Whats Insurance
Insurance is a vital financial tool that provides individuals, businesses, and organizations with protection against various risks and uncertainties. It serves as a safeguard, offering peace of mind and financial security in the face of potential losses or adverse events. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of insurance, exploring its fundamentals, different types, how it works, and its significance in modern society.
Understanding the Concept of Insurance

At its core, insurance is a contractual agreement between an insurer (an insurance company or provider) and an insured (an individual, business, or entity seeking protection). This contract, known as an insurance policy, outlines the terms, conditions, and coverage details of the agreement. The insurer agrees to provide financial compensation or other specified benefits to the insured in the event of a covered loss or misfortune.
The primary objective of insurance is to transfer the financial risk of potential losses from the insured to the insurer. By paying regular premiums to the insurer, policyholders gain access to a safety net that can cover a wide range of unforeseen events, from natural disasters and accidents to medical emergencies and property damage.
The Importance of Insurance in Modern Life

Insurance plays a pivotal role in modern society, offering numerous benefits and protections that impact both individuals and the economy as a whole. Here are some key reasons why insurance is essential:
Financial Security and Risk Management
Insurance provides a crucial layer of financial security, shielding individuals and businesses from the potentially devastating financial consequences of unexpected events. Whether it’s a car accident, a house fire, or a serious illness, insurance policies help individuals and families recover financially and maintain their standard of living.
Encouraging Economic Growth
Insurance fosters economic growth and stability by facilitating business operations and investments. Companies can insure their assets, employees, and operations, enabling them to take calculated risks and pursue growth opportunities without the fear of catastrophic financial losses. This encourages innovation, job creation, and overall economic development.
Spreading Risk and Stability
The insurance industry operates on the principle of risk pooling, where a large number of policyholders contribute premiums to a collective fund. This fund is then used to compensate those who suffer losses. By spreading the risk across a diverse group of individuals or entities, insurance providers can offer stable and affordable coverage to all participants.
Promoting Social Welfare
Insurance policies contribute to the social welfare of a community by providing support and assistance during challenging times. Health insurance, for instance, ensures access to medical care and reduces the financial burden of illnesses. Life insurance policies provide financial security to families in the event of the untimely demise of a loved one. These policies offer a safety net, reducing the impact of adverse events on vulnerable populations.
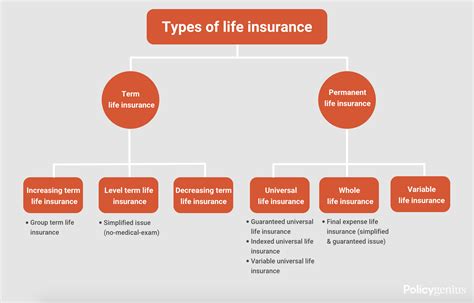
Types of Insurance
Insurance comes in various forms, each designed to address specific risks and needs. Here are some of the most common types of insurance:
Life Insurance
Life insurance policies provide financial protection to the policyholder’s beneficiaries in the event of their death. These policies can help cover funeral expenses, pay off debts, and provide ongoing financial support to the insured’s family. Life insurance is essential for individuals with dependents or those who wish to leave a legacy behind.
Health Insurance
Health insurance plans cover the costs associated with medical treatments, hospitalizations, prescription medications, and preventive care. With rising healthcare expenses, health insurance is crucial for individuals and families to access necessary medical services without incurring excessive financial burdens.
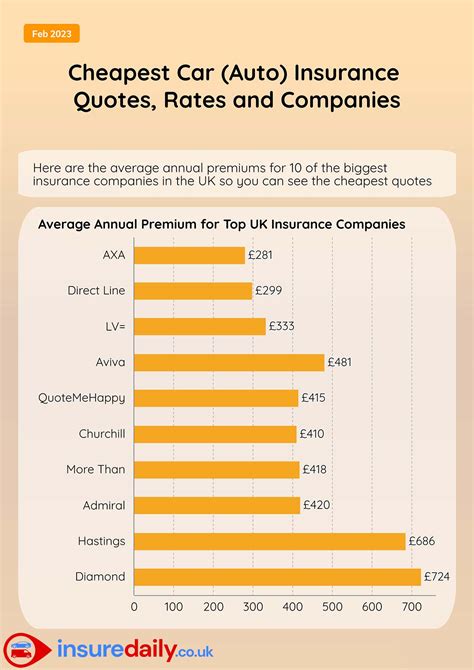
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance provides financial protection in the event of accidents, theft, or damage to vehicles. It covers liability for bodily injury and property damage caused to others, as well as the cost of repairing or replacing the insured vehicle. Many states mandate auto insurance to ensure financial responsibility on the roads.
Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance protects residential property owners against losses from damage to their homes and personal belongings. It covers a range of perils, including fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. Homeowners insurance also provides liability coverage for injuries that occur on the insured property.
Business Insurance
Business insurance is tailored to the unique needs of companies and organizations. It can include property insurance, liability insurance, workers’ compensation, and professional indemnity insurance. Business insurance protects against financial losses arising from lawsuits, property damage, employee injuries, and other business-related risks.
Travel Insurance
Travel insurance provides coverage for unexpected events that may occur during a trip, such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, lost luggage, or travel delays. It offers peace of mind and financial protection for travelers, ensuring that their vacations or business trips remain enjoyable and stress-free.
Other Types of Insurance
In addition to the aforementioned types, there are numerous specialized insurance policies available, such as pet insurance, disability insurance, cyber insurance, and crop insurance. These policies cater to specific risks and needs, ensuring that individuals and businesses can obtain tailored coverage for their unique circumstances.
How Insurance Works: The Process Explained
The insurance process involves several key steps, from policy selection and application to claim settlement. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how insurance typically works:
Policy Selection and Application
Policyholders begin by identifying their insurance needs and researching available options. They can seek advice from insurance agents, brokers, or utilize online resources to compare policies and premiums. Once they find a suitable policy, they complete an application, providing relevant personal and financial information.
Underwriting and Policy Issuance
Insurance companies assess the risk associated with each applicant through a process called underwriting. Underwriters evaluate factors such as age, health status, driving record, property location, and business operations to determine the level of risk and set the premium accordingly. If the application is approved, the insurer issues a policy document outlining the coverage, exclusions, and terms.
Premium Payments
Policyholders are required to pay regular premiums to maintain their insurance coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the policy and the insurer’s requirements. Failure to pay premiums may result in policy cancellation and loss of coverage.
Claims Process
When a policyholder experiences a covered loss, they file a claim with their insurance company. The claims process involves providing detailed information about the incident, submitting supporting documentation, and sometimes undergoing investigations or inspections. Insurance companies assess the validity and extent of the claim and determine the amount of compensation to be paid.
Claim Settlement and Renewal
Once the claim is approved, the insurer settles the claim by providing the agreed-upon compensation, which can be a lump sum payment or ongoing benefits. Policyholders are then encouraged to renew their policies to maintain continuous coverage. Insurance companies often offer renewal discounts or incentives to encourage policy retention.
The Future of Insurance

