Mortgage Insurance Rates
Mortgage insurance is an essential aspect of homeownership, providing a financial safety net for lenders and borrowers alike. Understanding the intricacies of mortgage insurance rates is crucial for anyone considering purchasing a home or refinancing their existing mortgage. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of mortgage insurance, exploring its various facets, factors influencing rates, and strategies to navigate this complex landscape.
Unraveling Mortgage Insurance: An Essential Protection
Mortgage insurance, often referred to as private mortgage insurance (PMI), is a safeguard for lenders when borrowers make a down payment of less than 20% of the home’s purchase price. This insurance protects lenders from potential losses if a borrower defaults on their mortgage payments. While it’s an added expense for homeowners, it opens doors to homeownership for many, allowing them to secure a mortgage with a lower down payment.
The primary purpose of mortgage insurance is to mitigate the risk associated with high loan-to-value (LTV) ratios. Lenders require this insurance to ensure they can recover their investment if the borrower encounters financial difficulties and is unable to make payments. In essence, mortgage insurance serves as a contract between the lender, borrower, and the mortgage insurance company, providing peace of mind for all parties involved.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Insurance Rates
Mortgage insurance rates are not a one-size-fits-all proposition. Several factors come into play, influencing the cost and structure of this insurance. Understanding these factors is key to making informed decisions about your mortgage and financial future.
Loan-to-Value Ratio (LTV)
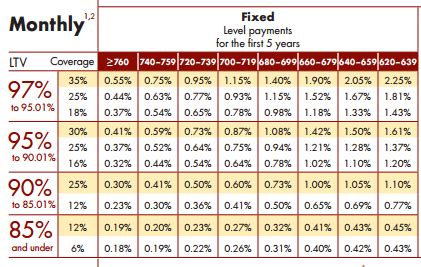
The loan-to-value ratio is a critical determinant of mortgage insurance rates. LTV represents the percentage of the home’s purchase price that is financed by the mortgage. A higher LTV ratio generally results in higher mortgage insurance premiums. For instance, a borrower with a 90% LTV ratio will likely pay more for mortgage insurance than one with an 80% LTV.
| Loan-to-Value Ratio | Mortgage Insurance Premium |
|---|---|
| 80% | $50 per month |
| 90% | $75 per month |
| 95% | $100 per month |

The table above illustrates how the LTV ratio affects mortgage insurance premiums. As the LTV increases, so does the cost of insurance. It's essential to consider this factor when deciding on the down payment amount to minimize insurance expenses.
Credit Score
Your credit score is a significant factor in determining mortgage insurance rates. Lenders and mortgage insurance companies use credit scores to assess the risk associated with a borrower. A higher credit score indicates a lower risk of default, leading to potentially lower mortgage insurance premiums. Conversely, a lower credit score may result in higher insurance costs.
| Credit Score Range | Mortgage Insurance Premium |
|---|---|
| 760-850 | $40 per month |
| 700-759 | $55 per month |
| 640-699 | $70 per month |
As demonstrated in the table, borrowers with higher credit scores often enjoy lower mortgage insurance premiums. Improving your credit score before applying for a mortgage can lead to significant savings over the life of the loan.
