation or specialized expertise. This patient-centric approach encourages healthcare providers to focus on quality and patient satisfaction.
Challenges and Inequalities
Despite its benefits, private health insurance also presents challenges and potential inequalities. Access to private insurance is often influenced by socioeconomic factors, with higher-income individuals and families more likely to afford comprehensive coverage. This can lead to disparities in healthcare access and outcomes.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
The presence of private health insurance within a healthcare system necessitates careful regulatory oversight. Governments and healthcare regulators must ensure that private insurers adhere to ethical practices, provide transparent pricing, and offer comprehensive coverage. Policy decisions around private insurance can significantly impact the overall healthcare landscape.
The Future of Private Health Insurance
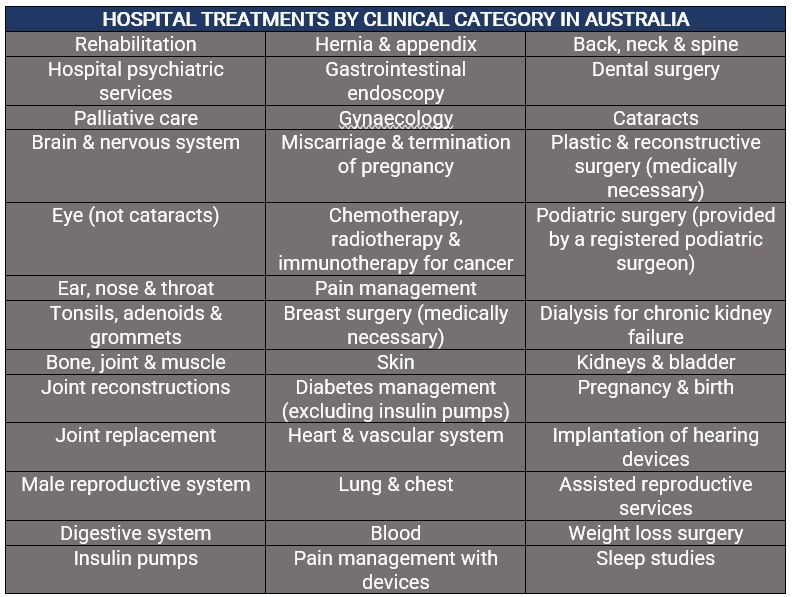
As healthcare systems evolve, so too will the role of private health insurance. Here’s a glimpse into the potential future of private health insurance:
Digital Transformation
The digital revolution is set to transform the private health insurance industry. Insurers will increasingly leverage technology to streamline processes, enhance customer experience, and improve overall efficiency. Expect to see more digital platforms for plan selection, claim submissions, and virtual healthcare services.
Personalized Medicine
The rise of personalized medicine, driven by advancements in genomics and precision healthcare, will likely shape private insurance plans. Insurers may offer tailored coverage based on individual genetic profiles, focusing on preventive care and early intervention.
Integrated Care Models
Private insurers may increasingly collaborate with healthcare providers to offer integrated care models. These models aim to provide seamless care across various specialties, improving coordination and reducing redundant treatments. Integrated care can lead to better patient outcomes and cost savings.
Global Collaboration
With the increasing mobility of individuals and the rise of global healthcare, private insurers may collaborate more closely across borders. This could lead to the development of international health plans, providing coverage for individuals traveling or working abroad.
Addressing Inequalities
Efforts to address healthcare inequalities will likely impact private insurance. Insurers may work towards making coverage more accessible and affordable for underserved populations, potentially through government partnerships or community-based initiatives.
Focus on Prevention
The future of private health insurance may place a stronger emphasis on preventive care. Insurers may offer incentives and rewards for maintaining healthy lifestyles, with a focus on preventing chronic conditions and promoting overall well-being.
Conclusion
Private health care insurance is a dynamic and evolving aspect of modern healthcare. It offers individuals the flexibility and control to choose their healthcare path, access specialized treatments, and prioritize their well-being. While private insurance provides numerous benefits, it also presents challenges and complexities that require careful consideration. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, private health insurance will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of medical care, influencing accessibility, innovation, and patient empowerment.
What are the key differences between public and private health insurance?
+Public health insurance, often provided by governments, aims to offer universal coverage, with benefits and services determined by public policy. In contrast, private health insurance is purchased individually or through employers, offering a wide range of plans with varying levels of coverage and benefits. Private insurance typically provides faster access to specialized care and more personalized options but may have higher costs.
How do I choose the right private health insurance plan for my needs?
+Choosing the right plan involves assessing your healthcare needs, understanding your options, and evaluating cost vs. coverage. Consider factors like your current health status, prescription needs, and preferred providers. Read policy documents carefully, and seek professional advice if needed.
What are some common exclusions or limitations in private health insurance plans?
+Common exclusions and limitations can include pre-existing conditions, cosmetic procedures, alternative therapies, and certain mental health treatments. It’s crucial to review the policy documents to understand any exclusions and limitations specific to your plan.
How does private health insurance impact the overall healthcare system?
+Private health insurance can impact healthcare systems by providing faster access to specialized care, driving innovation, and offering financial stability to healthcare providers. However, it can also contribute to inequalities in access and outcomes, especially in regions where private insurance is more prevalent among higher-income individuals.



