Health Insurance Califonia

Health insurance is a vital aspect of healthcare access and financial protection, especially in the diverse landscape of California. With a population of over 39 million people, California presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities when it comes to healthcare coverage. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the intricacies of health insurance in California, offering insights into the state's insurance landscape, the available plans, and the impact it has on the lives of its residents.
Understanding the California Health Insurance Market

California, known for its progressive healthcare policies, has implemented several measures to ensure accessible and affordable healthcare for its residents. The state’s health insurance market is regulated by the California Department of Insurance (CDI), which enforces consumer protections and ensures compliance with state and federal laws.
One of the key initiatives in California's health insurance market is the Covered California program. Launched in 2013 as part of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), Covered California is the state's official health insurance marketplace. It offers a range of affordable health plans from multiple insurance carriers, providing Californians with a centralized platform to compare and enroll in coverage.
The Covered California marketplace is particularly beneficial for individuals and families who may not have access to employer-sponsored health insurance. It offers financial assistance in the form of tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, making health insurance more affordable for low- and middle-income households. The marketplace also provides education and outreach programs to help residents understand their coverage options and navigate the enrollment process.
The Role of Medi-Cal
Medi-Cal, California’s Medicaid program, plays a crucial role in providing healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. It is a comprehensive healthcare program that covers a wide range of medical services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and mental health services. Medi-Cal is jointly funded by the state and federal governments, with the federal government covering a significant portion of the costs.
Eligibility for Medi-Cal is determined based on income and certain other factors, such as age, disability, and family size. In recent years, California has expanded Medi-Cal coverage to include more individuals, particularly under the ACA. This expansion has significantly increased the number of Californians with access to healthcare services, improving overall health outcomes in the state.
| Medi-Cal Enrollment Statistics (as of 2022) | Data |
|---|---|
| Total Enrollees | 14.3 million |
| Percentage of California's Population | 36.4% |
| Average Monthly Cost per Enrollee (State Contribution) | $653 |
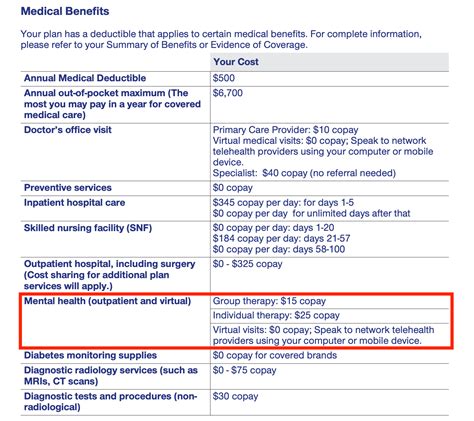
Health Insurance Plans in California