Loan Type and Program
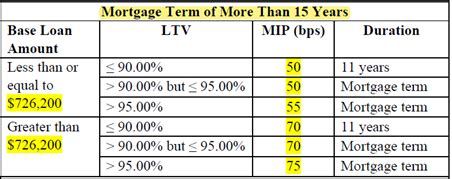
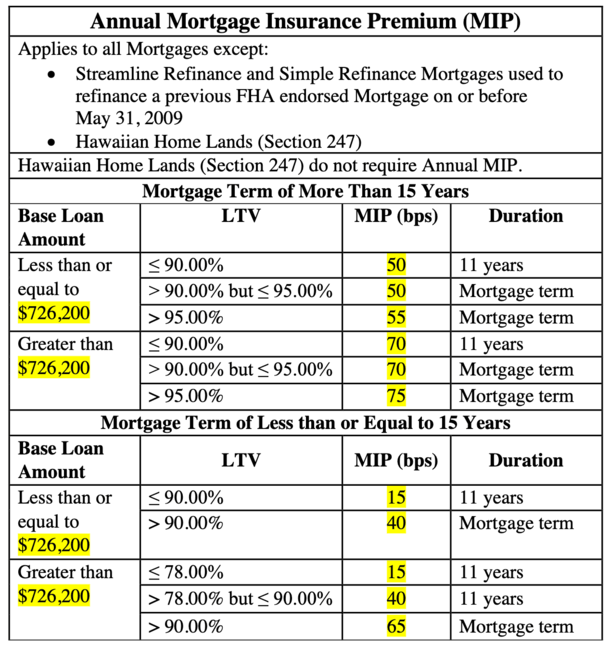
The type of loan and mortgage program you choose can also impact insurance rates. Different loan types, such as conventional, FHA, VA, or USDA loans, have varying insurance requirements and structures. For example, FHA loans typically require mortgage insurance for the life of the loan, while conventional loans may allow for the removal of insurance once a certain LTV ratio is reached.
Borrower’s Occupation and Employment Status
Your occupation and employment status can play a role in mortgage insurance rates. Lenders and insurance providers consider the stability and predictability of your income. Borrowers with a steady, long-term employment history may be viewed as lower risk, potentially leading to more favorable insurance rates.
Property Location and Value
The location and value of the property being purchased can influence mortgage insurance rates. Lenders and insurance companies assess the local real estate market, property values, and the potential risk associated with the property’s location. Properties in high-risk areas, such as those prone to natural disasters, may carry higher insurance costs.
Mortgage Insurance Company and Coverage Type
The mortgage insurance company you choose and the type of coverage selected can impact rates. Different insurance providers offer varying coverage options, premiums, and eligibility criteria. It’s essential to shop around and compare rates to find the most suitable and cost-effective coverage for your situation.
Strategies for Navigating Mortgage Insurance Rates
Understanding the factors that influence mortgage insurance rates is the first step. Now, let’s explore some strategies to navigate these rates effectively and potentially save on insurance expenses.
Increase Your Down Payment
One of the most straightforward ways to reduce mortgage insurance premiums is by increasing your down payment. By putting down a larger percentage of the home’s purchase price, you can lower your LTV ratio, which often results in lower insurance costs. Aiming for a 20% down payment or higher can eliminate the need for mortgage insurance altogether in many cases.
Improve Your Credit Score
A higher credit score can lead to better mortgage insurance rates. Take steps to improve your credit score before applying for a mortgage. Pay your bills on time, reduce credit card balances, and dispute any inaccuracies on your credit report. A higher credit score not only lowers insurance costs but also opens doors to more favorable loan terms and interest rates.
Explore Different Loan Programs
Research and compare various loan programs to find the one that best suits your financial situation. Some loan programs, like VA and USDA loans, offer more favorable insurance terms or even eliminate the need for mortgage insurance. Consider your eligibility for these programs and discuss your options with a mortgage professional.
Shop Around for Mortgage Insurance
Don’t settle for the first mortgage insurance quote you receive. Shop around and compare rates from multiple insurance providers. Each provider may have slightly different pricing structures and eligibility criteria. By obtaining quotes from several sources, you can negotiate better rates and find the most cost-effective coverage.
Consider Single-Premium Mortgage Insurance
Single-premium mortgage insurance is a one-time payment made at closing, rather than monthly premiums. This option can be more cost-effective for some borrowers, especially those with a short-term mortgage or a plan to refinance within a few years. Discuss this option with your lender to determine if it’s suitable for your financial goals.
Understand Cancellation and Removal Options
Certain loan types, like conventional mortgages, allow for the cancellation or removal of mortgage insurance once you reach a specific LTV ratio. Understand the terms and conditions for cancellation under your loan program. Building equity through regular payments or home value appreciation can lead to the removal of insurance, saving you money in the long run.
The Future of Mortgage Insurance: Trends and Innovations
The mortgage insurance industry is evolving, and several trends and innovations are shaping its future. Keeping an eye on these developments can provide valuable insights for homeowners and prospective borrowers.