The insurance industry is constantly evolving, adapting to technological advancements, changing consumer needs, and emerging risks. Here are some key trends and developments shaping the future of insurance:
Digital Transformation
The digital age has revolutionized the insurance industry, with insurers embracing technology to enhance customer experience and streamline processes. Online platforms and mobile apps allow policyholders to easily purchase, manage, and renew policies. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being leveraged to improve risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized insurance offerings.
Data Analytics and Risk Modeling
Insurance companies are harnessing the power of big data and advanced analytics to better understand risks and price policies accurately. By analyzing vast amounts of data, insurers can identify patterns, predict potential losses, and develop more precise underwriting models. This enables them to offer tailored coverage and premiums to individual policyholders.
Parametric Insurance
Parametric insurance is an innovative approach that provides coverage based on predefined parameters rather than actual losses. This type of insurance is particularly useful in industries or regions prone to natural disasters, where traditional insurance claims can be challenging to process. Parametric insurance offers rapid payouts based on triggers like earthquake intensity or hurricane wind speed.
Insurtech Innovations
Insurtech startups and established insurers are collaborating to bring innovative solutions to the market. These innovations include blockchain-based insurance platforms, peer-to-peer insurance models, and on-demand insurance coverage. Insurtech companies are disrupting traditional insurance models by offering efficient, flexible, and personalized insurance experiences.
Risk Mitigation and Prevention
The insurance industry is increasingly focused on risk mitigation and prevention rather than solely providing compensation after a loss. Insurers are partnering with businesses and individuals to implement risk management strategies, educate policyholders about potential risks, and offer incentives for adopting safer practices. By preventing losses, insurers can reduce claims and provide more sustainable coverage.
Conclusion
Insurance is an indispensable tool for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. It provides financial security, peace of mind, and stability in the face of uncertainty. By understanding the various types of insurance, how it works, and its evolving nature, individuals can make informed decisions to protect themselves, their families, and their businesses. As the insurance industry continues to innovate and adapt, it remains a vital component of modern life, ensuring that individuals and organizations can thrive and recover from unforeseen events.
What is the main purpose of insurance?
+The primary purpose of insurance is to transfer financial risk from individuals or entities to an insurer. It provides a safety net by offering compensation or benefits in the event of covered losses, accidents, or unforeseen events, ensuring financial security and peace of mind.
How does insurance benefit society as a whole?
+Insurance plays a crucial role in promoting social welfare and economic stability. It encourages economic growth by enabling businesses to take risks and innovate. Additionally, insurance provides financial support during challenging times, reducing the burden on individuals and families, and ultimately strengthening the social fabric.
What are some common types of insurance and their purposes?
+Common types of insurance include life insurance (provides financial protection to beneficiaries), health insurance (covers medical expenses), auto insurance (protects against vehicle-related risks), homeowners insurance (safeguards residential properties), business insurance (covers various business-related risks), and travel insurance (offers coverage for trip-related emergencies). Each type serves a specific purpose based on individual or business needs.