California offers a diverse range of health insurance plans to cater to the varying needs of its residents. These plans can be broadly categorized into four main types: employer-sponsored plans, individual market plans, Medicare, and Medicaid (Medi-Cal in California). Each type of plan has its own set of benefits, eligibility criteria, and cost structures.
Employer-Sponsored Plans
Employer-sponsored health insurance is the most common form of coverage in California. Many employers offer health benefits as part of their employee compensation packages. These plans are typically group policies, meaning that the employer contracts with an insurance company to provide coverage for all eligible employees and their dependents.
The specific benefits and coverage details of employer-sponsored plans can vary widely depending on the employer and the insurance carrier. However, these plans generally offer comprehensive coverage, including preventive care, doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and specialty services. Some plans may also include additional benefits such as dental, vision, and mental health coverage.
One of the key advantages of employer-sponsored plans is that the cost is often shared between the employer and the employee. Employers typically contribute a significant portion of the premium, making health insurance more affordable for employees. Additionally, group plans often have lower administrative costs and can negotiate better rates with insurance carriers due to the larger pool of enrollees.
Individual Market Plans
For individuals who are not eligible for employer-sponsored coverage or those who prefer to choose their own plan, the individual market offers a range of options. In California, individuals can purchase health insurance directly from insurance carriers or through the Covered California marketplace.
Individual market plans come in various metal tiers, such as Bronze, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, which indicate the level of coverage and cost-sharing. Bronze plans typically have lower premiums but higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs, while Platinum plans have higher premiums but lower out-of-pocket expenses. The choice of plan depends on individual preferences and financial circumstances.
The Covered California marketplace plays a vital role in the individual market by offering a centralized platform for plan comparison and enrollment. It provides financial assistance in the form of premium tax credits to eligible individuals, making health insurance more affordable. The marketplace also ensures that all plans offered meet certain standards for essential health benefits, consumer protections, and affordability.
Medicare and Medi-Cal
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. It is divided into different parts, with Part A covering hospital stays and Part B covering outpatient services. Part D, which is an optional component, covers prescription drugs.
In California, Medicare beneficiaries can choose from a variety of Medicare Advantage plans, which are private insurance plans that offer Medicare benefits. These plans often include additional benefits, such as dental and vision coverage, and may have lower out-of-pocket costs compared to traditional Medicare.
Medi-Cal, as mentioned earlier, is California's Medicaid program. It provides comprehensive healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families, with eligibility determined by income and certain other factors. Medi-Cal covers a wide range of services and often includes additional benefits, such as long-term care and mental health services.
Health Insurance Coverage and Access in California
California has made significant strides in improving health insurance coverage and access to healthcare services. The implementation of the ACA and the expansion of Medi-Cal have played a crucial role in reducing the number of uninsured individuals in the state.
According to a study conducted by the UCLA Center for Health Policy Research, the uninsured rate in California has significantly decreased since the implementation of the ACA. In 2013, before the ACA's major provisions took effect, the uninsured rate in California was estimated to be around 17.2%. By 2020, this rate had dropped to 7.3%, with over 3.5 million previously uninsured individuals gaining coverage.
The expansion of Medi-Cal has been particularly beneficial for low-income communities and vulnerable populations. It has provided access to essential healthcare services for individuals who may not have been able to afford insurance otherwise. As a result, California has seen improvements in various health outcomes, including reduced rates of preventable hospitalizations and increased access to preventive care.
Addressing Disparities
Despite the progress made, California still faces challenges in ensuring equitable access to healthcare. Certain populations, such as undocumented immigrants and individuals with pre-existing conditions, may face barriers to coverage and access to care.
In recent years, California has taken steps to address these disparities. The state has implemented several initiatives to expand coverage for undocumented immigrants, including the Healthy California for All program, which aims to provide comprehensive healthcare coverage to all residents, regardless of immigration status. Additionally, California has enacted laws to protect individuals with pre-existing conditions, ensuring that they cannot be denied coverage or charged higher premiums based on their health status.
The Future of Health Insurance in California
As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, California is poised to make further advancements in health insurance coverage and access. The state’s commitment to progressive healthcare policies and its focus on equity and affordability are expected to drive future initiatives.
One potential area of focus is the continued expansion of Medi-Cal and the exploration of innovative payment models. California has already implemented value-based payment models in certain healthcare settings, which reward providers for delivering high-quality, cost-effective care. Expanding these models and integrating them into Medi-Cal could further improve health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Additionally, California may continue to explore ways to enhance the affordability and accessibility of health insurance. This could include advocating for federal policies that support state-based initiatives, such as increased federal funding for Medicaid and the continuation of premium tax credits for individuals purchasing coverage through the individual market.
FAQ
How do I know if I’m eligible for Medi-Cal in California?
+
Eligibility for Medi-Cal in California is primarily based on income and certain other factors. Generally, individuals and families with incomes below a certain threshold may qualify. Additionally, pregnant women, children, and individuals with disabilities may have different eligibility criteria. It’s recommended to use the Covered California eligibility tool or consult with a Medi-Cal enrollment specialist to determine your eligibility.
Can I purchase health insurance outside of the open enrollment period in California?
+
Yes, in California, individuals may be able to purchase health insurance outside of the open enrollment period if they qualify for a special enrollment period. Special enrollment periods can be triggered by certain life events, such as losing job-based coverage, moving to a new state, getting married, or having a baby. These events allow individuals to enroll in a health plan outside of the typical open enrollment timeframe.
What is the difference between Medicare and Medi-Cal in California?
+
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as those with certain disabilities. It covers hospital stays, outpatient services, and prescription drugs. Medi-Cal, on the other hand, is California’s Medicaid program, which provides comprehensive healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Medi-Cal covers a wide range of services and often includes additional benefits.



