Car Diagnostic Codes And Meanings
When it comes to modern vehicles, car diagnostic codes play a crucial role in understanding and troubleshooting various issues. These codes, often referred to as OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) codes, provide valuable insights into the vehicle's health and performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of car diagnostic codes, exploring their meanings, functions, and how they assist in maintaining your vehicle's optimal condition.
Understanding Car Diagnostic Codes
Car diagnostic codes are a vital component of the vehicle’s self-diagnostic system. They are generated by the vehicle’s computer system, known as the ECM (Engine Control Module) or ECU (Engine Control Unit), when it detects a potential issue or malfunction. These codes are designed to provide a standardized way of identifying and addressing problems, ensuring efficient troubleshooting and repairs.
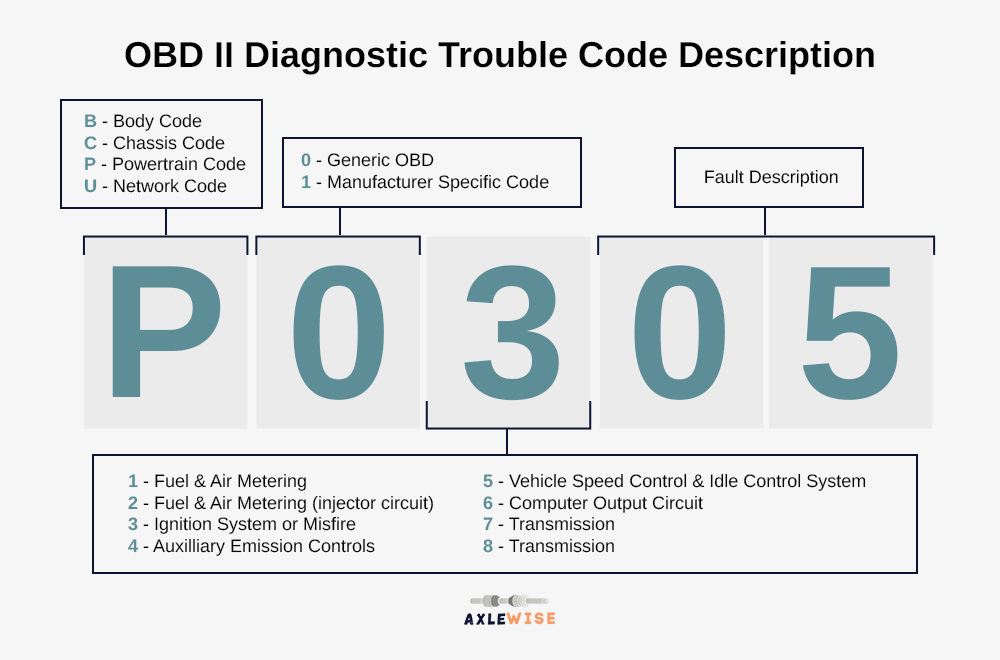
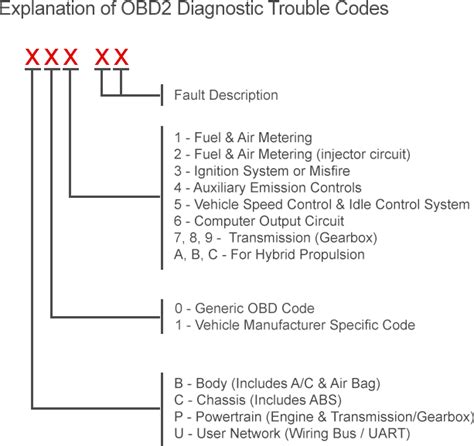
The diagnostic codes consist of a combination of letters and numbers, each representing a specific fault or condition. For instance, P0123 might indicate a problem with the throttle position sensor, while B1234 could point to an issue with the body control module. By interpreting these codes, mechanics and vehicle owners can pinpoint the root cause of the problem and take appropriate action.
The OBD System and Its Evolution
The On-Board Diagnostics system has evolved significantly since its introduction. The first generation, OBD-I, was introduced in the early 1980s and primarily focused on emission control systems. It used proprietary connectors and varied widely between vehicle manufacturers, making diagnostics challenging.
The second generation, OBD-II, was a game-changer. Introduced in the mid-1990s, it standardized the diagnostic process and connector design. All vehicles manufactured after this period are equipped with a universal OBD-II connector, typically located under the dashboard on the driver's side. This standardization made it easier for mechanics and enthusiasts to diagnose issues across different vehicle makes and models.
OBD-II systems are capable of monitoring a wide range of vehicle systems, including the engine, transmission, brakes, airbags, and more. They provide real-time data and generate diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) when issues are detected. These DTCs, or diagnostic codes, are the key to understanding and addressing vehicle problems.
Interpreting Diagnostic Codes
Interpreting diagnostic codes requires a basic understanding of their structure and meaning. Here’s a breakdown of how they are typically formatted:
- Code Format: Diagnostic codes usually consist of 5 characters, with the first character indicating the system or component affected.
- System Indicators:
- P: Powertrain (Engine and Transmission)
- B: Body and Chassis
- C: Chassis and Restraint Systems (Airbags, Seatbelts)
- U: Network and Diagnostics
- Code Specificity: The remaining characters provide more detailed information about the fault.