Digital Transformation
The mortgage industry is embracing digital technologies, and mortgage insurance is no exception. Online platforms and digital tools are streamlining the insurance application and management process. Borrowers can now obtain quotes, compare rates, and manage their insurance policies more efficiently through user-friendly interfaces.
Alternative Risk Assessment Models
Traditional credit scoring models are being complemented by alternative risk assessment tools. These models consider a broader range of factors, including rental payment history, utility payments, and banking activity. By incorporating these additional data points, lenders and insurance providers can make more informed decisions, potentially leading to better rates for borrowers.
Enhanced Data Analytics
Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms are being utilized to improve risk assessment and pricing models. These technologies enable mortgage insurance companies to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make more accurate predictions about borrower behavior. This enhanced data analysis can lead to more precise insurance rates and better risk management.
Innovative Insurance Products
Mortgage insurance companies are introducing innovative products to meet the diverse needs of borrowers. These products may include options for lower-down-payment mortgages, flexible cancellation terms, and tailored coverage for specific loan types. Keeping abreast of these innovations can help borrowers make more informed choices.
Regulatory Changes and Consumer Protection
The mortgage insurance industry is subject to regulatory oversight and consumer protection laws. Stay informed about any changes in regulations that may impact mortgage insurance rates and borrower rights. Understanding these changes can help borrowers navigate the market and make more empowered decisions.
FAQs: Mortgage Insurance Rates
What is the average cost of mortgage insurance per month?
+
The average cost of mortgage insurance varies depending on several factors, including loan amount, down payment, credit score, and loan type. As a general guideline, borrowers can expect to pay between 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount annually, which is typically divided into monthly payments. For example, on a 200,000 loan, the annual premium could range from 1,000 to 2,000, resulting in monthly payments of 83 to $167.
Can I avoid mortgage insurance if I have a low down payment?
+
While mortgage insurance is typically required for low down payment loans, there are alternative loan programs that may allow you to avoid it. For instance, the VA loan program for veterans and active-duty military offers 100% financing without the need for mortgage insurance. Additionally, some lenders offer piggyback loans, which combine a first mortgage with a smaller, secondary loan to avoid mortgage insurance. However, these options may have other requirements or trade-offs.
How long do I have to pay mortgage insurance?
+
The duration of mortgage insurance payments depends on the loan type and your down payment. For conventional loans, mortgage insurance is typically required until your loan-to-value ratio reaches 78% or 80%. At this point, the insurance can be canceled. However, for FHA loans, mortgage insurance is generally required for the life of the loan, unless you refinance or meet certain criteria for cancellation.
Can I refinance to eliminate mortgage insurance?
+
Refinancing can be a viable strategy to eliminate mortgage insurance. If you have built sufficient equity in your home or your home’s value has appreciated, you may be able to refinance into a new loan with a lower loan-to-value ratio, allowing you to cancel the insurance. Additionally, refinancing to a different loan type, such as a conventional loan, may provide opportunities to remove insurance requirements.
What happens if I don’t pay my mortgage insurance premiums?
+
Failing to pay your mortgage insurance premiums can have serious consequences. Lenders often require that mortgage insurance premiums be paid alongside your regular mortgage payments. If you miss payments, your loan may go into default, and the lender may initiate foreclosure proceedings. It’s crucial to stay current on your insurance payments to maintain your homeownership and avoid legal complications.
Conclusion: Navigating Mortgage Insurance with Confidence
Mortgage insurance rates are a critical consideration for anyone embarking on the journey of homeownership. By understanding the factors that influence these rates and implementing strategic approaches, borrowers can navigate the mortgage insurance landscape with confidence. From increasing down payments to exploring innovative loan programs, there are numerous ways to optimize your financial position and secure more favorable insurance terms.
As the mortgage insurance industry continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and innovations is essential. Embracing digital tools, alternative risk assessment models, and enhanced data analytics can empower borrowers to make well-informed decisions and potentially unlock more affordable mortgage insurance options. Remember, the key to success in this complex realm lies in education, comparison, and strategic planning.