For example, let's consider the code P0420. In this case, P indicates it is related to the powertrain, while 0420 specifically refers to a problem with the catalytic converter efficiency. Each code has its own unique meaning, and understanding these codes is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Common Diagnostic Codes and Their Meanings
While there are numerous diagnostic codes, some are more commonly encountered than others. Here are a few examples:
P0171 and P0174: Lean Air-Fuel Mixture
These codes indicate that the air-fuel mixture in the engine is too lean, meaning there is an excess of air and not enough fuel. This can lead to reduced performance and potential damage to the engine. Common causes include a faulty oxygen sensor, a vacuum leak, or issues with the fuel system.
P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Fault
This code is related to the vehicle’s evaporative emission control (EVAP) system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. It could indicate a leak in the fuel tank, a faulty fuel cap, or issues with the EVAP canister or vents.
P0300: Random Misfire Detected
A misfire code like P0300 suggests that one or more cylinders are not firing correctly. This can result in reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to the catalytic converter. Possible causes include ignition system issues, spark plug problems, or a malfunctioning fuel injector.
B1444: Front Passenger Airbag Circuit Malfunction
This code indicates a problem with the front passenger airbag circuit. It could be due to a faulty airbag sensor, a damaged wiring harness, or issues with the airbag control module. Addressing this code promptly is crucial for ensuring the safety of vehicle occupants.
Diagnosing and Troubleshooting
When faced with a diagnostic code, the first step is to consult a reliable source, such as a manufacturer’s service manual or an online database, to understand the specific meaning of the code. This provides a starting point for further investigation.
Next, it's essential to gather more information. Modern vehicles often provide additional data through their onboard systems, such as live data readings and freeze frame data. These readings can offer valuable insights into the conditions under which the code was generated, helping to narrow down the potential causes.
Mechanics and enthusiasts can then use specialized tools, such as scan tools and oscilloscopes, to further diagnose the issue. These tools can provide detailed information about sensor readings, voltage levels, and other critical data points.
Based on the diagnostic code and additional data, a systematic approach to troubleshooting can be employed. This may involve visual inspections, component testing, and replacement of faulty parts. It's important to follow a logical flowchart or a step-by-step guide to ensure a thorough and efficient diagnosis.
The Benefits of OBD Diagnostics
OBD diagnostics offer several advantages to vehicle owners and mechanics:
- Early Detection: Diagnostic codes can alert vehicle owners to potential issues before they become major problems, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Efficiency: With standardized codes and data, mechanics can quickly identify and address problems, reducing diagnostic time and costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Codes related to critical systems, such as airbags and brakes, ensure that safety features are functioning correctly.
- Environmental Impact: OBD systems help monitor and control emissions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
Future of Car Diagnostics
The field of car diagnostics is constantly evolving. With the advent of advanced technologies like electric vehicles and autonomous driving, diagnostic systems are becoming even more sophisticated.
In the future, we can expect to see even more comprehensive and integrated diagnostic systems. These systems may utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of data, providing more accurate and timely diagnoses. Additionally, remote diagnostics and over-the-air updates may become standard, allowing for real-time monitoring and issue resolution.
As vehicles become increasingly connected, diagnostic codes may also play a role in predictive maintenance, where vehicles can anticipate and address potential issues before they occur, further enhancing the reliability and longevity of our vehicles.
How often should I check for diagnostic codes in my vehicle?
+It’s a good practice to check for diagnostic codes regularly, especially if you notice any changes in your vehicle’s performance or behavior. Many modern vehicles have built-in systems that can alert you to potential issues, but a proactive approach is always beneficial. Regularly scanning for codes, especially before long trips or during routine maintenance, can help identify and address problems early on.
Can I clear diagnostic codes myself, or should I seek professional help?
+Clearing diagnostic codes, also known as resetting the check engine light, can be done using a scan tool. While some basic issues can be addressed by clearing the codes and monitoring the vehicle’s performance, it’s essential to remember that codes are indicators of potential problems. If the code reappears or if you’re unsure about the cause, seeking professional help is recommended. A qualified mechanic can provide a thorough diagnosis and ensure the issue is resolved effectively.
Are all diagnostic codes equally critical, or are some more urgent than others?
+Diagnostic codes can vary in their urgency and severity. Some codes may indicate minor issues that can be addressed during routine maintenance, while others may point to critical safety concerns or potential engine damage. It’s important to prioritize the codes based on their nature. For instance, codes related to emissions, airbags, or braking systems should be addressed promptly, as they directly impact safety and environmental compliance.
Can diagnostic codes be misleading, or do they always accurately reflect the problem?
+Diagnostic codes are designed to provide accurate indications of potential issues, but they are not foolproof. Sometimes, a code may be triggered by a temporary glitch or a sensor malfunction, and the underlying problem may not be as severe as it seems. On the other hand, certain issues may not generate a code, especially if they are intermittent or not directly related to a specific sensor. That’s why it’s crucial to combine code interpretation with additional diagnostic techniques and expert analysis to ensure an accurate diagnosis.